Borneole
The borneols are a naturally occurring group of chemical compounds . The isomeric representatives are solid, colorless substances that are structurally monohydric, secondary alcohols from the class of bicyclic monoterpenes .
Occurrence
As secondary plant substances, borneols are components of many essential oils . (+) - Borneol (Borneo Camper) is mainly found in the essential oil of Drybalanops camphora, a tree native to Sumatra and Borneo. In contrast, (-) - Borneol (Ngai Camper) is found in coriander oil, valerian oil, citronella oil, thuja oil and other essential oils.
Representative
The molecular structure of borneols contains chiral carbon atoms and therefore occurs in two diastereomeric forms, commonly called borneol and isoborneol. Since each of these two forms has an (enantiomeric) mirror image, there are a total of four stereoisomers , two of which are enantiomeric to one another and form the racemates (±) -borneol and (±) -isoborneol:
| Isomers of borneol | |||||||
| Surname | (+) - Borneol | (-) - Borneol | (+) - isoborneol | (-) - Isoborneol | |||
| IUPAC name | (1 R , 2 S , 4 R ) -1,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-ol |
(1 S , 2 R , 4 S ) -1,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-ol |
(1 S , 2 S , 4 S ) -1,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-ol |
(1 R , 2 R , 4 R ) -1,7,7-trimethyl bicyclo [2.2.1] heptan-2-ol |
|||
| other names |
endo- borneol |
exo -Isoborneol |
|||||
|
2-borneol |
|||||||
| Structural formula |

|

|

|
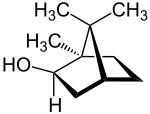
|
|||
| CAS number | 464-43-7 | 464-45-9 | 16725-71-6 | 10334-13-1 | |||
| 507-70-0 (racemate) | 124-76-5 (racemate) | ||||||
| PubChem | 6552009 | 1201518 | 6321405 | ? | |||
| ? (Racemate) | 24900674 (racemate) | ||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O | ||||||
| Molar mass | 154.25 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | firmly | ||||||
| Brief description | colorless, odorless solid | crystalline, white solid | crystalline, white solid with a pleasant smell of vanilla and wood | ||||
| Melting point | 208-209 ° C | 208-209 ° C | 212-214 ° C | 212-214 ° C | |||
| 212 ° C racemate | 210-215 ° C racemate | ||||||
| Optical rotation value [α] D | + 37.7 ° | - 37.7 ° | + 34.1 ° | - 33.6 ° | |||
| solubility | insoluble in water | insoluble in water | insoluble in water | ||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
||||
| H-phrases | 228 | 228 | 315-319-335 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| P-phrases | 210-280 | 210-240-241-280-370 + 378 | 261-302 + 352-305 + 351 + 338-321 | ||||
| Toxicological data | 5800 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) |
1750 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , mouse , oral )
5033 mg kg −1 ( LD 50 , rat , oral ) |
|||||
Manufacturing
Borneol can be obtained by the Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley reduction of camphor . In contrast, the reduction of camphor with sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride mainly produces the stereoisomer isoborneol :
- Diastereoselectivity of the reduction of (1 R , 4 R ) - (+) - camphor to (1 R , 2 R , 4 R ) -isoborneol (approx. 95%) and (1 R , 2 S , 4 R ) -borneol ( approx. 5%).
Chemical properties
Borneol can be oxidized to camphor with chromic acid or nitric acid . Dehydration with dilute acids leads to camphene .
With acetic anhydride it can be esterified to form bornyl acetate .
The bacterial biosynthesis of 2-methylisoborneol has been researched by researchers at the TU Braunschweig with the Helmholtz Center for Infection Research in Braunschweig and the University of Saarbrücken.
use
As a component of essential oils, borneol is partly responsible for the smell and taste of various spices. It is also used in this form in cosmetics .
Derivatives of borneol such as (2 S ) - (-) - exo - (dimethylamino) isoborneol (DAIB) are used in modern asymmetric synthesis .
structure
Rod model of ( S ) -borneol
literature
- H. Surburg and J. Panten: Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: preparation, properties, and uses. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2006, ISBN 3-527-31315-X .
Individual evidence
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 206, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ a b c d data sheet (+) - Borneol (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on April 29, 2010.
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet (-) - Borneol at AlfaAesar, accessed on April 29, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Data sheet (±) -Isoborneol from AlfaAesar, accessed on April 29, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet (±) -Isoborneol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on Borneole. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 29, 2011.
- ^ A b Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich, 2006, p. 60, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 .
- ↑ a b Hamada, Hiroki, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 61 ( 1988 ) 869-878.
- ↑ Ashok Pandey: Industrial Biorefineries & White Biotechnology. Elsevier, 2015, ISBN 978-0-444-63464-1 , p. 132 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren, Peter Wothers: Organic Chemistry , Orford University Press, 2001, p. 862. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0 .
- ↑ Biosynthesis of the Off-Flavor 2-Methylisoborneol by the Myxobacterium Nannocystis exedens in: Angew. Chem. 2007 , 119 , 8436-8439.
- ↑ James D. White, Duncan J. Wardrop, and Kurt F. Sundermann: (2S) - (-) - exo- (dimethylamino) isoborneol [(2S) - (-) - DAIB] In: Organic Syntheses . 79, 2002, p. 130, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.079.0130 ( PDF ).





