Carbocysteine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
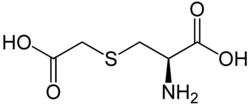
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Carbocisteine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 9 NO 4 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 179.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
206 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Carbocysteine ( international non- proprietary name Carbocistein ) is a chiral drug that is used as a mucolytic against stubborn coughs , such as those that occur in bronchitis .
Effect and use
Carbocisteine does not work by splitting the disulfide bridges of the secretion in the bronchi like acetylcysteine , but rather intracellularly: more thin-flowing mucus is produced and less viscous mucus. Carbocysteine has been one of the indications since the 1970s
- acute or chronic bronchitis
- Asthma and emphysema bronchitis
- Bronchiectasis
- Bronchopneumonia
used.
The effectiveness of carbocysteine is controversial, some experts attribute the expectorant effect to the increased consumption of water.
properties
The specific rotation value of carbocysteine [α D 20 ] is 0.5 ° in 1 M hydrochloric acid .
chemistry
Manufacturing
Carbocysteine is made from chloroacetic acid and the natural α- amino acid L - cysteine with the help of sodium hydroxide solution through a nucleophilic substitution reaction with the elimination of sodium chloride.
Isomerism
Carbocisteine is used exclusively in the enantiomerically pure L form as a medicinal substance. S -carboxymethyl- L -cysteine has ( R ) configuration at the stereogenic center (α-carbon atom of the cysteine substructure unit) .
The resolution of S -carboxymethyl- DL- cysteine is described in the literature.
Trade names
Mephathiol (CH), Mucoseptal (CH), Pectorex (CH), Rhinathiol (CH), Transbronchin (D), Tussantiol (CH), Siroxyl (B / L)
Triofan (CH)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine (PDF) from Fisher Scientific , accessed on February 13, 2014.
- ↑ a b Entry on carbocysteine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 27, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ B. Staffeld: Studies on the metabolism of carbocysteine in humans. Dissertation, FU Berlin, 1993. DNB 931876559
- ^ Axel Kleemann , Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher and Dieter Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances. 4th edition (2000), Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, page 346, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9 .
- ↑ Axel Kleemann and Jürgen Martens : Optical Resolution of Racemic S- (Carboxymethyl) cysteine. In: Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 1982, pp. 1995–1998. doi : 10.1002 / jlac.198219821108 .