Chlorfenapyr
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
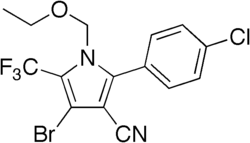
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chlorfenapyr | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
4-Bromo-2- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 11 BrClF 3 N 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 407.61 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.543 g cm −3 (bulk density) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
100-101 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Chlorfenapyr is a chemical compound from the pyrroles group .
history
On December 12, 1994, the American Cyanamid Company (now part of BASF ) filed for approval of chlorfenapyr in cotton.
Extraction and presentation
Chlorfenapyr can be obtained from p -chlorobenzaldehyde by a series of reactions ( Strecker synthesis , then bipolar addition of acrylonitrile to pyrroline , via splitting off of hydrogen to pyrrole and subsequent bromination ).
properties
Chlorfenapyr is a white solid that is practically insoluble in water.
use
Chlorfenapyr is used as insecticide and acaricide on ornamentals in commercial greenhouse cultivation against mites, feeding caterpillars, thrips and fungus gnats , but not food crops used. It is a pro-insecticide, meaning its biological activity depends on activation by another chemical compound. The oxidative removal of the N -ethoxymethyl group from chlorfenapyr by mixed-functional oxidases produces the compound CL 303268 ( NH-pyrrole ). This decouples the oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria , which results in an interruption of ATP production, and thus cell death and ultimately the death of the organism.
In the US, the EPA withdrew its approval for cotton against the armyworm ( Spodoptera frugiperda ) because it had severe effects on the reproduction of birds and there are alternatives to chlorfenapyr.
Starting in 2010, BASF has developed a product for malaria prophylaxis based on chlorfenapyr. A mosquito net impregnated with chlorfenapyr was recommended by the World Health Organization ( WHO) for malaria prevention in July 2017 .
In Germany, Switzerland and Austria, no pesticides containing this active ingredient are approved. It has been approved as a biocide for product type 8 ( wood preservatives ) since May 1, 2015 . The application for approval for inclusion in product type 18 is pending. It is offered as a remedy for bed bugs .
Web links
- R. N'Guessan, P. Boko, A. Odjo, M. Akogbéto, A. Yates, M. Rowland: Chlorfenapyr: A pyrrole insecticide for the control of pyrethroid or DDT resistant Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes. In: Acta Tropica. 102 (1), 2007, pp. 69-78, doi: 10.1016 / j.actatropica.2007.03.003 , PMID 17466253 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on chlorfenapyr in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c US EPA: Chlorfenapyr
- ↑ Entry on 4-bromo-2- (4-chlorophenyl) -1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethylpyrrole-3-carbonitrile in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b c data sheet chlorfenapyr from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ EPA: Denial of Registration of Chlorfenapyr (PDF; 8.6 MB)
- ↑ Studies on the Synthesis of Chlorfenapyr and Bis (1,4-diacylthiosemicarbazide) Compounds ( Memento from December 16, 2015 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Viacheslav A. Petrov: Fluorinated heterocyclic compounds: synthesis, chemistry, and applications . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-45211-0 ( page 413 in Google Book Search).
- ↑ EPA: EPA Determines that Chlorfenapyr does not meet the Requirements for Registration; American Cyanamid Withdraws Application
- ↑ BASF: New solution to control malaria ( Memento from January 17, 2013 in the web archive archive.today )
- ↑ BASF presents the first new class of insecticides for malaria prevention in 30 years
- ↑ FAZ: WHO recommends new BASF idea against malaria In: FAZ.net . July 13, 2017. Retrieved July 14, 2017.
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on chlorfenapyr in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved March 3, 2016.
- ↑ Directive 2013/27 / EU of the Commission of May 17, 2013 amending Directive 98/8 / EC of the European Parliament and of the Council to include the active substance chlorfenapyr in Appendix I.
- ^ BASF: bed bug spray

