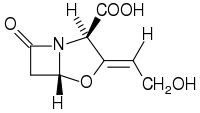
Clavulanic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Clavulanic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
3- (2-Hydroxyethylidene) -7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo [3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 9 NO 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 199.16 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Clavulanic acid is a by Streptomyces clavuligerus produced active ingredient that some of bacteria formed β-lactamases (from the group of enzymes inhibits).
By inhibiting the enzyme, the spectrum of antibacterial activity of β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins (especially amoxicillin ) and cephalosporins is expanded against germs that would render β-lactam antibiotics ineffective through enzymatic degradation.
use
Clavulanic acid itself has no clinically significant antibacterial effect and is therefore never used alone, but always in combination with amoxicillin in the treatment of infections as amoxicillin-clavulanic acid
- the upper and lower respiratory tract,
- of the urogenital tract,
- the skin and soft tissues and
- the bones ( osteomyelitis ) in the tooth and jaw area
used. The potassium salt of clavulanic acid is used. Combination drugs are mainly available in the form of tablets and dry juices, but also as infusion preparations. The ratio of amoxicillin to clavulanic acid in oral combinations is 4: 1, mainly for use in pediatrics and veterinary medicine , there are also combinations with 7: 1 for the treatment of adults.
pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
When ingested, clavulanic acid is rapidly absorbed ( absorbed ) by the body . It hardly gets into the cerebrospinal fluid ( liquor cerebrospinalis ). The drug is excreted through the kidneys ; the half-life in the body is about one hour with normal kidney function.
Pharmacodynamics
Clavulanic acid protects amoxicillin from being broken down by most of the staphylococcal β-lactamases .
It also inhibits some plasmid-encoded β-lactamases and certain chromosome-encoded β-lactamases from Gram-negative bacteria. These β-lactamases come e.g. B. in Escherichia coli , Klebsielle , Proteus mirabilis and Haemophilus influenzae .
The enzyme is inhibited by covalent bonding .
Side effects
Side effects (of amoxicillin-clavulanic acid) can often occur in the form of nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, as well as (in elderly patients or for longer treatment periods) cholestasis (very rare, even weeks after treatment, is cholestatic jaundice). Occasionally, headaches, dizziness, enanthemums of the oral mucosa and rashes occur, but also more serious side effects such as seizures or liver damage (liver dysfunction with increased liver enzymes, rarely hepatitis ), anemia or, very rarely, interstitial kidney inflammation ( nephritis ). In very rare cases, the bleeding time and prothrombin time can be prolonged as well as allergic reactions (contraindication to penicillin allergy) and pseudomembranous colitis . During pregnancy, the use of clavulanic acid in conjunction with the antibiotic amoxicillin can increase the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis in the newborn. Amoxicillin / clavulanic acid medications are better tolerated if food is consumed at the same time .
chemistry
Chemically, clavulanic acid is a structural analogue of penicillanic acid. Salts of the acid are called clavulanates. Potassium clavulanate, for example, is explosive and is stabilized by adding microcrystalline cellulose (ratio 1: 1 or 7: 3).
Trade names
- Combination preparations with amoxicillin
Amoclav (D), Amoxiclav (D), Augmentan (D), Aziclav (CH), Amoxi-Clavulan (D), Clavaseptin (D, veterinary medicine), InfectoSupramox (D), Nicilan (D, veterinary medicine), Xiclav (A) , Augmentin (A, CH), Clavamox (A) and Co-Amoxicillin (CH).
Web links
- Ursula Gresser: Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid as a possible cause of severe liver disease . In: Deutsches Ärzteblatt . tape 99 , no. 8 . Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag , 2002, p. A-505 / B-407 / C-384 .
- Embryotox: toxicology in pregnancy
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Entry on clavulanic acid in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Specialist information Augmentan dry juice, tabs, as of January 2007.
- ↑ Severe liver dysfunction during previous therapy with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid is a contraindication.
- ↑ Ursula Gresser: Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid as a possible cause of severe liver disease . In: Deutsches Ärzteblatt . tape 99 , no. 8 . Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag , 2002, p. A-505 / B-407 / C-384 .
- ^ Marianne Abele-Horn: Antimicrobial Therapy. Decision support for the treatment and prophylaxis of infectious diseases. With the collaboration of Werner Heinz, Hartwig Klinker, Johann Schurz and August Stich, 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Peter Wiehl, Marburg 2009, ISBN 978-3-927219-14-4 , p. 338 ( amoxicillin-clavulanic acid ).
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia online, as of March 2013.
- ↑ Pharmaceutical database
- ↑ Red List online, as of October 2009.
- ^ Entry on clavulanic acid in Pharmawiki , accessed on January 28, 2017.
- ↑ Austria Codex 2011.
- ↑ Swiss Medicines Compendium.