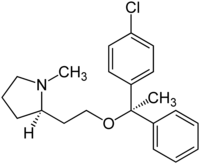
Clemastine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Clemastine | ||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 26 ClNO | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Antagonist at the H 1 receptor ( H 1 antihistamines ) |
||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 343.89 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Clemastine is a chiral drug from the group of antihistamines . It is used as an antiallergic agent for allergic reactions.
effect
Allergic reactions are mediated , among other things, by the release of the messenger substance histamine from mast cells . Histamine has an inflammatory effect by binding to histamine receptors on target cells. Clemastine inhibits the effect of histamine by also binding to histamine receptors, but not triggering the typical histamine effects (competitive antagonist ). Clemastine mainly binds to the group of H 1 receptors , which is why it is also known as an H 1 receptor antagonist. Clemastine also acts as a FIASMA (functional inhibitor of acid sphingomyelinase ).
scope of application
Clemastine is used for the symptomatic treatment of allergic rhinitis (such as hay fever), hives (urticaria), itching (pruritus) and Quincke's edema . Clemastine is also used in the emergency treatment of anaphylactic shock (allergic circulatory failure). Clemastine is also used to avoid allergic reactions when administering contrast media in the context of radiological examinations.
Possible use in multiple sclerosis
In a study published in the medical journal The Lancet in December 2017, which was already available in the meta-database for medical articles PubMed in October 2017, Ari Green and his team from the University of California, San Francisco Medical Center (UCSF Medical Center) a double-blind, randomized (placebo) -controlled (RCT) , cross-over study, which lasted 150 days and was carried out in 50 patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis .
Preclinical data clearly showed that clemastine fumarate promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation and remyelination without modulating the immune system.
The 25 patients in group 1 initially received 5.36 mg clemastine fumarate in one capsule twice a day for 90 days , while the 25 patients in group 2 received a placebo twice a day in the same capsule for 90 days . After one, after three and after five months a measurement of visual evoked potentials (VEP) was carried out which showed that the latency of the VEP within group 1 (who received clemastine fumarate during the first three months) decreased significantly within the first 90 days the latency of the VEP within group 2 (who received a placebo for the first three months) did not change significantly; after the subsequent two months (during which group 2 received clemastine fumarate and group 1 received the placebo), however, the latency times of the VEP improved (i.e. shortened) significantly within group 2 , while the latency times within group 1 no longer increased changed. The study also showed that the legibility of low-contrast letters improved during treatment with clemastine fumarate, although this was not statistically significant within the study structure there .
Contraindications and restrictions on use
Clemastine must not be used in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency or in patients with porphyria . Since clemastine has undesirable anticholinergic effects in addition to its desired effect as an antihistamine , there is a restriction on use in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma , symptomatic prostate enlargement with residual urine or bladder neck obstruction, and with other bladder emptying disorders. In these cases, the administration of clemastine can trigger an acute worsening of the diseases mentioned. Clemastine must also not be used in the presence of narrowing gastric ulcers and narrowing in the area of the gastric porter and the duodenum (pyloroduodenal obstruction).
unwanted effects
Sedation is reported as the most common undesirable effect after taking clemastine by over 10% of patients . This occurs particularly at the beginning of treatment and is due to the antihistaminergic effect of the active ingredient in the brain. The reduction in vigilance (alertness) and delayed reactions impair the ability to drive. In contrast, children can also develop states of excitement. Less than 1% of patients may experience a dry mouth, hypersensitivity reactions to the skin ( drug eruption ), headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms (such as nausea or constipation).
Interactions
Taking clemastine may increase the effects of other active substances taken at the same time. This applies in particular to alcohol, pain relievers (analgesics), sleeping pills (hypnotics), anesthetics (narcotics) and psychotropic drugs . If antidepressants or anti- Parkinson drugs of the type of MAO inhibitors are taken at the same time , this can increase the anticholinergic effect of clemastine.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There is a strict indication for the use of clemastine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Clinical data on pregnant women who took clemastine during pregnancy are not available. Therefore, the active ingredient may only be used after a careful medical risk-benefit assessment. Clemastine passes into breast milk; therefore, there is a strict indication even during breastfeeding.
chemistry
Stereoisomerism
Clemastine is chiral and contains two stereocenters. Hence there are four stereoisomers . The ( R , R ) form is used exclusively as a medicinal substance .
synthesis
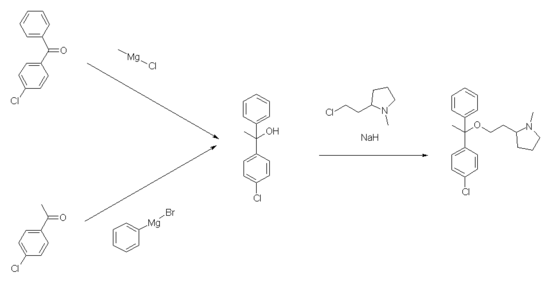
The synthesis of clemastine as a mixture of isomers takes place via two reaction steps, the intermediate product 1- (4'-chlorophenyl) -1-phenyl-ethanol being accessible either by reacting 4-chlorobenzophenone with methylmagnesium chloride or 4-chloroacetophenone with phenylmagnesium bromide . In the second step, the mixture of four stereoisomers is obtained by reaction with 2- (2-chloro-ethyl) -1-methyl-pyrrolidine in the presence of sodium hydride . The stereoisomers are separated and the target stereoisomers are obtained by fractional crystallization of the maleate salt and separation with the aid of (-) - dibenzoyl – L – tartaric acid.
Trade names
Clemastine is commercially available in Switzerland, Germany, Italy, France and Great Britain under the name Tavegil / Tavegyl.
literature
- K. Aktories, U. Förstermann, F. Hofmann, K. Starke (eds.): General and special pharmacology and toxicology. 9th edition. Elsevier, Munich 2005, ISBN 3-437-42521-8 , pp. 386-389.
- D. Schneider, F. Richling: Checklist Medicines A – Z. 2006-2007. 4th edition. Thieme, Stuttgart 2006, ISBN 3-13-130854-0 , p. 243.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet Clemastine fumarate salt from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 22, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b c d e A. Kleemann , J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications , 4th edition (2000), Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, ISBN 978-1-58890- 031-9
- ↑ J Kornhuber, M Muehlbacher, S Trapp, S Pechmann, A Friedl, M Reichel, C Mühle, L Terfloth, T Groemer, G Spitzer, K Liedl, E Gulbins, P Tripal: Identification of Novel Functional Inhibitors of Acid Sphingomyelinase . In: PLoS ONE . 6, No. 8, 2011, p. E23852. doi : 10.1371 / journal.pone.0023852 .
- ↑ Clemastine fumarate for promotion of optic nerve remyelination . In: The Lancet . doi: 10.1016 / S0140-6736 (17) 32639-9
- ↑ Clemastine fumarate as a remyelinating therapy for multiple sclerosis (ReBUILD): a randomized, controlled, double-blind, crossover trial . PMID 29029896
- ^ Ari Green, MD (Neurologist): Medical Director, Multiple Sclerosis Center
- ↑ University of California, San Francisco Medical Center (UCSF Medical Center): Link to the study
- ↑ PDF of the study: Clemastine fumarate as a remyelinating therapy for multiple sclerosis (ReBUILD): a randomized, controlled, double-blind, crossover trial (PDF)
- ↑ a b A. Ebnöther, H.-P. Weber: Synthesis and absolute configuration of clemastine and its isomers in Helv. Chim. Acta 59 (1976) 2462-2468. doi: 10.1002 / hlca.19760590721
- ↑ Red List 2008 . Verlag Rote Liste, Frankfurt am Main, ISBN 978-3-939192-20-6 , p. 53.
- ↑ JM Vernier, H. El-Abdellaoui, H. Holsenback, NDP Cosford, L. Bleicher, G. Barker, B. Bontempi, L. Chavez-Noriega, F. Menzaghi, TS Rao, R. Reid, AI Sacaan, C Suto, M. Washburn, GK Lloyd, IA McDonald: 4-2- (1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) ethylthio-phenol hydrochloride (SIB-1553A): A Novel Cognitive Enhancer with Selectivity for Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors . In: J. Med. Chem. , 42, 1999, pp. 1684-1686. doi: 10.1021 / jm990035d