Cyclododecanol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
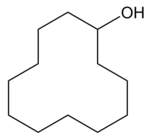
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cyclododecanol | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 24 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 184.32 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.908 g cm −3 at 80 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
75-78 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
272.7 ° C (1,013 hPa) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (0.04 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cyclododecanol is a secondary macrocyclic alcohol with a pronounced camphor-like odor, from which musky and woody odorous substances can be synthesized.
Manufacturing
Cyclododecanol (CDOL) is an intermediate product in the large-scale synthesis of cyclododecanone or 1,12-dodecanedioic acid and is a component of the so-called ol-on mixture.
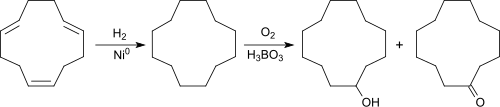
Starting from 1,5,9-cyclododecatriene (CDT), which is accessible from 1,3-butadiene , the macrocyclic alkane cyclododecane (CDAN) is produced virtually quantitatively by complete catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of Raney nickel at 200 ° C and 10-15 bar pressure receive.
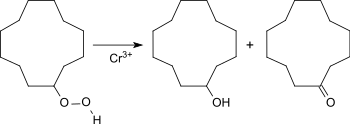
CDAN is - similar to the conversion of cyclohexane to cyclohexanol - oxidized with air or oxygen in the presence of boric acid at 150-160 ° C and normal pressure in the liquid phase ( Bashkirov oxidation ). The cyclododecane hydroperoxide formed as an intermediate reacts with boric acid to form cyclododecane triborate and is thus withdrawn from further oxidation to cyclododecanone (CDON).
The hydrolysis of the triborate provides the ol-on mixture with a composition of 80 to 90% CDOL and 10 to 20% CDON. The product Cyclododecanol tel quel from Evonik Industries is an oil-on mixture of unspecified composition.
Because of the low selectivity of the oxidation reaction, the reaction conversion is kept below 30%.
The process gives relatively high yields of cyclododecanol, which is synthetically less valuable than cyclododecane, and has considerable disadvantages because of the additional hydrolysis step, the necessary recycling of cyclododecane and the boric acid, which is toxic to reproduction , and expensive distillations.
A process that avoids boric acid and provides higher levels of CDON uses chromium octanoate (chromium (III) -2-ethylhexanoate) to decompose the cyclododecyl hydroperoxide, with ol-on mixture ratios of up to 1:35 being obtained. However, this process variant is also limited to low sales (here 10%).
In a continuous process described as less energy-intensive, CDT with oxygen at 100 ° C and approx. 790 kPa z. B. in a bubble column reactor with conversions of up to 96% to monooxidation products - in addition to the main product epoxycyclododeca-6,10-diene, CDOL and CDON are formed - and converted under optimal conditions with a selectivity of 97%.
The reaction mixture is after distillation at 220 ° C and about 9 hPa hydrogen pressure for 12 hours with palladium as a catalyst with a yield of 97% of theory. hydrogenated to cyclododecanol.
A newer, more environmentally friendly alternative is also based on CDT, which is produced in the presence of a long-chain alkylammonium salt of a heteropolyacid , here hexadecyltrimethylammonium heteropolyphosphatotungstate [(nC 16 H 33 NMe 3 ) 3 PW 4 O 16 , HAHPT], with hydrogen peroxide in water as a solvent at 55 ° C after one hour in a homogeneous phase with an average yield of 61.8% of theory. to two isomeric epoxycyclododecadienes [63% 1,2-trans-epoxy-5,9-cis, trans-cyclodecadiene (I) and 37% 1,2-cis-epoxy-5,9-trans, trans-cyclododecadiene (II) ] is epoxidized.
The catalyst precipitates from the reaction mixture after the hydrogen peroxide has been consumed, but retains its activity even after several reaction cycles.
Subsequent catalytic hydrogenation with Raney nickel in ethanol gives CDOL in yields of up to 95% of theory.
According to a further process variant, CDT is partially hydrogenated to cyclododecene and this is converted into CDOL with water in carbon tetrachloride and the catalyst system chromium (III) acetate-acetic acid (1: 3) at 180 ° C. within 6 hours in 67% yield.
properties
Cyclododecanol is a colorless crystalline solid with a pronounced camphor odor and low water solubility (40 mg / l at 20 ° C). CDOL is soluble in most organic solvents, such as. B. in benzene, methanol and chloroform.
Applications
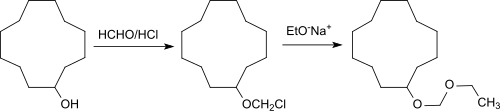
Cyclododecanol is mostly dehydrated to cyclododecanone, the starting material is for laurolactam , laurolactone and the linear dicarboxylic acid 1,12-dodecanedioic acid , as well as through ring expansion, cyclopentadecanone and the macrolides cyclopentadecanolide, and cyclohexadecanolide, which are used as musk. Cyclododecyl methyl ether, cyclododecane ethyl and vinyl ether and ethoxymethoxy cyclododecane are etherification products of cyclododecanol with methyl chloride or acetylene or the latter with paraformaldehyde / hydrogen chloride gas to form CDOL chloromethyl ether and subsequent Williamson ether synthesis with sodium ethoxide .
The ethers are characterized by a wood-like odor note.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on cyclododecanol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 9, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet for cyclododecanol synthesis (PDF) from Merck , accessed on October 1, 2014.
- ^ A b Evonik Industries: High Performance Building Blocks
- ^ A b Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg: Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: Preparation, Properties and Uses, Fourth completely revised edition . Wiley-VCH, 2001, ISBN 3-527-30364-2 .
- ↑ a b c H.-J. Arpe: Industrial Organic Chemistry . 6th completely revised edition. Wiley-VCH, 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6 .
- ↑ A. Chauvel, G. Lefebvre: Petrochemical Processes: 2 Major oxygenated, chlorinated and nitrated derivatives, 2nd Edition . Editions Technip, 1989, ISBN 2-7108-0563-4 .
- ↑ G. Oenbrink, T. Schiffer: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 6th Edition . Cyclododecanol, Cyclododecanone and Laurolactam. Wiley-VCH, 2000, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a08_201.pub2 .
- ↑ Patent US5892123 : Process for reproducing a mixture containing cyclododecanone and cyclododecanol. Published April 6, 1999 , Applicant: EI du Pont de Nemours and Company, Inventor: HW Anderson, JB Sieja.
- ↑ Patent EP2407444 : Process for the preparation of dodecanedioic acid. Registered on March 18, 2009 , published on January 18, 2012 , applicant: Invista Technologies Sarl, inventor: G. Rajendran.
- ↑ Qi Feng et al .: Eco-friendly synthesis of cyclododecanone from cyclododecatriene . In: Green and Sustainable Chemistry . tape 1 , no. 3 , 2011, p. 63-69 , doi : 10.4236 / gsc.2011.13011 .
- ↑ TM Oshnyakova, NA Shchadneva, RI Khusnutdinov, and UM Dzhemilev: Addition of Water and Carbon Tetrachloride to Cyclododecene in the Presence of Chromium Catalysts . In: Russ. J. Org. Chem. Volume 44 , no. 8 , 2008, p. 1240-1242 , doi : 10.1134 / S1070428008080241 .
- ↑ Acros Organics: Cyclododecanol 99%
- ↑ Patent EP0359117A2 : Cycloalkyl vinyl ethers , their production and use. Filed on September 7, 1989 , published on March 21, 1990 , Applicant: BASF AG, inventor G. Lauterbach et al ..