Cyclododecanone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
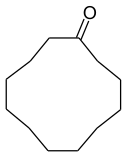
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cyclododecanone | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 22 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless crystals smelling like camphor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 182.31 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.97 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
59 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
13 Pa (132 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (45 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4571 (60 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Cyclododecanone is a chemical compound from the group of alicyclic ketones ( cycloalkanones ). It can be derived from the hydrocarbon cyclododecane and can also be obtained from this.
Manufacturing
Cyclododecanone, along with other ring ketones, was first synthesized in the Chemistry Institute of the ETH Zurich in Leopold Ruzicka's group . In his research on animal odoriferous substances ( muscon , civetone ), Ruzicka expanded the method of pyrolysis ( thermolysis ) of dicarboxylic acid salts by using cerium, thorium and yttrium salts instead of calcium or barium salts.
The thorium salt was produced from undecanedicarboxylic acid (= tridecanedioic acid) ; this was heated to 350-400 ° C. in vacuo. During this thermolysis - among other compounds - the volatile (distillable) 12-ring ketone was formed in low yield. The substance contained in the reaction products was purified by producing the semicarbazone . The latter was converted into the ketone by hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid or aqueous oxalic acid .
After 1,5,9-cyclododecatriene had become industrially available, cyclododecanone could also be produced from it on a large scale. In a synthesis used by BASF, cyclododecadienone is obtained from triene by reaction with nitrous oxide , which is converted to cyclododecanone by hydrogenation .
properties
Physical Properties
The skeletal formula shown in the info box does not reflect the “real” molecular structure. As with the hydrocarbon cyclododecane , the twelve carbon atoms are not in one plane. The molecule is "flexible"; That is, its atoms are internally in constant motion ( pseudorotation ). This means that different conformations are possible. They are very similar to those found in hydrocarbons.
In the crystalline state - as an X-ray crystal structure analysis at minus 160 ° C showed - there is a conformer with C 2 symmetry. It has been called "square" ( " square ") is because the carbon atoms C-2, C-5, C-8 and C-11 can be used as corner points of a square interpret. This conformation, which is preferred in the crystal, could also be detected in solution by means of NMR spectroscopy at low temperatures.
Chemical properties
Cyclododecanone is a flammable colorless solid that smells like camphor and is practically insoluble in water.
use
Cyclododecanone is used to make dodecanedioic acid and laurolactam and is used in the perfume industry. It is also used to make other macrocyclic compounds such as muscon .
safety instructions
Applied to mineral fibers or kieselgurstein, cyclododecanone tends to self-ignite well below the ignition point of 230 ° C.
Trivia
On September 12, 2012, there was a chemical accident in a BASF SE sewage treatment plant in Ludwigshafen, in which around 500 kilograms of the compound, which is long-term toxic for aquatic organisms, flowed into the Rhine. Due to the amount leaked and the dilution of the product in the Rhine, according to BASF, no risk to aquatic organisms can be assumed.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d L. Ruzicka, M. Stoll, H. Schinz, Helvetica Chimica Acta 9 (1926), pp. 249–264, here: p. 256.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry for CAS no. 830-13-7 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on November 3, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Cyclododecanone data sheet (PDF) from Merck , accessed on November 3, 2012.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-126.
- ↑ Data sheet Cyclododecanone, ≥99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 3, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann, Organic Chemistry, p. 219, Verlag Harri Deutsch, Thun-Frankfurt am Main, 1985, ISBN 3-87144-902-4 .
- ^ Fabrizio Cavani, Gabriele Centi, Siglinda Perathoner, Ferruccio Trifirò: Sustainable Industrial Chemistry . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 3-527-62912-2 , pp. 384 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ P. Groth: On the Crystal Structure of Cyclododecanone . In: Acta Chemica Scandinavica . 33a, 1979, p. 203–205 , doi : 10.3891 / acta.chem.scand.33a-0203 (free full text).
- ↑ Tarik N. Rawdah: NMR spectroscopic study of the conformational features of cyclododecanones . In: Tetrahedron . tape 47 , no. 40 , 1991, pp. 8579-8586 , doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 82401-7 .
- ↑ Tse-Lok Ho: Symmetry: A Basis for Synthesis Design - Tse-Lok Ho . John Wiley & Sons, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-57376-0 , pp. 442 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ BASF: Leakage of cyclododecanone into the Rhine. ( Memento from January 17, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ) BASF.

