Dihydroergotamine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
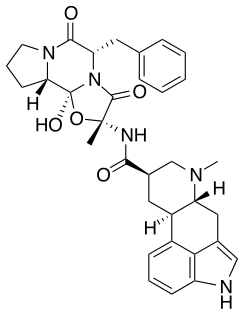
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Dihydroergotamine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
(5 S , 10 R ) -5-Benzyl-12-hydroxy-2-methyl-9,10-dihydroergotaman-3,6,18-trione |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 33 H 37 N 5 O 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 583.68 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
239 ° C; 230-235 ° C (mesilate); 210–215 ° C (tartrate, decomp.) |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
6.8 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Dihydroergotamine ( DHE for short ) is a medicinal substance derived from the ergot alkaloid ergotamine , which was used for the therapy of hypotonic circulatory disorders as well as for the therapy of migraines and cluster headaches and is subject to medical prescription . The active ingredient was patented by Sandoz in 1942 . The mesilate and the tartrate of the alkaloid are used.
Mechanism of action
Dihydroergotamine is an antagonist or a partial agonist of various subtypes of α 1 -adrenoceptors , α 2 -adrenoceptors , dopamine receptors and serotonin receptors . Its migraine effectiveness is u. a. explained with a partial agonism of serotonin 5-HT 1B / 1D receptors.
application
Dihydroergotamine is used in the therapy of acute blood vessel-related (migraine) headache, in some countries also for the treatment of dementia . Dihydroergotamine is no longer permitted in the EU for the prophylaxis of migraine headache, for the treatment of orthostatic hypotension and for the symptomatic treatment of venous-lymphatic insufficiency. In a risk assessment based on current knowledge of the verdict CHMP (Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency in June 2013 that in some indications the fibrosis and Ergotismusrisiko outweigh the benefits of therapy with dihydroergotamine. The Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices thereupon ordered the suspension of the approval for drugs with the active ingredient dihydroergotamine, which were only approved for the areas of application no longer indicated, on February 1, 2014. In June 2013, the Austrian AGES medical market supervisory authority recommended that dihydroergotamine no longer be used in areas of application with an unfavorable risk-benefit ratio.
It is administered orally (as tablets, capsules or drops), as an injection (ampoules), intranasally (as a nasal spray) or orally by inhalation using a special inhaler. With oral inhalation, dihydroergotamine achieves a higher bioavailability than with nasal administration, which was shown in a randomized double-blind phase III study .
Side effects
The most common side effects observed with dihydroergotamine include restlessness, nausea and headache. Furthermore, angina and peripheral circulatory disturbances.
Due to severe and potentially fatal side effects such as fibrosis in various organs and tissues and ergotism (poisoning by ergot alkaloids), a red-hand letter from the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices ( BfArM ) in January 2014 prohibited use as a prophylaxis for migraine headaches, orthostatic hypotension and as symptomatic treatment for venous-lymphatic insufficiency.
Interactions and contraindications
Since dihydroergotamine is metabolized via the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, inhibitors such as B. Macrolide antibiotics , the effects and side effects of dihydroergotamine. Dihydroergotamine must not be given at the same time as triptans (anti- migraine drugs).
Trade names
- Monopreparations
Dihydergot (A, CH), Ergont (A), Migranal (A)
Related links
- Dihydroergotamine mesylate
- Dihydroergotamine tartrate
Web links
- New restrictions on the use of medicines containing ergot derivatives . English. Press release of the European Medicines Agency of June 28, 2013. Online at ema.europa.eu.
- Safety information Ergot derivatives . Federal Office for Safety in Health Care (A) of June 28, 2013. Online at basg.gv.at.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on dihydroergotamine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 30, 2019.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Guidelines for the therapy of migraine of the German Society for Neurology, accessed on August 3, 2014
- ^ S1 guideline for cluster headaches and trigemino-autonomic headaches of the German Society for Neurology (DGN). In: AWMF online (as of 2015)
- ↑ a b New restrictions on use of medicines containing ergot derivatives ; EMA press release of June 28, 2013.
- ↑ a b Dihydroergotamine and Dihydroergotoxin: Implementation of the implementation decisions of the EU Commission. Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices April 1, 2014. Accessed April 24, 2014.
- ^ Ergot derivatives (various preparations) ( Memento from December 6, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), Agency for Health and Food Safety # Federal Office for Health Safety , June 28, 2013.
- ↑ Sheena K. Aurora, Stephen D. Silberstein, Shashidhar H. Kori, Steward J. Tepper, Scott W. Borland, Min Wang, David W. Dodick: MAP0004, Orally Inhaled DHE: A Randomized, Controlled Study in the Acute Treatment of Migraine . In: Headache: The Journal of Head and Face Pain . tape 51 , no. 4 , April 2011, p. 507-517 , doi : 10.1111 / j.1526-4610.2011.01869.x .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for dihydroergotamine mesylate: CAS number: 6190-39-2, EC number: 228-235-6, ECHA InfoCard: 100.025.669 , PubChem : 71171 , ChemSpider : 64311 , DrugBank : DBSALT000997 , Wikidata : Q27126884 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to dihydroergotamine tartrate : CAS number: 5989-77-5, EC number: 227-816-1, ECHA InfoCard: 100.025.287 , GESTIS substance database : 119399 , PubChem : 3037136 , ChemSpider : 2300960 , Wikidata : Q27126885 .