Methine dyes
Methine dyes (polymethine dyes) are dyes whose chromophoric system consists of conjugated double bonds ( polyenes ), which are flanked by two end groups - an electron acceptor A and an electron donor D :
The methine dyes contain an odd number of methine groups . The end groups can also be part of a heterocycle and the double bonds part of an aromatic system. This results in different subclasses for the methine dyes. The methine dyes can be cationic , anionic or neutral.
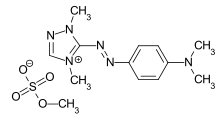
If one or more methine groups are replaced by a heteroatom - usually nitrogen - one speaks of heteroanalogous (aza-analogous) methine dyes.
Principal properties and classification
Methine dyes can be characterized as polyene dyes with terminal electron donor and acceptor groups. In the majority of cases, the end groups of the methine dyes contain nitrogen or oxygen atoms . However, while the polyene dyes usually occurring as natural dyes , such as the carotenoids , are limited to yellow to yellow-red shades, almost all colors of the spectrum can be achieved with the predominantly synthetic methine dyes.
Cyanine dyes
The best-known group of methine dyes are the cationic cyanine dyes . Both terminal groups of the chromophore contain nitrogen atoms, the amino or imino group in each case being part of a heterocycle .
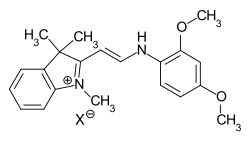
Hemicyanine dyes
In the case of hemicyanine dyes, one terminal amino group is part of a heterocycle, while the second terminal group is open-chain.
Streptocyanin dyes
If the two terminal amino or imino groups of the chromophore are open-chain, one speaks of streptocyanin dyes.
Merocyanine dyes
The merocyanine dyes have an amino and a carbonyl group as end groups of the polyene structural element. Both a neutral and a zwitterionic mesomeric boundary structure can be formulated for this type of compound .
Oxonol dyes
Representatives of the oxonol dyes, the terminal groups of which contain oxygen as a hetero atom, play a role in analog color photography.
Styryl dyes
Condensation of an active methylene compound , for example malononitrile , with a benzaldehyde derivative gives the styryl dyes, which belong to the methine dyes. By integrating a benzene ring in the poly part, these compounds have a styrene partial structure. The styryl dyes are used as disperse dyes in the dyeing of polyester fibers .
Example: Preparation of CI Disperse Yellow 31 ( 3 ) by condensation of ethyl cyanoacetate ( 1 ) with p -aminobenzaldehyde derivative ( 2 ).
Di- and triarylmethine dyes
Amino- and hydroxy-substituted di- and triarylmethines also have the structural element of methine dyes:
Triarylmethine dyes, mesomeric boundary structures (R = H, alkyl)
The triarylmethine dyes are derived from triphenylmethane , in which at least two of the aromatic rings have electron-donating substituents (e.g. amino groups, secondary and tertiary alkylamino groups or hydroxyl groups). They are therefore also referred to as triarylmethane dyes in the older literature . For the dyes, mesomeric boundary structures can be formulated as a carbenium ion or with an iminocyclohexadiene or cyclohexadienone partial structure. The central carbon atom in the dyes is therefore not sp 3 - but sp 2 - hybridized.
Triarylmethine dyes usually produce intense, bright colors with varying degrees of lightfastness. In addition to dyeing and printing textiles, leather and paper, they are also used for printing inks, inks, in ballpoint pen pastes and as microscopic dyes. As functional dyes, some representatives of this dye class are used as indicators ( phenolphthalein ), as disinfectants , anthelmintics and antimycotics (e.g. malachite green , crystal violet ).
Examples:
Aza-analogous methine dyes
If a methine group of the methine dyes is replaced by a nitrogen atom, the azamethine dyes are obtained (example: CI Basic Yellow 28). The diazamethine dyes are obtained accordingly by replacing two methine groups with nitrogen atoms. In particular, the diazahemicyanine dyes (examples: CI Basic Red 22 and CI Basic Blue 41) are an important class of methine dyes and are used as cationic dyes in the dyeing of polyacrylonitrile fibers .
Examples:
The quinoneimine dyes are aza-analogous representatives of the diarylmethine dyes:
General structure of the quinonimine dyes
with X = OH, NH 2 or NR 2 Y = O or NH
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Heinrich Zollinger: Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments . 3. Edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ Entry on polymethine dyes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on February 1, 2019.
- ^ A b c Klaus Hunger (Ed.): Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications . WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 978-3-662-01950-4 ( limited preview in the Google book search).
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Red 12 : CAS number: 6320-14-5, EC number: 228-668-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.026.062 , PubChem : 6540442 , ChemSpider : 4645019 , Wikidata : Q72444849 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Yellow 11 : CAS number: 4208-80-4, EC number: 224-132-5, ECHA InfoCard: 100.021.939 , PubChem : 6436295 , ChemSpider : 66308 , Wikidata : Q27251133 .
- ↑ Entry on Merocyanine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 22, 2019.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for Oxonole Blue dipotassium salt : CAS number: 51858-17-4, EC number: 257-479-6, ECHA InfoCard: 100.052.237 , PubChem : 20833147 , ChemSpider : 29272125 , Wikidata : Q82869407 .
- ↑ Entry on Oxonol dyes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 22, 2019.
- ↑ Entry on triarylmethane dyes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on February 1, 2019.
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Yellow 28 : CAS number: 54060-92-3, EC number: 258-946-7, ECHA InfoCard: 100.053.570 , PubChem : 9570625 , ChemSpider : 7845092 , Wikidata : Q27254755 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Red 22 : CAS number: 12221-52-2, EC number: 602-140-3, ECHA InfoCard: 100.115.765 , PubChem : 73759884 , ChemSpider : 21167832 , Wikidata : Q27268936 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Basic Blue 41 : CAS number: 12270-13-2, EC number: 235-546-0, ECHA InfoCard: 100.032.302 , PubChem : 83008 , ChemSpider : 74891 , Wikidata : Q27252322 .