Triphenylmethane dyes
The triphenylmethane dyes are derived from triphenylmethane . Compounds with an intact triphenylmethane partial structure are colorless. By introducing electron-donating substituents (so-called auxochromes ) on at least two of the aromatic rings, a quinoid system can be formed as a chromophore , which determines the color of the compounds. Triphenylmethane dyes are mainly used in printing technology or (due to their low acid resistance) as indicators, but also as textile and food dyes. They are generally not lightfast .
According to a suggestion made by Siegfried Dähne in 1965 , the triphenylmethane dyes should better be referred to as triphenylmethine dyes , since the central carbon atom is not sp 3 - but sp 2 - hybridized.
Substance groups
Aminotriphenylmethane dyes
The representatives of this group are characterized by at least two amino groups as auxochromes .
Derivatives with sulfonic acid group:
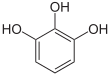
Hydroxytriphenylmethane dyes
The compounds in this subgroup contain at least one hydroxyl group as auxochrome .
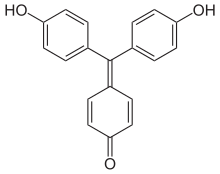
- Fuchson (diphenylquinomethane) is the parent compound, but it does not yet have the character of a dye.
- Benzaurine (p-Hydroxyfuchson) is a phenol derivative, is yellow-red and has acidic properties. With diluted alkalis, purple salts are formed.
- Aurin (p, p'-Dihydroxyfuchson) dissolves in alkalis with a red color and is used as a pH indicator .
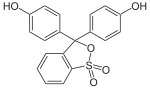
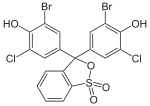
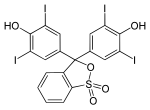
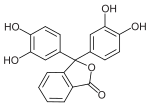
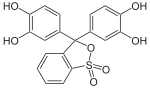
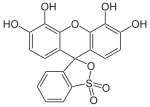
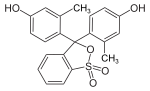
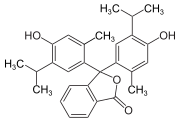
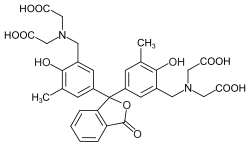
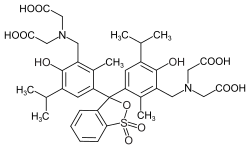
Phthaleins and sulfonphthaleins
This class of dyes is derived from the o -carboxylic acid of triphenylmethanol .
presentation
The phthaleins are prepared by heating 1 equivalent of phthalic anhydride with 2 equivalents of the phenol component (in the presence of small amounts of concentrated sulfuric acid). To prepare the sulfonphthaleins, the 2-sulfobenzoic anhydride is reacted with the phenol component. Phenolphthalein forms the basic compound of phthaleins and is one of the best-known indicators. Similarly, phenol red forms the basic compound of sulfonphthaleins.
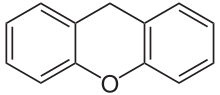
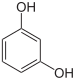
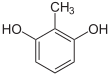
If resorcinol , pyrogallol or 2,6-dihydroxytoluene is used as the phenol component , an ether bridge is also formed (e.g. fluorescein , eosin Y , calcein ). The xanthene is also to be regarded here as the basic structure to be derived.
Structures at different pH values
At a low pH , the phthaleins are in the colorless lactone form 1 and the sulfonphthaleins in the likewise colorless sultone form . The phenolic hydroxyl protons dissociate in an alkaline solution and the + M effect causes the lactone or sultone ring to open into the colored, mesomeric-stabilized quinoid form 2 . The colorless triphenylmethanol derivative 3 is obtained in a strongly alkaline solution , while the colored, mesomeric-stabilized protonated form 4 is formed in a strongly acidic solution .
use
Almost all dyes are used as indicators .
Examples
literature
- Z. Tamura, M. Maeda: Differences between phthaleins and sulfonphthaleins , in: Yakugaku Zasshi 1997 , 117 (10-11), pp. 764-770. PDF (Japanese)
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Heinrich Zollinger: Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments . 3. Edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3 , p. 101 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organic chemistry . Basics, substance classes, reactions, concepts, molecular structure. 5th edition. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, New York 2005, ISBN 3-13-541505-8 , pp. 725 ( limited preview in Google Book search).