demagnetization
The demagnetization (also demagnetization , in connection with picture tubes also English degaussing - literally degaussing ) is a process by which a permanent magnet or a ferromagnetic material that has become permanently magnetic loses its magnetic polarization in whole or in part.
Procedure
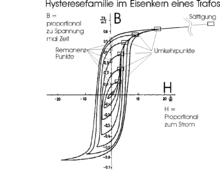
Demagnetize materials usually only by a strong exchange - magnetic field , which then gradually subsides. This must first be so strong that the coercive field strength of the magnetized material is achieved. The decreasing alternating field then results in a reversal of magnetization of the permanent magnetic materials with decreasing amplitude . The hysteresis curve is thus traversed with decreasing amplitude of the magnetic field strength and the magnetic flux density until the permanent magnetic field is zero. In the adjacent picture, for example, you start at the top right, then you always go counter-clockwise to the bottom left, then back to the top right, but not that far, etc. When after many revolutions the smallest loop is reached at the intersection of the two axes, you can switch off the external magnetic field, the iron is largely demagnetized.
There are two methods for weakening the alternating field:
- either slowly removing a portable electromagnet running at 50 Hz , or
- a PTC thermistor is placed in series with the coil, which makes the current lower. According to the manufacturer, 5 to 10 magnetizations are sufficient.
Demagnetization can also be caused by mechanical vibrations or by heating ferromagnetic materials above the Curie temperature .
Applications
Tools
Demagnetization is important for tools in order to reduce their attraction to chips or components, or in cases where magnetic fields interfere (e.g. alignment of coils ). If you have no anti-magnetic tools available, you may have to demagnetize magnetic tools. There are also electromagnets operated with mains voltage . Permanently magnetic, step-shaped components are also in use, over which the tools are pulled and thus a fading alternating field is generated in them. Such devices can often also be used to magnetize tools for specific assembly tasks.
Magnetic playback and storage media
In analog video recorders and tape recorders there is an erase head , which is an electromagnet operated with high frequency. With this it is possible to locally erase the information present as magnetization on the tape in order to have unmagnetized tape available for a subsequent recording. With digital magnetic storage media, on the other hand, it is sufficient to overwrite the information.
By degaussing with so-called degaussers , which generate a large-scale alternating field, large quantities of magnetic storage media such as floppy disks , hard drives and magnetic tapes can be quickly erased in order to ensure data security when they are disposed of .
Devices and storage systems for magnetic tapes , but also for picture tubes and these themselves, must be free of permanent magnetization. This is why loudspeakers in tube televisions have a permanent magnet circuit that - unlike conventional electrodynamic loudspeakers - hardly has a magnetic field around it or is shielded.
Magnetization and demagnetization also play a role in many article security labels .
Picture tubes
Color picture tubes in monitors and televisions contain magnetizable parts ( pinhole or slit mask ) which, when they have become permanently magnetic, deflect the electrons, which leads to color distortions. Therefore, in the devices of the mains voltage is demagnetized (each time degaussing performed). This is done with a coil that is wound around the picture tube. When it is switched on, it is connected directly to the mains voltage via a PTC thermistor equipped with a heating element and generates a decaying alternating magnetic field through its own heating. The heating element is used to heat the PTC a little further so that the current through the degaussing coil is almost zero.
Ships

For military ships, the z. B. recorded by the geomagnetic field magnetization to make the ships for magnetic mines and torpedoes with magneto more difficult to find.
The demagnetization systems for ships of the German Navy are located in Wilhelmshaven , near Kiel in Friedrichsort and in Möltenort . The East German People's Navy used an artificial island in the Rügischer Bodden to the east of Vilm . The Peene shipyard in Wolgast (today part of the Lürssen Group), at that time the main supplier of the Volksmarine, had such a facility in the Peene river, which can still be viewed in ruins today.
Some ships also have their own magnetic self-protection system with which not only the permanent magnetic properties of the hull, but also other magnetic signatures, such as the electromagnetic fields from generators, are compensated. There were also earlier attempts to use coils placed around the hull for the remote ignition of sea mines.
Magnetically shielded rooms
For some applications in research it is necessary to shield the magnetic interference fields of the urban environment of the measuring location, which are many orders of magnitude stronger, and the ubiquitous geomagnetic field of approx. 40µT. These include, for example, the diagnostic examination of the magnetic fields that occur during brain, nerve or heart activity with a field strength of a few pT to nT , or the determination of the electrical dipole moment of the neutron . Magnetic shielding rooms made of highly permeable material (e.g. mu-metal ) are also used. A prominent representative is the BMSR-2, one of the best magnetically shielded rooms on earth, the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in Berlin. The currently best magnetically shielded room in the world is located on the campus of the Technical University of Munich in Garching . These rooms must be regularly demagnetized in order to keep the residual field within the room as low as possible and thus allow measurements of fields up to the fT range.
Precision mechanics
Fine mechanical constructions, e.g. B. mechanical clockworks , if necessary, must be demagnetized when using ferromagnetic materials to avoid unwanted adhesive and disruptive forces.
Specialist literature
- Günter Springer: Expertise in electrical engineering. 18th edition, Verlag - Europa - Lehrmittel, Wuppertal, 1989, ISBN 3-8085-3018-9
- Richard P. Feynman, Robert B. Leighton, Matthew Sands: Lectures on Physics. 3rd edition, Oldenbourg Verlag, Munich Vienna, 2001, ISBN 3-486-25589-4
- F. Thiel, A. Schnabel, S. Knappe-Grüneberg, D. Stollfuß, and M. Burghoff: Demagnetization of magnetically shielded rooms , Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 035106 (2007) (13 pages), doi : 10.1063 / 1.2713433
Individual evidence
- ↑ Construction site is making better progress than planned. Degaussing system. kn-online.de, September 6, 2017, accessed on March 31, 2018 .
- ^ Frank Pergande: "The Isle of Vilm". Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, July 2, 2009
- ↑ Location of the former demagnetization station
- ↑ Image of the BMSR-2 ( Memento of the original from November 9, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ New shield makes certain types of searches for physics beyond the standard model possible for first time . In: phys.org . Retrieved July 29, 2015.
- ↑ Igor Altarev, et al .: Minimizing magnetic fields for precision experiments . In: Journal of Applied Physics . 117, No. 23, 2015, p. 233903. arxiv : 1501.07408v1 . doi : 10.1063 / 1.4922671 .