Ethyl vanillin
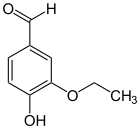
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ethyl vanillin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 10 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless scales with a sweet, creamy, floral odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 166.18 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
hardly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Ethylvanillin ( 3-ethoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde , Bourbonal , FEMA 2464 ) is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 9 H 10 O 3 . It is a derivative of benzaldehyde with an additional hydroxy and an ethoxy group . It differs from vanillin in that the methyl group is exchanged for an ethyl group . It doesn't happen naturally.
presentation
A common possibility is the substitution reaction of o -ethoxyphenol ( 1 ) with glyoxylic acid and subsequent oxidation of the acid ( 2 ) formed to 4-hydroxy-3-ethoxyphenylglyoxylic acid ( 3 ), which is decarboxylated to ethylvanillin ( 4 ) .
properties
Ethyl vanillin occurs in the form of colorless scales with a sweet-creamy, floral odor and melts at 77–78 ° C. It is hardly soluble in water, but soluble in ethanol and ether. Vanillin and ethyl vanillin also have a similar smell, ethyl vanillin is 2 to 4 times more intense. Vanillin and ethylvanillin can be easily separated using mixtures of n-hexane and ethyl acetate by thin-layer chromatography . With conc. Sulfuric acid turns it yellow in contrast to vanillin.
Isomers and structural relatives
Isoethylvanillin ( 3-hydroxy-4-ethoxybenzaldehyde ) is an isomer and differs from ethylvanillin in the position of the ethoxy group. Instead of position 3, this is found here in position 4. Hydroxy and ethoxy groups swap places compared to ethyl vanillin. The structural analogy corresponds to that between vanillin and isovanillin .
ortho- ethylvanillin ( novovanillin , 2-hydroxy-3-ethoxybenzaldehyde ) is also an isomer and differs from ethylvanillin in the position of the hydroxyl group. The prefix ortho indicates the position of the hydroxyl group in relation to the aldehyde group; in ethylvanillin these two groups are in the para position. The structural analogy corresponds to that between vanillin and ortho- vanillin .
 |
 |

|
| Isoethylvanillin | Ethyl vanillin | ortho- ethylvanillin (novovanillin) |
use
Today, ethyl vanillin is used as an artificial flavoring instead of vanillin. As a flavor additive, it is mainly used in ice cream, sodas, confectionery and baked goods. According to the Flavor Ordinance , a maximum of 250 mg / kg may be added to certain foods.
For the synthesis of isovanillin is u. a. Ethylvanillin ( 1 ), which is methylated with dimethyl sulfate to give 3-ethoxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde ( 2 ). The ethyl ether is then selectively cleaved with sulfuric acid .
literature
- Beilstein E IV 8, 1765.
Web links
- Entry on ethyl vanillin . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD, accessed December 14, 2012.
- chemgapedia (fragrances: vanillin / ethylvanillin as an example): Part 1 , Part 2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Entry on FEMA 2464 in the database of the Flavor and Extract Manufacturers Association of the United States .
- ↑ Entry on ETHYL VANILLIN in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on July 14, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on ethylvanillin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 20, 2014.
- ↑ a b c data sheet ethyl vanillin from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 31, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Toru Egawa, Akiyo Kameyama, Hiroshi Takeuchi: Structural determination of vanillin, isovanillin and ethylvanillin by means of gas electron diffraction and theoretical calculations. In: Journal of Molecular Structure . 2006 , 794 (1-3), pp. 92-102; doi : 10.1016 / j.molstruc.2006.01.042 ; PDF .
- ↑ AV Gerasimov, NV Gornova, NV Rudometova: Determination of Vanillin and Ethylvanillin in Vanilla Flavorings by Planar (Thin-Layer) Chromatography. In: Journal of Analytical Chemistry . 2003 , 58 (7), pp. 677-684; doi : 10.1023 / A: 1024764205281 .
- ↑ George A. Burdock: Fenaroli's Handbook of Flavor Ingredients. Sixth Edition, CRC Press, 2010, ISBN 978-1-4200-9077-2 , p. 674.
- ^ Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg: Flavors and Fragrances. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry . Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2002, ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4 , ( doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a11_141 ).
- ↑ AromV: Annex 5 (to Section 3) additives
- ↑ Patent specifications : PatentDE: Process for the production of isovanillin ; United States Patent 5648552: Process for the preparation of isovanillin .


