Fisetin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
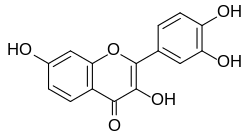
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Fisetin | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 10 O 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow needles |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 286.24 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
330 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Fisetin is a yellow dye which , as an oxidation product of fisetinidine, belongs to the group of flavonols and is therefore a derivative of chromene .
Occurrence
Fisetin occurs in the wig bush (also fiseth wood , hence the name); The alternative name cotinine is derived from its Latin name Cotinus coggygria or Rhus cotinus . Foods that contain fisetin include apples, persimmons, grapes, cucumbers, strawberries, and onions.
properties
Dilute solutions of the substance in ethanolic sodium hydroxide solution show dark green fluorescence .
Biological effects
Fisetin is slightly toxic and is said to have a mutagenic effect. It also reduces the toxicity of aflatoxins .
A study by P. Maher et al. shows that fisetin also promotes long-term memory .
Yousefzadeh et al. have demonstrated a senolytic effect of fisetin both in cell cultures and in mice. In the mice examined, oral administration of fisetin delayed disease symptoms and increased life span ( median and maximal). Zhu and Doornebaal et al. Had previously also discussed the senolytic effect of fisetin in cell cultures. reported.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on FISETIN in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on May 13, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e J. Falbe, M. Regitz (Ed.): Römpp Lexikon Chemie . 10th edition. Thieme, Stuttgart a. New York 1996-1999, p. 1347.
- ↑ Fisetin data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 1, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ N. Khan, DN Syed et al. a .: Fisetin: A Dietary Antioxidant for Health Promotion . In: Antioxidant Redox Signal . tape 19 , no. 2 , 2013, p. 151–162 , doi : 10.1089 / ars.2012.4901 , PMC 3689181 (free full text).
- ↑ VM Adhami et al. a .: Dietary flavonoid fisetin: A novel dual inhibitor of PI3K / Akt and mTOR for prostate cancer management . In: Biochem Pharmacol. tape 84 , no. 10 , 2012, doi : 10.1016 / j.bcp.2012.07.012 , PMC 3813433 (free full text).
- ↑ P. Maher, T. Akaishi, K. Abe: Flavonoid fisetin promotes ERK-dependent long-term potentiation and enhances memory . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . tape 103 , no. 44 , 2006, pp. 16568–16573 , doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0607822103 , PMC 1637622 (free full text).
- ↑ MJ Yousefzadeh et al. a .: Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan . In: EBioMedicine . No. 36 , 2018, p. 18–28 , doi : 10.1016 / j.ebiom.2018.09.015 , PMC 6197652 (free full text).
- ↑ Y. Zhu, EJ Doornebal u. a .: New agents that target senescent cells: the flavone, fisetin, and the BCL-XL inhibitors, A1331852 and A1155463 . In: Aging (Albany NY) . tape 9 , no. 3 , 2017, p. 955–963 , doi : 10.18632 / aging.101202 , PMC 5391241 (free full text).
