Florfenicol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
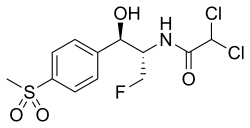
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Florfenicol | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
2,2-dichloro- N - [(1 S , 2 R ) -1- (fluoromethyl) -2-hydroxy-2- [4- (methylsulfonyl) phenyl] ethyl] acetamide |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 14 Cl 2 FNO 4 S | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 358.21 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Florfenicol is a chemical compound containing chlorine and fluorine that belongs to the classes of aromatics and sulfones . Like the related thiamphenicol, it is a synthetic analogue of the chloramphenicol found in bacteria . The antibiotic is used in veterinary medicine .
Properties and effects
Florfenicol is a substance that is sparingly soluble in water and readily soluble in lipids . It is used as an injection solution (300 mg / ml solution) in propylene glycol intramuscularly or subcutaneously against infections, predominantly of the respiratory tract of animals. The substance is a broad spectrum antibiotic with an effect against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria . The absorption is slow but complete, with a bioavailability of 78% after intramuscular injection. The half-life is between 2.65 (intravenous) and 18 hours (intramuscular) depending on the intake.
Florfenicol inhibits protein synthesis in bacterial and eukaryotic cells , binding to the peptidyl transferase in the ribosomes . The resistance situation is assessed as extremely good.
unwanted effects
Local swellings rarely occur at the injection site, which often only regress completely after weeks. Reduced feed consumption was observed in cattle, but this disappeared after the end of treatment. Pigs exhibited transient diarrhea , inflammation of the anus and edema upon completion of treatment.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Florfenicol data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 31, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on Florfenicol in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ Syriopoulou VP, Harding AL, Goldmann DA, Smith AL: In vitro antibacterial activity of fluorinated analogs of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol . In: Antimicrob Agents Chemother . 19, No. 2, February 1981, pp. 294-297. PMID 6957162 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Florfenicol at Vetpharm, accessed on August 5, 2012.
- ↑ Jim E. Riviere, Mark G. Papich: Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 9th edition, John Wiley and Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-8138-2061-3 , pp. 951-952.
- ^ Felix R. Althaus, Hans-Hasso Frey: Textbook of pharmacology and toxicology for veterinary medicine. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-8304-1070-6 , p. 376.
- ↑ animal-health-online.de: Florfenicol: Permanently reliable effectiveness , July 30, 2010.