Guanosine monophosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
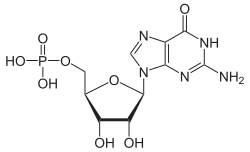
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Guanosine monophosphate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 14 N 5 O 8 P | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 363.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
190–200 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Guanosine monophosphate (GMP) is a nucleotide , the phosphoric acid ester of the nucleoside guanosine . Together with adenosine monophosphate ( AMP ), cytidine monophosphate ( CMP ) and uridine monophosphate ( UMP ), it forms the basic building blocks of ribonucleic acid ( RNA ).
Natural occurrence, importance, extraction
As a component of RNA, GMP occurs in all living things. The RNA is used in cells to convert genetic information from deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA ) into proteins . It is usually produced industrially with the help of microorganisms, which can also be genetically modified .
use
Guanosine monophosphate is approved in the EU as a food additive with the number E 626 up to a maximum amount of 500 mg / kg for all foodstuffs approved for additives. Like the disodium (E 627), dipotassium (E 628) and calcium salts (E 629), it is used as a flavor enhancer , the compounds being about 10 to 20 times more effective than glutamic acid ( glutamate ). With the addition of small amounts, the taste of many foods (especially ready-made products and canned meals) is enhanced and some undesirable taste nuances are eliminated. In connection with glutamate, GMP and its salts work synergistically and increase the taste-enhancing effect even in low proportions, around 1:10.
Dipotassium guanylate and calcium guanylate are also used as sodium-free salt substitutes.
Table of E numbers
| E number | Surname | Molecular formula | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| E 626 | Guanosine monophosphate | C 10 H 14 N 5 O 8 P | 85-32-5 |
| E 627 | Disodium guanylate | C 10 H 12 N 5 O 8 PNa 2 | 13474-02-7 |
| E 628 | Dipotassium guanylate | C 10 H 12 N 5 O 8 PK 2 | 3254-39-5 |
| E 629 | Calcium guanylate | C 10 H 12 N 5 O 8 PCa | 38966-30-2 |
Web links
- Guanosine monophosphate . Food lexicon
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 626: Guanylic acid in the European database on food additives, accessed on August 11, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on guanosine 5′-monophosphate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences . Vol. 60, Pg. 251, 1954.
- ↑ Entry on guanosine monophosphate in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ a b Wissenschaft-Online-Lexika: Entry on guanylic acid (E 626) in the Lexicon of Nutrition , accessed on January 7, 2009.
- ↑ E. Lück, H. Gölitz, P. Kuhnert: Lexicon of food additives. Behr's Verlag DE, 1998, ISBN 978-3-86022-462-5 , p. 97.