Heptabarbital
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
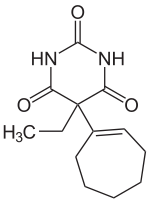
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Heptabarbital | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
5- (1-cycloheptene-1-yl) -5-ethyl- (1 H , 3 H , 5 H ) -pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 18 N 2 O 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless powder with a bitter taste |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 250.29 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
174 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
7.4 (at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Heptabarbital is a chemical compound from the group of barbiturates and thus a derivative of barbituric acid . The substance and its mono -sodium salt (trade name Medomin ® ) were classified as short-acting drug against falling asleep used. No preparation with heptabarbital is currently in use in Germany.
history
In 1946 the company has Geigy the patent registered for this substance. Like many other derivatives of barbituric acid , heptabarbital was also used in the form of its sodium salt as a sleep aid and sedative . Since barbiturates lead to a certain dependency and, moreover, abuse has occurred, heptabarbital (Medomin ® ) is no longer produced and used today.
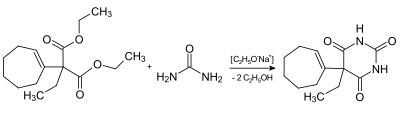
Extraction and presentation
Theoretically, it can be represented by the reaction of urea with the previously appropriately alkylated diethyl malonate ( diethyl malonate ).
An example of the theoretical production:
use
In the past, sodium heptabarbital, similar to pentobarbital , cyclobarbital and aprobarbital , was used as a sleeping and sedative. The mean dose was between 100 and 200 mg. However, the substance leads to physical dependence, which is comparable to alcoholism . Withdrawal leads to nervousness, tremors, impaired responsiveness, and irritability. In extreme cases, delirium tremens can even occur. Overdoses can also lead to death.
Like many other barbiturates , heptabarbital is therefore no longer used today.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f F. v. Bruchhausen, S. Ebel, AW Frahm, E. Hackenthal: Hagers Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice. Volume 8: Substances E-O. 5th edition, 1993, Springer, ISBN 3-540-52640-4 , pp. 422-423.
- ↑ a b c d Entry on heptabarbital in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Drug Research . Vol. 21, pp. 1727, 1971.
- ↑ a b Irving S. Rossoff: Encyclopedia of clinical toxicology: a comprehensive guide and reference. Informa Health Care, 2002, ISBN 1-84214-101-5 , p. 515.