Hexafluoroacetone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hexafluoroacetone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor (sesquihydrate) |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
|
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−26 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 0.1 ml m −3 or 0.7 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Hexafluoroacetone (HFA) is a derivative of acetone in which all hydrogen atoms have been replaced by fluorine . As a fine chemical, it is commercially available as sesquihydrate, i.e. with 1.5 water molecules per molecule.
It serves as a building block in the synthesis of organic compounds containing fluorine . By reacting with aromatics, crosslinking agents for rubbers and monomers for the production of polyamides are produced. Further, the place deutero-hydrate as NMR -solvent and as a reagent in the protective groups technique use.
Manufacturing
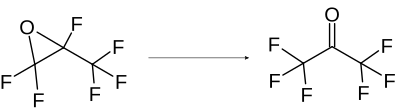
For the production of hexafluoroacetone, the isomerization of hexafluoro-1,2-epoxypropane is usually chosen industrially. It is obtained by reaction in the presence of Lewis acidic catalysts such as Al 2 O 3 , TiO 2 , WO 2 , AlCl 3 , AlBr 3 , SnCl 4 , VOCl 3 , TiCl 4 , FeCl 3 , CuCl 2 or ZrOCl 2 .
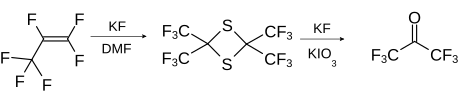
A laboratory method is based on the conversion of perfluoropropene with sulfur and potassium fluoride and subsequent ring opening of the dithietane with potassium fluoride and potassium iodate to form HFA.
properties
In hexafluoroacetone, the carbonyl carbon atom is very poor in electrons due to its neighboring trifluoromethyl radicals and therefore reactive towards nucleophiles such as aromatics or olefins. Stable hydrates are formed with water . Similarly, HFA reacts with ammonia to form the corresponding hemiaminals (CF 3 ) 2 C (OH) (NH 2 ), the dehydration of which with phosphorus oxychloride (POCl 3 ) yields the hexafluoro-2-propylimine (CF 3 ) 2 CNH.
Since HFA has no hydrogen atoms adjacent to the carbonyl group, it does not show any behavior comparable to keto-enol tautomerism .
use
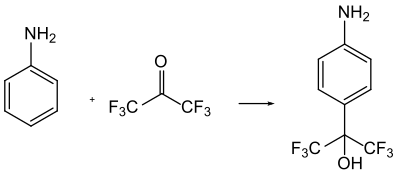
HFA is important as an electrophilic reagent for the substitution of aromatics. It usually reacts in the presence of acids to form the corresponding hexafluoro-2-hydroxy-2-aryl compounds, which serve as intermediate products in the synthesis of active ingredients.
The hydroperoxide of HFA, i.e. the hydrogen peroxide adduct, is a potent epoxidation agent .
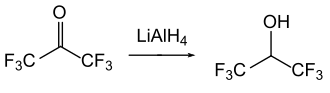
The reduction of HFA with lithium aluminum hydride or sodium borohydride yields the important solvent hexafluoro-2-propanol . This reduction can also be achieved by catalytic hydrogenation (e.g. with hydrogen).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet hexafluoroacetone (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 14, 2015.
- ↑ a b c d Datasheet Hexafluoroacetone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 3, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on hexafluoroacetone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for hexafluoroacetone ), accessed on March 4, 2020.
- ↑ External identifiers of or database links to hexafluoroacetone sesquihydrate : CAS number: 13098-39-0, EC number: 670-379-0, ECHA -InfoCard: 100.196.107 , PubChem : 3032602 , ChemSpider : 2297537 , Wikidata : Q27275779 .
- ↑ CG Krespan, WJ Middleton, In: . Fluorine Chem Rev. , 1, 1967, p.145.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 3,321,515.
- ↑ M. Van Der Puy, Louis G. Anello: Hexafluoroacetone In: Organic Syntheses . 63, 1985, p. 154, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.063.0154 ; Coll. Vol. 7, 1990, p. 251 ( PDF ).
- ↑ WJ Middleton, HD Carlson: Hexafluoroacetone Imine In: Organic Syntheses . 50, 1970, p. 81, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.050.0081 ; Coll. Vol. 6, 1988, p. 664 ( PDF ).
- ↑ H. Hacklin: Phosphorinane: Syntheses, properties and behavior towards hexafluoroacetone , University of Bremen, Dissertations Druck, Darmstadt, 1987.
- ↑ Waldemar Adam, Chantu R. Saha-Möller, Pralhad A. Ganeshpure: Synthetic Applications of Nonmetal Catalysts for Homogeneous oxidation. In: Chemical Reviews. 101, 2001, pp. 3499-3548, doi : 10.1021 / cr000019k .