Hydrazine sulfate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
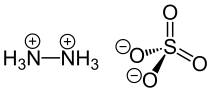
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Hydrazine sulfate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | N 2 H 6 SO 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, crystalline, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 130.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.37 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
254 ° C (with decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (30 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Hydrazine sulfate is a salt of hydrazine and sulfuric acid . The colorless substance is an intermediate product in the pure preparation of hydrazine.
Extraction and presentation
By the reaction of sulfuric acid with hydrazine
or hydrazine hydrate
the sulfate can be represented.
On a laboratory scale, the N 2 H 6 SO 4 can be represented by the reaction of a urea solution with a based NaOCl solution and subsequent acidification with sulfuric acid:
In a further laboratory synthesis, a hydrazinium azide solution is reacted with sulfuric acid, whereby the sparingly soluble hydrazinium sulfate precipitates.
properties
Hydrazine sulfate forms colorless crystals . It is much less soluble in cold water than in hot water, which is used in the laboratory synthesis of hydrazine (N 2 H 4 ) by letting the hydrazine crystallize out as sulphate for purification and then recrystallizing it again to restore the To release hydrazine (hydrate).
The salt crystallizes in an orthorhombic crystal lattice with the space group P 2 1 2 1 2 1 (space group no. 19) . An N 2 H 6 2+ SO 4 2− structure was detected in the solid phase , which is preferred to an N 2 H 5 + HSO 4 - structure because of a significantly higher lattice energy . In aqueous solution, because of the very low second K B2 value of the hydrazine, an equilibrium with N 2 H 5 + and HSO 4 - ions is immediately established .
At 254 ° C, the N 2 H 6 SO 4 melts , whereby it begins to decompose at a temperature of about 250 ° C. When calcining the pure product, no residue remains, which can be used as a purity test for hydrazine sulfate.
use
The sulfate is used as a reducing agent (mineral analysis) and it serves as a separation reagent in the production of polonium . It is also used for the synthesis of azides and hydrazine hydrate .
In thin-layer chromatography, hydrazinium sulfate is used as a spray reagent for the detection of piperonal and vanillin . To this end, 90 mL saturated aqueous hydrazinium sulfate solution are mixed with 10 mL 4 mol / L hydrochloric acid . After this solution has been sprayed on and then vaporized with ammonia , the evaluation is carried out in UV light.
safety instructions
Hydrazine sulfate is a powerful reducing agent and should therefore not be brought into contact with oxidizing agents . In humans, a dose of 201 mg / kg body weight over a period of eight days resulted in drowsiness, nausea and paresthesia . There is a risk of sensitization upon skin contact. In addition, hydrazinium sulfate is likely to be carcinogenic in humans .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on hydrazine sulfate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Not explicitly listed in Regulation (EC) No. 1272/2008 (CLP) , but with the specified labeling it falls under the group entry salts of hydrazine in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturer or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Cancer Chemotherapy Reports , Part 1. Vol. 59, p. 1151, 1975.
- ↑ Gigiena Truda i Professional'nye Zabolevaniya. Labor Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. Vol. 28 (12), p. 56, 1984.
- ↑ Sbornik Vysledku Toxixologickeho vyšetření Latek A přípravku, Marhold, JV, Institute Pro Vychovu Vedoucicn pracovníků Chemickeho Prumyclu Praha, Czechoslovakia, p.15. 1972
- ↑ a b Datasheet hydrazine sulfate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on February 11, 2012.
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, p. 468.
- ↑ a b c d Klapötke, TM ; White, PS; Reaction of hydrazinium azide with sulfuric acid: The X-ray structure of [N 2 H 6 ] [SO 4 ] in Polyhedron 15 (1996) 2579-2582, doi : 10.1016 / 0277-5387 (95) 00527-7 .
- ^ E. Merck AG (Ed.): Staining reagents for thin-layer and paper chromatography . Darmstadt 1965, p. 27 .







