Iraklia
|
Iraklia parish Δημοτική Ενότητα Ηρακλείας (Ηράκλεια) |
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Basic data | ||
| State : |
|
|
| Region : |
South Aegean
|
|
| Regional District : | Naxos | |
| Municipality : | Naxos and Lesser Cyclades | |
| Geographic coordinates : | 36 ° 51 ′ N , 25 ° 27 ′ E | |
| Height above d. M .: | 420 m dads |
|
| Area : | 17.795 km² | |
| Residents : | 141 (2011) | |
| Population density : | 7.9 inhabitants / km² | |
| Code No .: | 670204 | |
| Structure: |
1 municipality |
|
| Located in the municipality of Naxos and Lesser Cyclades and in the regional unit of Naxos | ||
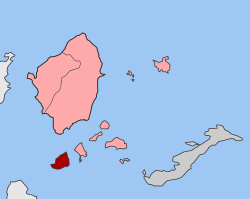
The Greek island of Iraklia ( Greek Ηράκλεια ( f. Sg. ), Ancient Greek Ἡράκλεια Herakleia ) is the largest island of the Lesser Cyclades , which form a subgroup of the Cyclades . Together with three uninhabited islets, it forms the municipality of Iraklia in the municipality of Naxos and the Lesser Cyclades within the South Aegean region .
location
With 18.078 km², Iraklia is the largest and most south-westerly island of the Small Cyclades. Naxos is less than 6 km north, Amorgos 24 km east, and Ios about 10 km southwest. Schinoussa , the closest island, is northeast. The distance is 2.5 km. The maximum extent of the island is about 7 km from southwest to northeast, less about 4 km from northwest to southeast.
On the east side, the uninhabited island of Venetiko is less than 400 m away. The small rock islands Megalos Avelas and Mikros Avelas are 400 m and 1.7 km away to the west.
The highest elevations of the mountainous island of Papas (Πάπας, 420 m) are in the south. The landscape is largely shaped by the bushy vegetation forms of the Phrygana and Macchia .
history
Archaeological excavations of two early Cycladic settlements near Agios Mamas (Άγιος Μάμας) and Kambos Agios Athanasios (Κάμπος Αγίου Αθανασίου) and a burial ground with box tombs near Agios Mamas enabled the settlement of the island in the 3rd millennium BC. Be proven. The livelihood of Bronze Age society was based on agriculture, livestock and fishing. The discovery of an obsidian blade from Milos at Cape Agios Georgios (Ακρωτήριο Άγιος Γεώργιος) also provided evidence that the island was involved in sea trade, which is characterized by the development of trade routes and navigation.
The fortress Kastro (Κάστρο) near Livadi south of the port of Agios Georgios was probably built between the 4th and 2nd centuries. v. Built in BC. As in other parts of the island, it was used up to Roman times.
During the Middle Ages and Ottoman rule, Iraklia was a shelter for pirates.
During the Second World War , Italy first occupied Iraklia from 1941 to 1943 and then until 1944 by the German Wehrmacht .
structure
The municipality of Iraklia has 141 inhabitants and is divided into
- Iraklia (Ηράκλεια ( f. Sg. )) Also Panagia (Παναγιά ( f. Sg. )) Or Pano Mera (Πάνω Μερά), 36 inhabitants, located in the center of the island
- Agios Georgios (Άγιος Γεώργιος ( m. Sg. )) Also Limani (Λιμάνι ( n. Sg. )), 105 inhabitants, port
- as well as the uninhabited islands
Attractions
- Agios Ioannis cave
The stalactite cave Agios Ioannis (Σπήλαιο Αγίου Ιωάννη) is located in the immediate vicinity of the southwest coast. A narrow corridor just over half a meter in diameter leads to the first large chamber, about 27 × 17 m and 10 m high. This is followed by five more chambers. Numerous stalagmites and stalactites have formed in the cave. The total length is 80 m and the area about 2000 m². At the lowest point there is a small pond. Oral tradition has it that the cave got its name from an icon of St. John when a shepherd sought refuge from a storm, discovered the cave by accident and found the icon inside.
Every year on August 28, the eve of the death of John the Baptist , an evening service is celebrated in the first two candlelit cave chambers.
In addition to the main cave, there is a smaller cave of 8 × 30 m and a ceiling height of 5 m.
natural reserve
Iraklia is part of the Natura 2000 area
- GR 4220013 Mikres Kyklades: Irakleia, Schinoussa, Koufonisia, Keros, Antikeri kai thalassia zoni (Μικρές Κυκλάδες: από Κέρο μέχρι Ηράκλεια, Σχοικκοραλάτηνατικκονατανατινσιν ραλκοθατηνατιντκο ραληνανατιν ροικοθ ραληνσανατιν έοικοθ ραληνσατινσιν θρλκοθ ρΚέατηνατοην ρΚέατην ραληνανατανσινατανατανατανατανατανσανσινατανσινατανανατανατησν (Also classified as an Important Bird Area .)
- GR 4220021 Nisos Irakleia, Nisi Makares, Mikros kai Megalos Avela, Nisida Venetiko Irakleias (Νήσος Ηρακλειά, Νήσοι Μακάρες, Μικρός και Μεγάλ ίδαατος) ικλεος Αβελάς, ιησεάς, Νιησεάς, Νιησεάς
economy
In addition to the very sparse agriculture and fishing, tourism, which is still in its infancy, is a source of income for the population. In the meantime, the island is regularly approached by ferries.
Others
The island's water supply is provided by tankers that ensure transport from the mainland. A floating pilot desalination plant was built by the University of the Aegean with the help of EU funding, but it produced far less than the planned 70 m³ of water and has therefore been idle since 2007. It is now no longer functional due to neglected maintenance work. The electricity required should be generated from wind and solar energy.
Web links
- General information about Iraklia (Greek)
- Information about the Lesser Cyclades, Iraklia (Greek)
- Iraklia . amorgos-island.gr (Greek)
- Iraklia . (PDF; 129 kB) traveling-aegean.gr (Greek)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Results of the 2011 census, Greek Statistical Office (ΕΛ.ΣΤΑΤ) ( Memento from June 27, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) (Excel document, 2.6 MB)
- ↑ Ελληνική Στατιστική Αρχή [ΕΛΣΤΑΤ] (Ed.): Στατιστική Επετηρίδα της Ελλάδος (Statistical Yearbook of Greece) 2009 & 2010 . Piraeus 2011, p. 47 .
- ↑ Natura 2000 area GR4220013, Greek minenv.gr ( Memento from March 11, 2010 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ BirdLife International: GR 155 Mikres Kyklades (English)