Isoprenaline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
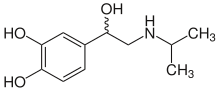
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Isoprenaline | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 11 H 17 NO 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 211.26 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
155.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
8.64 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Isoprenaline or isoproterenol is a structural isomer to orciprenaline a synthetic racemic noradrenaline - derivative , as the sympathomimetic agent is used. The drug was patented by Boehringer Ingelheim in 1943 .
pharmacology
As a catecholamine, isoprenaline is an adrenaline- like substance that only activates β-adrenoceptors , while noradrenaline has a high affinity for α-adrenoceptors. The N -isopropyl substituent is responsible for this selectivity, at the same time an optimum of β-adrenoceptor affinity is achieved.
It causes the bronchial and vascular muscles to relax, as well as (in adults dosed at 1–5 µg / min) an increase in the contraction force and beat frequency of the heart as well as a decrease in blood pressure (while the systolic blood pressure increases slightly, the diastolic pressure decreases sharply, which overall leads to a decrease in mean arterial pressure). The pronounced effect on the heart occurs through the stimulation of the β 1 -adrenoceptors , and renin is also released from the kidney cortex. The enzyme adenylyl cyclase , which catalyzes the synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) , which leads to an increased production of the same, is activated via the receptors . Due to the increased cAMP concentration, the enzyme protein kinase A is activated , which leads to the phosphorylation of voltage-dependent calcium ion channels . These are responsible for an increase in the slow Ca 2+ inward current during cell depolarization . The increased concentration of Ca 2+ results in the increased heart rate. The heartbeat and the conduction of excitation are accelerated, especially in the AV node , because the increase in the slow influx of Na + and Ca 2+ ions accelerates the spontaneous diastolic depolarization in all heart sections.
In addition, isoprenaline slows down the antigen-induced release of the messenger substance histamine , which slows down the transmission of anaphylaxis , and increases the production of lactates . It also has a relaxing effect on the uterus (tocolysis).
It is compatible with almost all common solutions for intravenous injection, with the exception of sodium hydrogen carbonate . In the treatment of bronchial asthma , local application in the form of an aerosol is preferred to systemic administration, since the onset of action occurs earlier and the systemic effect, the excitation of β 1 -adrenoceptors, is less.
The administration of isoprenaline is contraindicated in hyperthyroidism , coronary and arteriosclerosis , as well as in cardiac insufficiency , tachycardiac arrhythmias and arterial hypertension .
Stereochemistry
Isoprenaline is used as a 1: 1 mixture (racemate) of the ( R ) - and ( S ) -enantiomers, although the importance of the enantiomeric purity of the synthetically produced active ingredients is increasingly being paid attention, because the two enantiomers of a chiral drug almost always show a different one Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. In the past, this was often ignored due to a lack of knowledge of stereochemical relationships. For fundamental considerations, it would be preferable to use the enantiomer which is more effective or has fewer side effects. The ( R ) - and the ( S ) -isomers of isoprenaline bind significantly differently to human serum proteins.
Drug market
There are no finished medicinal products with this active ingredient available in Germany.
literature
- Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. (1st edition 1986) 5th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 1999, ISBN 3-540-65024-5 , p. 46 f.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b entry on isoprenaline. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Reinhard Larsen: Anesthesia and intensive medicine in cardiac, thoracic and vascular surgery. (1st edition 1986) 5th edition. Springer, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York et al. 1999, ISBN 3-540-65024-5 , pp. 44-47 and 76.
- ↑ EJ Ariëns, Stereochemistry, a basis for sophisticated nonsense in pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacology , European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26 (1984) 663-668, doi : 10.1007 / BF00541922 .
- ↑ G. Sager, D. Sandnes, A. Bessesen and S. Jacobsen: Andrenergic ligand binding in human serum , Biochemical Pharmacology 34 (1985) 2812.
- ↑ Federal Drug Information System - accessed on December 25, 2012.