Cape Verde Islands
| Cape Verde Islands | ||
|---|---|---|
| Location of the Cape Verde Islands | ||
| bodies of water | Atlantic Ocean | |
| Geographical location | 15° 55′ N , 24° 5′ W | |
|
|
||
| number of islands | about 15 | |
| main island | Santiago | |
| Total land area | 4033 km² | |
| resident | 427,000 | |
The Cape Verde Islands , also known as Cape Verde for short , are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean . They lie about 570 kilometers off the west coast of Africa and are part of Macaronesia . Since 1975, the territory of the islands has formed the independent island republic of Cape Verde .
geography
The Cape Verde Islands are subdivided as follows:
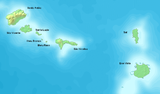
|
Northern Group: Ilhas de Barlavento (Leeward Islands) |
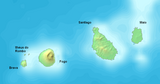
|
Southern Group: Ilhas de Sotavento (Leeward Islands) |
| Island | population | % | Area in km² | population density | assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boa Vista | 4.209 | 1.0% | 620 | 6.8 | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Ilheu Branco | – | – | 3 | – | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Ilheu Raso | – | – | 7 | – | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| salt | 14,816 | 3.4% | 216 | 68.6 | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Santa Lucia | – | – | 34 | – | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Santo Antao | 47,124 | 10.8% | 779 | 60.5 | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Sao Nicolau | 13,661 | 3.1% | 388 | 33.2 | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| Sao Vicente | 67,163 | 15.5% | 227 | 295.9 | Ilhas de Barlavento |
| mayo | 6,754 | 1.6% | 269 | 25.1 | Ilhas de Sotavento |
| Sao Tiago | 236,717 | 54.5% | 991 | 238.9 | Ilhas de Sotavento |
| fogo | 37,421 | 8.6% | 476 | 78.6 | Ilhas de Sotavento |
| brave | 6,804 | 1.6% | 67 | 106.3 | Ilhas de Sotavento |
| Ilheus do Rombo | – | – | 5 | – | Ilhas de Sotavento |
| Cape Verde | 434,669 | 100% | 4082 | 116.8 |
The group of about 15 islands is located on the African plate , is of volcanic origin and was discovered in 1445 by Portuguese seafarers. Nine of the islands are inhabited today - on the island of Santiago in the southern group of Cape Verde lies Praia , the capital of the Republic of Cape Verde.
The islands in the southwest are of recent origin and high mountainous, with the 2829 meter high Pico do Fogo as the highest point. The islands to the north are much older and have been eroded apart from a few rocky outcrops. Islands such as Sal , Boavista and Maio have sandy beaches from the Sahara sand that has been blown on , on the uninhabited islands such as Ilhéu Raso and Ilhéu Branco , the coasts drop down to the sea as sometimes very steep cliffs.
climate
The Cape Verde Islands belong climatologically to the Sahel zone , a savannah landscape, and are characterized by a warm, oceanic climate with small temperature differences between summer and winter. The amount of precipitation is low all year round, there is a short rainy season between August and October - but even in these months there are rarely more than two to three rainy days per month. The temperature differences between day and night are also small and rarely exceed five degrees Celsius.
|
Monthly average temperatures, hours of sunshine and rainy days for the Cape Verde Islands
Source: missing
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Flora and fauna
The dry climate of the Cape Verde Islands causes a few species-rich, semi-desert-like vegetation . The northern and western islands are partly covered with grasslands, on the southern islands there are also mangrove swamps ; In addition, some palm species are native to Cape Verde, which are adapted to the great drought.
Only a few animal species are native to the Cape Verde Islands, most notably seabirds. The Rasolerche ( Alauda razae ) is endemic to the Ilhéu Raso, which is only 7 km² in size , and is therefore one of the birds with the smallest distribution areas. The population was estimated at 130 birds in 2001. In addition, some reptiles such as geckos and skinks inhabit Cape Verde, including Tarentola gigas , the Cape Verdean giant gecko and the skink Mabuya stangeri . The Ilhéu Raso and the Ilhéu Branco were the only habitat of the Cape Verde giant skink until the beginning of the 20th century ; this species of lizard is now considered extinct.
Numerous seabirds use the island's cliffs as nesting sites.
The underwater flora and fauna are richer in species than on land. From March to May humpback whales cross the Atlantic off the Cape Verde Islands, from July to November manta rays and whale sharks can be sighted. Sharks live in and around coral reefs all year round . The sea around the Cape Verde Islands is not yet overfished, so the reefs are home to numerous species of fish and marine life. Sea turtles also come ashore on Boa Vista Island from July to October to lay their eggs.
tourism
The Cape Verde Islands have not yet become a destination for mass tourism. Tourist attractions are primarily the islands of Sal, which has salt flats filled with warm salt water, Santiago with its capital Praia, and Boavista, where a significant part of the nightlife takes place. The Cape Verde Islands are particularly popular with divers who visit the archipelago because of the underwater landscape rich in species. For mass tourism, there is a lack of reliable infrastructure and reliable flight and ferry connections between the nine inhabited islands.
Attractions
- Salt pans on the island of Sal
- Pedra de Lume volcanic crater on the island of Sal
- Boavista, next to Sal, the tourist center of the Cape Verde Islands
- From July to October: Sea Turtles on Boa Vista Island
- Praia , the capital of the island nation of Cape Verde, on the largest island of Santiago
- Ribeira Grande de Santiago (formerly "Cidade Velha"), former capital on the island of Santiago
- Pico do Fogo (active volcano, last eruption 2014) on Fogo Island
- Pass at the Cova crater (about 1000 m altitude on the old road from Porto Novo to Ribeira Grande) on the island of Santo Antão
- Mindelo as the cultural center of the island nation and the country's second largest city on the island of São Vicente
literature
- Rolf Bökemeier, photos: Michael Friedel: Cape Verde Islands: Cape without hope . In: Geo Magazine. Hamburg 1978.5, pp. 8-32. (“…Europe’s oldest overseas possession has been independent from Portugal for three decades – and is poorer than ever”). ISSN 0342-8311
See also
web links
- Database of content-related literature on the social, political and economic situation on the Cape Verde Islands
- Cape Verde Islands
- CIA World Factbook : Cape Verde Islands
itemizations
- ↑ Sunna Lipps, Oliver Breda (2009): Cape Verde Islands , p. 166 ff.
- ↑ Paul Donald: Raso Lark (Alauda razae). in Josep del Hoyo, Andrew Elliott, David Christie: Handbook of the Birds of the World . Volume 9: Cotingas to Pipits and Wagtails. Lynx Edicions 2004 (Revision 2013), p. 600.
- ↑ Cape Verde Islands at Birdlife Data Zone.
- ↑ Fauna of the Cape Verde Islands
- ↑ Susanne Lipps, Oliver Breda (2009): Cape Verde Islands , pp. 55–60
- ↑ Fauna of the Cape Verde Islands
- ↑ Federal Foreign Office: Cape Verde Islands

