Kynurenine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
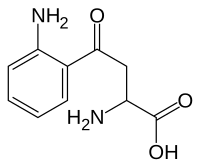
|
||||||||||||||||
| Structural formula without representation of the stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Kynurenine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 12 N 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless leaflets |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 208.22 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
Slightly soluble in water, forms water-soluble salts with acids |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Kynurenine (Greek kýon dog and ouron urine) is an aromatic, non- proteinogenic amino acid .
Isomers
There are two stereoisomers of kynurenine: ( S ) -Kynurenine [synonym: L -Kynurenine] and ( R ) -Kynurenine [synonym: D -Kynurenine]. Only the ( S ) - or L -form shows biological activity.
| Isomers of kynurenine | ||
| Surname | ( S ) -ynurenine | ( R ) -ynurenine |
| other names | L -ynurenine | D -ynurenine |
| Structural formula |  |

|
| CAS number | 2922-83-0 | 13441-51-5 |
| 343-65-7 (unspec.) | ||
| EC number | - | - |
| 206-445-9 (unspec.) | ||
| ECHA info card | - | - |
| 100.005.860 (unspec.) | ||
| PubChem | 161166 | 1152206 |
| 846 (unspec.) | ||
| DrugBank | DB02070 | - |
| - (unspec.) | ||
| Wikidata | Q415768 | Q27077082 |
| Q32908783 (unspec.) | ||
History and occurrence
( S ) -Kynurenine is a metabolic intermediate in the breakdown of tryptophan in many living things. It was first found in the urine (Latin urina ) of dogs (Greek kyon ), from which the name of the compound is derived. In his inaugural dissertation in 1940, Adolf Butenandt and the geneticist Alfred Kühn investigated the influence of kynurenine, which was initially thought to be a hormone , on the formation of eye pigmentation in insects.
(Bio) synthesis and characteristics
In humans, an important metabolic pathway runs from L- tryptophan via L -ynurenine and its metabolites to nicotinic acid . The synthesis of L -ynurenine in living things takes place with the help of the enzyme arylformamidase , which catalyzes the hydrolytic splitting of formic acid from N -formylkynurenine . In the urine of female Masu salmon ( Oncorhynchus masou ), L- kynurenine acts as a pheromone . Racemic kynurenine can be obtained industrially in several steps in good yield from o -chloroaniline . The oxidation product 3-hydroxy- L- kynurenine is also an intermediate product in the formation of ommochromes (eye pigments) in crabs and insects.
Kynurenine has been scientifically researched for a long time, including in its function as a precursor of the NMDA receptor - antagonist kynurenic acid . In animal models, increased levels of L- kynurenine in the brain due to the intake of L- kynurenine sulfate showed neuroprotective effects in neurodegenerative diseases . As a metabolic product of tryptophan in the organism, L- kynurenine is excreted daily in the urine in amounts of approx.
properties
As a monohydrate , L- kynurenine forms colorless, lamellar crystals that dissolve little in water, but readily in acids . By oxidative deamination , the cyclic kynurenic acid, which is the actual NMDA receptor antagonist, is formed from L- kynurenine on heating .
Disorders of the kynurenine metabolism
A disruption of the kynurenine metabolism in various metabolic steps has been described for numerous diseases and is of clinical relevance in humans. Typically, cytokine - induced changes in the tryptophan / kynurenine metabolism lead to an accumulation of the metabolic product that was generated in the previous metabolic step and that should actually serve as a substrate for the defective or dysregulated enzyme . Depending on the enzyme concerned, different metabolic products accumulate. The accumulation of xanthurenic acid, quinolinic acid , kynurenine, kynurenic acid and anthranilic acid is of particular importance . A reduced enzymatic activity of kynurenine-3-monooxygenase (KMO deficiency) typically leads to an accumulation of kynurenine and a shift in tryptophan metabolism towards kynurenic acid, anthranilic acid and their other metabolic products. Since the efficiency of some of the enzymes on the metabolic pathway from tryptophan to kynurenine to nicotinic acid depends on vitamin B6, a vitamin B6 deficiency can in some cases lead to a significantly increased amount of kynurenine excreted in the urine. One consequence of the dysregulation of the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism is the increased formation of kynurenic acid , which in turn leads to an inhibition of the glutamate and dopamine release in the synaptic cleft .
Web links
- www.reactome.org: L -Kynurenine
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on l-kynurenine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet L-Kynurenine, crystalline from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 19, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Beate Zsizsik: Oxidative metabolism of kynurenic acid and its analogues. (PDF) Dissertation at the Georg-August-Universität Göttingen , 2001.
- ↑ Wolfgang Schieder, Achim Trunk (ed.) :: Adolf Butenandt and the Kaiser Wilhelm Society: Science, industry and politics in the Third Reich. (= History of the Kaiser Wilhelm Society during National Socialism. Volume 7). Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, 2004, ISBN 3-89244-752-7 , p. 178.
- ^ EM Gál, AD Sherman: L-kynurenine: its synthesis and possible regulatory function in brain . In: Neurochem. Res. Band 5 , no. 3 , March 1980, p. 223-239 , PMID 6154900 .
- ↑ H. Yambe, S. Kitamura, M. Kamio et al .: L-Kynurenine, an amino acid identified as a sex pheromone in the urine of ovulated female masu salmon . In: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA band 103 , no. 42 , October 2006, p. 15370–15374 , doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0604340103 , PMID 17030810 , PMC 1622830 (free full text).
- ↑ US Patent 3766261
- ^ A b K. Sas, H. Robotka, J. Toldi, L. Vécsei: Mitochondria, metabolic disturbances, oxidative stress and the kynurenine system, with focus on neurodegenerative disorders . In: J. Neurol. Sci. tape 257 , no. 1–2 , June 2007, pp. 221-239 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jns.2007.01.033 , PMID 17462670 .
- ↑ K. Sas, H. Robotka, E. Rózsa et al .: Kynurenine diminishes the ischemia-induced histological and electrophysiological deficits in the rat hippocampus . In: Neurobiol. Dis. tape 32 , no. 2 , November 2008, p. 302-308 , doi : 10.1016 / j.nbd.2008.07.013 , PMID 18761090 .
- ^ A b Arnold Willmes: Pocket book chemical substances: elements - inorganics - organic substances - natural substances - polymers. 3. Edition. Harri Deutsch Verlag, 2007, ISBN 978-3-8171-1787-1 , p. 648.
- ↑ Rossen Donev (Ed.): Inflammation in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. (= Advances in protein chemistry and structural biology. Volume 88). Academic Press, 2012, ISBN 978-0-12-398314-5 , p. 57 ff.
- ↑ Maria Holtze, Peter Saetre, Göran Engberg et al: Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase polymorphisms: relevance for kynurenic acid synthesis in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. In: J Psychiatry Neurosci. 37, 2012, pp. 53-57.
- ^ PJ Hoekstra, GM Anderson, PW Troost: Plasma kynurenine and related measures in tic disorder patients. In: Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 16 Suppl 1, 2007, pp. 71-77.
- ↑ A. Buness, A. Roth, A. Herrmann, O. Schmitz, H. Kamp et al .: Identification of Metabolites, Clinical Chemistry Markers and Transcripts Associated with Hepatotoxicity. In: PLoS ONE 9 (5), 2014, e97249, doi: 10.1371 / journal.pone.0097249 .
- ↑ Hirata Yukiko, Kawachi Takashi, Sugimura Takashi: Fatty liver induced by injection of L-tryptophan. In: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta . (BBA) - Lipids and Lipid Metabolism. Volume 144, 1967, pp. 233-241.
- ↑ a b Lucile Capuron, Andrew H. Miller: Immune System to Brain Signaling: Neuropsychopharmacological Implications. In: Pharmacol Ther . 130, 2011, pp. 226-238. doi: 10.1016 / j.pharmthera.2011.01.014 .
- ↑ a b Ikwunga Wonodi, O. Colin Stine, Korrapati V. Sathyasaikumar and others: Downregulated kynurenine 3-monooxygenase gene expression and enzyme activity in schizophrenia and genetic association with schizophrenia endophenotypes . In: Archives of General Psychiatry . tape 68 , no. 7 , July 1, 2011, ISSN 0003-990X , p. 665-674 , doi : 10.1001 / archgenpsychiatry.2011.71 .
- ↑ a b N. Müller, AM Myint, MJ Schwarz: Inflammatory Biomarkers and Depression. In: Neurotox Res. 19, 2010, pp. 308-318.
- ↑ Michael Maes, Robert Verkerkc, Stephania Bonaccorso: Depressive and anxiety symptoms in the early puerperium are related to increased degradation of tryptophan into kynurenine, a phenomenon which is related to immune activation. In: Life Sciences . 71, 2002, pp. 1837-1848.
- ↑ Brian Campbell, Erik Charych, Anna Lee, Thomas Möller: Kynurenines disease in CNS: regulation byinflammatory cytokines. In: Frontiers in Neuroscience. Neuroendocrine Science. Volume 8, 2014, Article 12.
- ^ Norbert Müller: The impact of neuroimmune dysregulation on neuroprotection and neurotoxicity in psychiatric disorders - relation to drug treatment. In: Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 11, 2009, pp. 319-332.
- ↑ Robert Dantzer, Jason C. O'Connor, Gregory G. Freund et al .: From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nature Publishing Group. Volume 9, January 2008.