Lama lake
| Lama lake | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
|
Lama lake with Kapchuk lake (top) and Glubokojesee (bottom left) in the Putorana Mountains ( NASA photo) |
||
| GKZ | RU / 17020000111116100011222 | |
| Geographical location |
Putorana Mountains , Krasnoyarsk Region ( Russia ) |
|
| Tributaries | Miktschangda and other streams like Kapchuk, Kygam, Neralach | |
| Drain | lama | |
| Data | ||
| Coordinates | 69 ° 31 ' N , 90 ° 36' E | |
|
|
||
| Altitude above sea level | 45 m | |
| surface | 318 km² | |
| length | approx. 80 km | |
| width | Max. approx. 7 km | |
| scope | approx. 200 km | |
| Maximum depth | 300 m (probably up to 600 m) | |
| Catchment area | 6210 km² | |
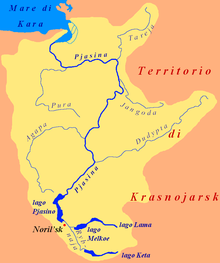
| Catchment area of the Lama lake | ||
The Lama Lake ( Russian Озеро Лама ), formerly known as Davydovo Lake ( Озеро Давыдово), is a 318 km² lake in the Putorana Mountains , the northwest part of the Central Siberian Mountains in the Krasnoyarsk region , Siberia , Russia ( Asia ).
Geographical location
The Lama Lake is located around 330 km north of the Arctic Circle in the western part of the Putorana Mountains (max. 1701 m ). It extends an average of almost 100 km east-northeast of Norilsk . There are no settlements either by the lake or in its vicinity, but in some places there are isbas , traditional Russian wooden huts.
The surrounding mountains are up to 956 m high in the northwestern Charaelach Mountains, up to 1167 m in the northern Miktschangdabergen, up to 1297 m in the northeastern Butscharama Mountains and up to 1267 m in the southern Lamskieberge ; south-east of its eastern end they reach a maximum height of 1582 m . While the lake is fed by the Miktschangda and other streams such as Kapchuk, Kygam and Neralach, the Lama is its only drain; the latter drains over the short Talaja into the Melkojesee , whose water ultimately flows over the Pyassina into the Kara Sea .
The lake is about 45 m high and around 80 km long and 7 km wide. Its maximum depth in the lake basin of tectonic origin is around 300 m; it is believed that the little explored lake is up to 600 m deep. Its catchment area is about 6210 km².
Neighboring is the northern Kapchuksee , which belongs to the catchment area of the lake, and outside this area lie south-southeast of Sobatschjesee , southwest of Glubokojesee and west-southwest of Melkojesee .
history
Surname
On the map of Asiatic Russia published by the Russian General Staff in 1911, the lake, which is distant from its real shape, is named Lake Davydovo . Today's Hydronym Lama comes from the Tungusian word Laamu , which means lake , ocean or great water .
exploration
The Lama Lake was first explored and described by the Russian-Soviet geologist and polar explorer Nikolai Urwanzew and his colleague Basanov during an expedition in 1921.
Gulag
After the annexation of the Baltic states into the Soviet Union , on June 28, 1941, a total of 42 Baltic officers from Estonia (15), Latvia (13) and Lithuania (14) were arrested as enemies of the new Stalinist state system and taken to a gulag (penal camp) without charge. sent at lama lake. With a train they were to Krasnoyarsk , then continue by boat on the Yenisei to Dudinka , then a train to Norilsk finally and by boat to the camp deported . One of them died in Norilsk, the remaining 41 people were interned in one large hut in the camp. By 1945 everyone died of hunger, cold and disease. Neither facilities nor huts have been preserved, but there are several memorial sites with memorials and plaques by the lake.
Nuclear explosions for the national economy
During the Soviet program nuclear explosions for the national economy , with the aim of making nuclear weapons usable for civil purposes, two underground nuclear weapon tests were carried out north of Lake Lama near Cape Tonki ( ⊙ ) as part of seismic probes :
- Horizont-3 ( ⊙ ), September 29, 1975, explosive force 7.6 kilotons TNT equivalent , 830 m depth
- Meteorite-2 ( ⊙ ), July 26, 1977, explosive force 13 kilotons TNT equivalent, 850 m depth
Climate, flora and fauna
The region of Lake Lama lies in the area of permafrost . The lake is covered by ice (approx. 80 to 100 cm) every year from October or November to June . Boreal coniferous forests (taiga) thrive on its banks and the tundra with mosses and lichens dominates the surrounding mountains . For example, perch fish , pike and salmon fish live in the fish-rich lake .
tourism
The remote Lama Lake is an attractive tourist destination. In summer, excursion boats bring many visitors to the lake. They drive there from the pier between Norilsk and its northeastern part of Talnach at the settlement Valjok over the rivers Norilka and Talaja, through the Melkoje lake and over the river Lama . The outward journey, upstream, takes about five hours and the way back about three hours.
Web links
- Article Lama Lake in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Lama Lake in the State Water Directory of the Russian Federation (Russian)
-
↑ a b topographic map (1: 1,000,000, p. R-45,46, ed. 1990), u. a. with the entire lake (center) on mapr46.narod.ru (with height above sea level )
see also (detailed maps):
- Topographical map (1: 200,000, p. R-45-XXIII, XXIV, edition 1989), u. a. with western part of the lake (bottom right) on mapr45.narod.ru,
- topographic map (1: 200.000, p. R-46-XIX, XX, ed. 1984), u. a. with the main part of the lake (below) on mapr46.narod.ru - ↑ a b c d Number of officers (Gulag Lamasee) , info according to gulagmuseum.org
- ↑ Deportation of Baltic officers, camps and memorials on Lake Lama (1941–1945) , information according to memorial.krsk.ru (Russian)