Languedoc
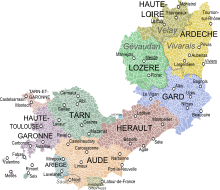
The Languedoc (from the French. Langue "Language" and Occitan oc "yes", fr. Oui ) is a historical province of France . It comprised the central part of southern France between the Rhone as the border with Provence and the Garonne as the border with Gascony . Their territory covered most of today's Occitania region as well as the Ardèche department and parts of the Haute-Loire department , both of which are now part of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region . Their capital was Toulouse .
Cities
The area has a population of around four million people. The most important cities are - besides the former capital Toulouse - Montpellier , Nîmes , Béziers , Narbonne , Albi , Carcassonne and Sète .
Agriculture
The Languedoc wine region looks back on a long tradition. In the 19th and 20th centuries there were several radical changes in the cultivation. The cultivation was severely damaged by phylloxera and downy mildew ; It was not until the 1960s that the targeted expansion of high-yielding varieties began. The region became an important wine producer again , but the wine stuck to the image of a "cheap wine". The Languedoc was mainly responsible for an EC-wide production surplus, which became known as the "wine lake" , until the 1970s .
In the 1970s people began to think again about quality wines; some very good wines were and are produced. This development is recognized by many wine critics ; Today they equate some of the Languedoc wines qualitatively with the best Bordeaux wines . Overall, Languedoc produces more than a third of all French grapes. In addition to olive , fruit and rice grown. Sheep and goats are raised for meat and cheese in the mountains . A lot of fish is caught in the coastal area, as well as shellfish . The area is a popular tourist destination.
archeology
An extremely well-preserved Iron Age necropolis was discovered in Languedoc . It testifies to cremation that is common in the West . 235 small mounds made of earth and stone, which are closed on the inside with heavy stone slabs, characterize the tombs. Around 4000 vessels and 600 metal objects have been found so far.
history
The Mediterranean coast of Languedoc was settled in antiquity by the Greeks , Phoenicians and Romans and conquered by the Alemanni , Vandals , Visigoths and Saracens .
The name Languedoc is derived from Occitan (French: Langues d'oc ); This regional Romance language was the national language before the French period , see also Languedoc language .
In the Middle Ages , the county of Toulouse, established by Charlemagne, was the dominant power in Languedoc. It has been the center of the Cathar religious movement since the 12th century . The Roman Catholic Church declared them heretics and took action against them in the Albigensian Crusade (1209-29). The fighting continued thereafter. The Montségur castle became a refuge for the Catholic Church. With the support of the French crown, the siege of Montségur began in 1243 by soldiers and crusaders . In 1244 the residents of the castle were given the choice of either renouncing their faith or ending up at the stake . 225 Cathars, including their bishop, were burned. With the marriage of the heiress of the county to a brother of the French king, the county came under the rule of a branch of the Capetians in 1229 . This line ended in 1271 and the county became the province of Languedoc under the direct rule of the king. Since 1346 an assembly of estates, the États de Languedoc , represented the regional interests of the nobility, clergy and cities vis-à-vis the king. With the integration into the Kingdom of France a process began of the displacement of the native language and culture in favor of that of Paris . Occitan was superseded from written language in the 16th century and largely also from oral use since the 19th century.
The exceptional inland waterway Canal du Midi from the 17th century, which connects the Atlantic with the Mediterranean, was added to the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites in 1996 . There are impressive structures along the canal, for example the Fonserannes lock staircase near Béziers , the birthplace of the canal's founder, Pierre-Paul Riquet .
literature
in alphabetical order by authors / editors
- Marie-Nicolas Bouillet , Alexis Chassang (ed.): Dictionnaire universel d'histoire et de geographie , Languedoc article.
- Christian Freilang : Imitare ecclesias nobiles. The cathedrals of Narbonne, Toulouse and Rodez and the northern French Rayonnant Gothic in Languedoc . Wernersche Verlagsgesellschaft, Worms 1992, ISBN 978-3-88462-085-4
- Dominique Garcia: La Celtique méditerranéenne . Editions Errance, Paris 2004, ISBN 2-87772-286-4 .
- Manfred Hammes Tell me about the south. A literary journey through Provence, Languedoc and along the Côte d'Azur. Wunderhorn Verlag, Heidelberg 2005
- Ralf Nestmeyer : Languedoc-Roussillon . A travel guide. Michael Müller, Erlangen 2012, ISBN 978-3-89953-696-6 .