Mometasone furoate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
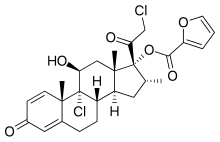
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Mometasone furoate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 27 H 30 Cl 2 O 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white powder with a faint odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Glucocorticoid |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 521.4 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
218-220 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Mometasone furoate is a drug from the group of glucocorticoids that is used to treat various skin diseases , allergic rhinitis and nasal polyps as well as bronchial asthma . It is a highly effective synthetic glucocorticoid.
discovery
The compound was synthesized by Elliot L. Shapiro in the US company Merck Sharp & Dohme (now Merck & Co. ) and a patent applied for in 1984. The results of the US researchers were submitted for publication in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry in 1986 and published in 1987.
Pharmacological properties
Mometasone is based on the basic structure of prednisolone . The structural chemical modification and esterification makes mometasone more lipophilic, which is why it penetrates the skin better. The furoate group (ester of furan-2-carboxylic acid) simultaneously causes a longer retention time in the skin, which leads to a long duration of action.
The effects of mometasone furoate are threefold:
- anti-inflammatory through an intervention in the arachidonic acid metabolism and the resulting decrease in the production of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes ,
- antiallergic by reducing the number and activity of B and T lymphocytes and
- Antiproliferative by reducing the metabolism and DNA synthesis rate, which leads to an inhibition of cell growth and cell division .
The inhibitory effect on inflammation mediators also comes into play when inhaling mometasone furoate preparations (see below). In addition, it has been shown that mometasone furoate lowers the reactivity of the airways of allergy sufferers to adenosine monophosphate and methacholine . The effectiveness against nasal polyps results from the antiproliferative effect.
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
In ointments , creams and fat creams Mometasone is used in the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases such. B. atopic dermatitis and psoriasis . Since the substance is sparingly soluble in water and ethanol, it must be inhaled as a suspension , i.e. H. be brought into micronized form. So it became a component of metered dose inhalers , which are prescribed for chronic bronchial asthma of all degrees of severity . Mometasone furoate is available in the form of a suspension as a nasal spray for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and nasal polyps. It is not suitable for the therapy of asthma cardiale due to its different etiology .
Type and duration of application
Use on the skin should be limited to three weeks and a maximum of 20% of the body surface, and use on the face to five days. There are no time restrictions for inhalation use.
Contraindications (contraindications)
Mometasone furoate is generally contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the substance. In this context, the remaining components of the preparation must also be taken into account. Additional contraindications for topical use are rosacea , acne vulgaris , perioral dermatitis and use under an occlusive dressing , to name a few important ones . As a nasal spray, it must not be used in cases of pulmonary tuberculosis (active or inactive) , untreated fungal infections , systemic bacterial or viral infections, ocular herpes , infections of the nasal mucosa and after nasal injuries or operations.
Drug interactions
No interactions are known. However, there may be a slight risk of systemic side effects with inhalation and simultaneous use of drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 3A4 (e.g. ketoconazole ).
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There are no suitable studies on the use of mometasone furoate during pregnancy and breastfeeding. In animal experiments, however, deformities in the fetus including cleft palates and a transfer of small amounts of active ingredient into breast milk have been found, so that the substance should only be administered after extremely careful risk-benefit assessment. In this case, the newborn must be monitored for adrenal insufficiency , especially if it is inhaled or used over a large area.
Special patient groups (diabetics, kidney patients)
There are no recommendations for use by inhalation (except as a nasal spray) for children under 12 years of age.
Adverse effects (side effects)
Mometasone furoate can have a wide variety of undesirable effects, see Glucocorticoids: Side Effects . A characteristic of mometasone furoate, however, is that the skin at the application site can often tingle.
Trade names
- Germany
- Ecural, 1 mg / g
- Asmanex
- MomeGalen, 1 mg / g
- Nasonex
- Momecutane
- Mometa Hexal
- Mometason
- Switzerland
- Elocom
- Mometason
- Mometasone furoate Sandoz
- Monovo
- Nasonex
- Ovixan
literature
- Wolfgang Blaschek et al. (Ed.): Hager's encyclopedia of medicinal substances and drugs. Volume 10. 6th edition. Knowledge Verlagsges., Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-8047-2384-9 , pp. 974-977.
- Axel Kleemann et al .: Pharmaceutical substances: syntheses, patents and applications of the most relevant APIs. 5th edition. Thieme, Stuttgart 2009, pp. 915-916.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Safety data sheet for mometasone furoate from Fagron, accessed on July 21, 2019.
- ↑ nlm.nih.gov: NASONEX® (mometasone furoate monohydrate) Nasal Spray, 50 mcg calculated on the anhydrous basis FOR INTRANASAL USE ONLY .
- ↑ a b Aktories, Förstermann, Hofmann, Starke: General and special pharmacology and toxicology. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Munich 2009, ISBN 978-3-437-42522-6 .
- ↑ Andrea Hämmerlein, Martin Schulz: Ciclesonide and Mometason - two new inhaled glucocorticoids. In: Pharmazeutische Zeitung , issue 1/2006, accessed on January 21, 2014.
- ↑ Mometasone Furoate Galen 1 mg / g cream. In: medikamio.com . December 17, 2012, accessed March 18, 2017.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 4,472,393, Chemical Abstracts 1985, Vol. 102, 95905h.
- ↑ El Shapiro, MJ Gentles et al., 17-Heteroaroyl Esters of Corticosteroids. 2. 11-β-Hydroxy Series . Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1987, Vol. 30, pp. 1581-1588.
- ↑ Schürer, Ruzicka: Eczema. Springer Verlag, Berlin / Heidelberg / New York 1999, ISBN 3-540-63952-7 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g Specialist information Asmanex. (PDF) MSD SHARP & DOHME, July 2012, accessed January 24, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f Specialist information Ecural. (PDF) MSD SHARP & DOHME, March 2012, accessed January 24, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e Specialist information Nasonex. (PDF) MSD SHARP & DOHME, July 2012, accessed January 24, 2014.