Nalidixic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Nalidixic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
1-Ethyl-7-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acid ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 12 N 2 O 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to pale yellow, monoclinic crystals |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 232.24 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
229.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
6.0 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
low in water (100 mg l −1 at 23 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Nalidixic acid is a synthetically produced chemical compound from the group of diazanaphthalenes , which have a strong structural similarity to quinolones . Its action as a gyrase inhibitor made it the first compound in this class to be used as an antibiotic in 1962 .
Extraction and presentation
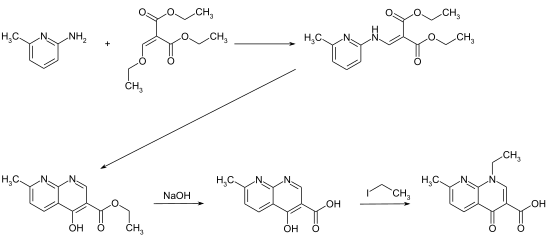
The four-step synthesis starts in the first step with the reaction of 2-amino-6-methylpyridine with ethoxymethylene malonic acid diethyl ester. The resulting intermediate is then cyclized to the 1,8-naphthyridine structure. After the ethyl ester group has been saponified with sodium hydroxide solution , the target compound is obtained by N -alkylation using ethyl iodide .
effect
The active ingredient inhibits the enzyme gyrase in bacteria. Nalidixic acid was discovered in 1962 as an antibiotic with low toxicity , mainly effective against Gram-negative bacteria ( LD 50 for oral administration in mice of approx. 3 g · kg −1 ). Based on nalidixic acid, similar but more effective antibiotics were sought. It was subsequently supplanted by the much more potent fluoroquinolones . Nalidixic acid is effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria . In low concentrations it has a bacteriostatic effect, i.e. it prevents the reproduction of bacteria, while in higher concentrations it has a bactericidal effect and kills them.
use
It is mainly used to treat urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli , Proteus , Shigella , Enterobacter or Klebsiella . Due to the rapid development of resistance and a narrow spectrum of activity in Europe, the active ingredient is no longer on the market. A better alternative to the quinolonecarboxylic acids of the first generation is pipemidic acid , which is also effective against gram-negative pathogens thanks to a 7-piperazinyl substituent .
Trade names
- Wintomylon ( Brazil )
Web links
- MedlinePlus: Nalidixic Acid
- HealthDigest.org: Nalidixic acid
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on nalidixic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 11, 2017.
- ↑ a b Entry on Nalidixic acid in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), accessed on November 10, 2017.
- ↑ a b data sheet Nalidixic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 14, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b c d e A. Kleemann , J. Engel, B. Kutscher, D. Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances - Synthesis, Patents, Applications , 4th edition (2000), Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, ISBN 978-1-58890- 031-9 .
- ↑ a b G. Y. Lesher, EJ Froehlich, MD Gruett, JH Bailey, PR Brundage: 1,8-Naphthyridine Derivatives. A New Class of Chemotherapeutic Agents in J. Med. Chem. 5 (1962) 1063-1065, doi: 10.1021 / jm01240a021 .
- ↑ Patent US 3,149,104 (Sterling Drug, September 15, 1964).
- ↑ RK Hamatake, R. Mukai, M. Hayashi: Role of DNA gyrase subunits in synthesis of bacteriophage phi X174 viral DNA March 1981; PMID 6262812 ; PMC 319165 (free full text).
- ↑ Schubert-Zsilavecz, Manfred., Roth, Hermann J .: Medicinal Chemistry: Targets - Drugs - Chemical Biology; 191 tables . 2., completely reworked. and exp. Ed. Dt. Apotheker-Verl, Stuttgart 2010, ISBN 978-3-7692-5002-2 .