Babia Góra National Park
| Babia Góra National Park | ||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Location: | Lesser Poland , Poland | |
| Specialty: | UNESCO - Biosphere Reserve , highest mountain: Diablak (1725 above sea level) | |
| Next city: | Zawoja and Sucha Beskidzka | |
| Surface: | 33.92 km² | |
| Founding: | 1954 | |
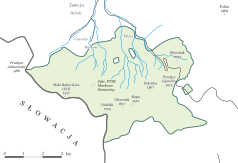
| National park map | ||
| The summit of Babia Góra | ||
The Babia Góra National Park (Polish: Babiogórski Park Narodowy ; German translated Weiberberg National Park ) is one of 23 national parks in Poland . It is located southwest of Krakow on the border with Slovakia . The national park is located in the village of Zawoja . The park comprises the northern and southern sides of the Babia Góra massif with the highest mountain in the Beskid Żywiecki range , the Diablak (1725 m above sea level). On the Slovak side there is also a nature reserve called “Babia Hora”.
history
Babia Góra National Park was established on October 30, 1954. In 1977 the Babia Góra National Park was declared a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO and included in the Man and Biosphere ( MAB ) program.
flora
The Babia Góra massif has tiered mountain vegetation. The national park is home to more than 500 plant species, including over 200 different mosses and lichens . A rarity is the angelica laser herb that grows here , which can also be found in the park logo, and the alpine hornwort . Both plants can only be found here in Poland.
In the lower high forest zone (700–1150 m above sea level) a beech forest dominates, in which trees reach a height of up to 40 m and a circumference of more than 350 cm. The peculiarity of these forests is that they are primeval forests that have never been used economically. In the upper high forest zone (1150–1350 m above sea level) tall, narrow spruce trees predominate. In the area above the upper high forest there is a plant community of dwarf pines with a mixture of mountain ash and herbaceous plants.
fauna
The wildlife of the national park includes 127 species of birds, over 100 of which also breed in the park. Of special significance is the park in that it habitat for three species grouse offers, namely for the capercaillie , the black grouse and hazel grouse . The woodpeckers are represented by the species three-toed woodpecker , green woodpecker , great spotted woodpecker , black woodpecker and white-backed woodpecker . Also, six species of owls ( Ural , pygmy owl , boreal owl , eagle owl , tawny owl and long-eared owl ) occur in the park.
Many mammals are also at home here. In addition to numerous deer also live lynx , wolves and bears and small forest rodents like dormouse , dormice and garden dormouse here.
tourism
The national park is particularly popular with Poles from Krakow and Katowice as a weekend getaway destination. It is best explored from Zawoja. There are also numerous accommodation options here. There are hourly buses from Krakow to Zawoja.
particularities
Dogs are totally prohibited in the entire national park area.
Web links
- Official website of the Babia Góra National Park (Polish / English / Slovak)
- Babia Góra National Park on poland.gov.pl
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Information from the park administration on bird life ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.