Sodium lauryl sulfate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium lauryl sulfate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 25 NaO 4 S | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, odorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 288.4 g · mol -1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.1 g cm −3 at 20 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
204-207 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
easily soluble in water (150 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Sodium lauryl sulfate or sodium dodecyl sulfate , also SLS or SDS (from English sodium lauryl sulfate and sodium dodecyl sulfate ), is an anionic surfactant , i.e. a washing substance that is used as a detergent , e.g. B. in detergents and toothpaste.
Extraction and presentation
Sodium lauryl sulfate can be prepared by esterification of dodecanol with sulfuric acid , chlorosulfonic acid or sulfur trioxide and subsequent neutralization are obtained. The addition of sulfuric acid to 1-dodecene is also possible. Since the starting products used are mostly technical fatty alcohols , which are obtained reductively from the corresponding fats or fatty acids , for example , most commercial products contain tetradecyl and hexadecyl chains in different proportions in addition to dodecyl. In technical data sheets, the corresponding products (mixtures of substances) are often marked with the addition (C12-C16).
properties
Sodium lauryl sulfate is an anionic surfactant with a strong denaturing effect on proteins . Sodium lauryl sulfate is considered to be allergenic and skin irritant, which is why its use in cosmetics is controversial. In particular, people with special sensitivity observe the cause of aphthous ulcers in the oral cavity by toothpastes containing sodium lauryl sulphate . However, SDS has an antibacterial and antiviral effect. To what extent it is able to destroy HI viruses is the subject of current research.
use
Sodium Lauryl Sulphate was previously used as a cleansing component in most shampoos and shower gels. Today it is almost completely replaced by sodium dodecyl poly (oxyethylene) sulfate (sodium laureth sulfate) in these applications . Sodium lauryl sulfate is used as an emulsifier in ointments and lotions as well as cleaning agents, especially in hand dishwashing detergents and liquid detergents. The claim that SLS in cosmetic products can lead to hair loss has not been scientifically proven according to current data (2015).
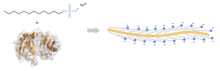
The intensive use as a denaturant for proteins is one reason for the importance of sodium lauryl sulfate in higher concentrations in biochemistry and biotechnology. The effect on proteins is based on the fact that non- covalent bonds of the proteins are broken and their quaternary and tertiary structure is destroyed. Sodium lauryl sulfate binds in a ratio of around 1.4 grams of SDS per gram of protein. Due to the property of forming micelles , sodium lauryl sulfate protein solutions cannot be dialyzed ; Sodium lauryl sulphate can be removed by extractions with organic solvents.
In the biochemical analysis is sodium lauryl sulfate in the polyacrylamide - gel electrophoresis ( SDS-PAGE , of Engl. Sodium dodecyl sulfate poly acrylamide gel electrophoresis + ) is used. Since most proteins are almost neutral overall, they are treated with lauryl sulfate. It not only denatures the proteins, but also adds negative charges to them. Thus they migrate to the positive pole in electrophoresis.
proof
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on December 28, 2019.
- ↑ a b c Data sheet sodium lauryl sulfate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 17, 2008.
- ↑ a b c d e record with sodium dodecyl sulfate in the GESTIS database of IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ oekotest.de, advice health and fitness 9: 2009, test toothpastes
- ↑ CA Bondi, JL Marks, LB Wroblewski, HS Raatikainen, SR Lenox, KE Gebhardt: Human and Environmental Toxicity of Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS): Evidence for Safe Use in Household Cleaning Products. In: Environmental health insights. Volume 9, 2015, pp. 27-32, doi : 10.4137 / EHI.S31765 , PMID 26617461 , PMC 4651417 (free full text) (review).
- ↑ JA Reynolds, Charles Tanford : Binding of dodecyl sulfate to proteins at high binding ratios. Possible implications for the state of proteins in biological membranes. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 66, Number 3, July 1970, pp. 1002-1007, PMID 5269225 , PMC 283150 (free full text).
- ↑ LE Henderson, S. Oroszlan, W. Konigsberg: A Micromethod for Complete Removal of Dodecyl Sulfate from Proteins by Ion-Pair Extraction. In: Analytical Biochemistry . Vol. 93, 1979, pp. 153-157, PMID 434458 , doi: 10.1016 / S0003-2697 (79) 80129-3 .
- ↑ Ulrich K. Laemmli : Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. In: Nature . Vol. 227, 1970, pp. 680-685, PMID 5432063 , doi: 10.1038 / 227680a0 .