Okadaic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
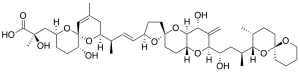
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Okadaic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 44 H 68 O 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 805.00 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
144-146 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Okadaic acid is a toxin produced by some marine algae ( dinoflagellates ). It accumulates in clams and causes fish poisoning .
Occurrence
Okadaic acid was named after the marine sponge Halichondria okadai , which occurs on the Japanese Pacific coast and from which okadaic acid was isolated for the first time. It was also isolated as a cytotoxin from the H. malanodocia sponge found in the Caribbean . Originally okadaic acid is produced by marine algae belonging to the dinophytes ( dinoflagellates ) , such as Dinophysis sp. or Prorocentrum sp. that produce okadaic acid in a precursor that is harmless to them, the so-called dinophysistoxin-4 . The dinophysistoxin-4 is released from the dinophytes to the surrounding medium or escapes upon death and is hydrolyzed in the medium to give okadaic acid diol ester.
properties
Okadaic acid diolester is fat-soluble, so it can pass through biomembranes and penetrate into cells of other organisms , where the okadaic acid diolester is hydrolyzed again to the actual, toxic okadaic acid.
toxicology
The toxicity of okadaic acid based on the inhibition of the serine - / threonine -specific protein - phosphatases 2b (PP2B), whereupon the classification of okadaic acid as type 1 (PP1), 2a (PP2A) and hepatotoxin and as a tumor promoter is based. The inhibitory effect on the individual phosphatase types is dependent on the concentration. Type 2a phosphatase , which is already 50% inhibited at okadaic acid concentrations in the range of 1 nM ( IC 50 ), is most strongly inhibited . The IC 50 for PP1 is 0.3 - 1 μM and for PP2B is over 1 μM. So induces Okada acid, for example, a permanent. Muscle contraction , as the dephosphorylation of the contraction of the involved protein myosin by the serine - / threonine -specific protein - phosphatases can no longer take place.
The lethal concentration of okadaic acid in mice ( LD 50 ) is 192 μg / kg, ip. ( intraperitoneal )
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Okadaic acid from Prorocentrum concavum at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet okadaic acid from Acros, accessed on February 20, 2010.
- ↑ Kazuo Tachibana, Paul J. Scheuer, Yasumasa Tsukitani, Hiroyuki Kikuchi, Donna Van Engen, Jon Clardy, Yalamanchili Gopichand, Francis J. Schmitz: Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic polyether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 103, 9, 1981, pp. 2469-2471. doi: 10.1021 / ja00399a082 .
- ^ Robert Edward Lee: Phycology. 4th edition. Cambridge University Press, New York 2008, ISBN 978-0-521-68277-0 .
- ↑ a b c H. Ishihara, BL Martin, DL Brautigan, H. Karaki, H. Ozaki, Y. Kato, N. Fusetani, S. Watabe, K. Hashimoto, D. Uemura et al: Calyculin A and okadaic acid: inhibitors of protein phosphatase activity. In: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications . 159, 3, March 31, 1989, pp. 871-877.
- ↑ H. Ibelgaufts: okadaic acid. ( Memento of February 10, 2013 in the web archive archive.today ) Retrieved on July 7, 2010.
literature
- Robert Edward Lee: Phycology 4th Edition. Cambridge University Press, New York 2008, ISBN 978-0-521-68277-0 .
- CJ Forsyth, RA Urbanek: An Efficient Total Synthesis of Okadaic Acid. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 119, 35, 1997, pp. 8381-8382, doi: 10.1021 / ja9715206 .
