Oxo alcohols
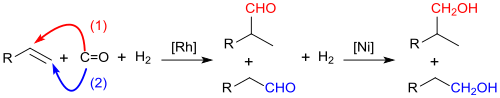
Oxo alcohols are alcohols that result from the catalytic hydrogenation of aldehydes from the hydroformylation reaction of olefins with synthesis gas .
Which in this by Otto Roelen in Ruhrchemie also known as the oxo synthesis reaction discovered in 1938 among cobalt -, today mainly under rhodium - catalysis formed so-called oxo aldehydes can be prepared by aldol condensation with itself or preferably with formaldehyde in α, β- unsaturated aldehydes are transferred whose hydrogenation products also belong to the oxo alcohols.
The group of so-called oxo products includes, in addition to the oxoaldehydes and oxo alcohols, the oxo acids obtainable therefrom by oxidation, such as. B. valeric acid or 2-ethylhexanoic acid .
Oxo alcohols are among the large-volume organic chemicals with an annual global production volume of approx. 8 million tons. They are used as solvents and as alcohol components for esters, which in turn are used as solvents, as plasticizers for polyvinyl chloride PVC, as monomers (e.g. acrylic acid esters ) and as additives for fuels and lubricating oils .
Manufacture and use
The hydroformylation has been optimized over the past 80 years with regard to energy efficiency, aldehyde yield and n - / iso isomer ratio and delivers aldehyde yields> 95% and n -butanal / iso - at relatively low temperatures (<130 ° C) and pressures (<60 MPa) Butanal ratios up to 97: 3.
More than 90% of the aldehydes obtained in this way are hydrogenated practically quantitatively to the oxo alcohols under catalysis with Raney nickel or noble metals.
The most important oxo alcohols are n-butanol and isobutanol by hydroformylation of propene , which together make up about 70% of the total volume of the oxo alcohols.
The 2-ethylhexenal obtained by aldol condensation of two n-butanal molecules is hydrogenated to the oxo alcohol 2-ethylhexanol 2-EH (isooctanol), which is very important in the EU because of the ban on the PVC plasticizer bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate DEHP has lost. The longer-chain oxo alcohols isononanol INA and 2-propyl-1-heptanol 2-PH - due to aldol condensation of two n-pentanal molecules and subsequent hydrogenation - have become increasingly important as substitutes .
The trihydric alcohol trimethylolethane , accessible from propionaldehyde by double addition of formaldehyde to the 2-position of the propanal and subsequent Cannizzaro reaction , is, like the trimethylolpropane obtained analogously from n- butanal, a crosslinker for polyesters and polyurethanes . The dihydric alcohol neopentyl glycol , derived analogously from isobutanal , is an important alcohol component for u. a. Polyester resins , paints , lubricants and hydraulic fluids .
Long -chain alkenes (e.g. from the SHOP process) as precursors for fatty alcohols or alkene mixtures (e.g. the so-called raffinate II (mainly 1-butene and 2-butenes ) obtained during steam cracking ) are also suitable as precursors, e.g. B. for the flavoring pentyl acetate of interest.
Oxo alcohols are suitable as starting compounds for a large number of carboxylic acid esters , carboxylic acids and amines .
The most important manufacturers of oxo alcohols are BASF , DuPont de Nemours , Eastman Chemical , Evonik Industries , ExxonMobil , Grupa Azoty , INEOS , LG Chem , Mitsubishi Chemical , Oxea , Perstorp AB , PetroChina , Sabic , Sasol and Sinopec .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Historic sites of chemistry, 2013-Dr. Otto Roelen and the Ruhrchemie plant in Oberhausen. Society of German Chemists, accessed April 18, 2018 .
- ↑ Patent DE849548B : Process for the production of oxygen-containing compounds. Published on September 20, 1938 , applicant: Chemische Verwertungsgesellschaft Oberhausen mbH, inventor: O. Roelen.
- ↑ Hans-Jürgen Arpe: Industrial Organic Chemistry, 6th fully revised. Edition . Miley-VCH, Weinheim 2007, ISBN 978-3-527-31540-6 , pp. 137-152 .
- ↑ a b Product Range. (PDF; 2.1 MB) In: oxea-chemicals.com. Oxea GmbH, accessed April 18, 2018 (English).
- ↑ CW Kohlpaintner, RW Fischer, B. Cornils: Aqueous biphasic catalysis: Ruhr chemistry / Rhône-Poulenc oxo process . In: Appl. Catal. A. Band 221 , no. 1–2 , 2001, pp. 219-225 , doi : 10.1016 / S0926-860X (01) 00791-8 .
- ^ R. Tudor, A. Shah: Industrial low pressure hydroformylation: Forty-five years of progress for the LP Oxo R process . In: Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. Band 61 , no. 3 , 2017, p. 246-256 , doi : 10.1595 / 20565131X695875 ( matthey.com ).