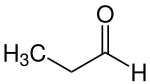
Propionaldehyde
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Propionaldehyde | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 6 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a pungent odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 58.08 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.81 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−81 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
49 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3650 |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−215.6 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Propionaldehyde (according to IUPAC nomenclature: propanal , sometimes also referred to as propylaldehyde ) is an organic-chemical compound from the group of aldehydes . It is an important basic and intermediate product in the chemical industry that is widely used.
Extraction and presentation
Propanal can be produced by the hydroformylation of ethene .
The oxidation of n- propanol with potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid also leads to propanal. Atmospheric oxygen in the presence of the catalysts copper or platinum can also be used as the oxidizing agent .
Propanal can also be synthesized by isomerizing propylene oxide at 300 ° C over silica gel :
Another synthesis option is the catalytic hydrogenation of acrolein :
Finally, the synthesis of propanal is also possible by a Grignard reaction of ethyl magnesium bromide with ethyl formate .
properties
Physical Properties
Propanal is a volatile, colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It boils at 49 ° C under normal pressure . The heat of vaporization at the boiling point is 28.3 kJ mol −1 . According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in Torr, T in ° C) with A = 7.26342, B = 1277.1176 and C = 242.556 in the temperature range from -38.65 to 231.25 ° C. It has a dynamic viscosity of 0.375 mPas at 20 ° C.
| property | Type | Value [unit] | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard enthalpy of formation | Δ f H 0 liquid Δ f H 0 gas |
−218.3 kJ mol −1 −188.7 kJ mol −1 |
|
| Standard entropy | S 0 l S 0 g |
212.9 J mol −1 K −1 304.4 J mol −1 K −1 |
as a liquid as a gas |
| Enthalpy of combustion | Δ c H 0 liquid | −1816.5 kJ mol −1 | |
| Heat capacity | c p | 159.1 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) 80.73 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) |
as a liquid as a gas |
| Critical temperature | T c | 504.4 K | |
| Critical pressure | p c | 52.6 bar | |
| Critical density | ρ c | 4.91 mol·l −1 | |
| Enthalpy of fusion | Δ f H | 8.59 kJ mol −1 | at the melting point |
| Enthalpy of evaporation | Δ V H 0 | 29.96 kJ mol −1 |
Chemical properties
The aldol addition of two molecules of propanal yields 2-methyl-3-hydroxypentanal, which can react further to form 2-methyl-2-pentenal with elimination of water as part of the aldol condensation . This β-dehydration takes place in particular with acid catalysis and heating.
use
Propionaldehyde is an important precursor and intermediate in industrial organic chemistry . It is mainly used for the production of plastics , plasticizers , rubber auxiliary products , vulcanization accelerators , phenolic resins , demulsifiers , flavor - and fragrances , agricultural chemicals , pesticides and pharmaceuticals . Technically, numerous products are synthesized from propionaldehyde. These include, in particular, 1-propanol , 1-propylamine , propionic acid , trimethylolethane , methacrolein and propionitrile . In addition, propionaldehyde is reacted with acetaldehyde to form copolymers . Propionaldehyde is also an important starting material for the production of alkyl pyridines , imidazoles , 3-methylindole and other heterocycles . In organic synthesis chemistry , propionaldehyde is used in acetalizations , imine formations , olefinations , organometallic and aldol reactions .
proof
Propanal reacts with the indicator Schiff's reagent . This aldehyde turns the reagent pink to purple in color.
safety instructions
The vapors of propionaldehyde form with air explosive mixtures. Self-ignition can also occur when distributed over large surfaces . Propanal is mainly absorbed through the respiratory tract and skin . Furthermore, absorption via the digestive tract has been proven. Ingestion or exposure can cause acute irritation to the eyes , respiratory tract and skin. A narcotic effect is possible with prolonged inhalation . Liver and kidney damage can occur chronically . Sufficient information is not available on reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity , but a certain mutagenic effect was determined in some tests , which, however, is inconsistent and is therefore controversial. Propionaldehyde has a lower explosion limit (LEL) of 2.3% by volume (55 g / m 3 ) and an upper explosion limit (UEL) of 21.0% by volume (510 g / m 3 ). The ignition temperature is 190 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T4 and explosion group IIB. The limit gap width was determined to be 0.84 mm. With a flash point of −40 ° C, propionaldehyde is very easily inflammable.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Entry on propionaldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 19, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on propionaldehyde. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 19, 2019.
- ↑ Entry on propionaldehyde in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on April 19, 2019. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-24.
- ↑ JD Unruh, D. Pearson: n-Propyl Alcohol. In: Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology . doi: 10.1002 / 0471238961.1618151621141821.a01 .
- ↑ a b c C. D. Hurd, RN Meinert: Propionaldehyde In: Organic Syntheses . 12, 1932, p. 64, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.012.0064 ; Coll. Vol. 2, 1943, p. 541 ( PDF ).
- ↑ P. Sabatier, J.-B. Sanderens: Dédoublement catalytique des alcools par les métaux divisés: alcools primaires forméniques. In: Compt. Rend. Hebd. 136, 1903, pp. 921ff. (Full text)
- ↑ A. Trillat: Étude de l'oxidation catalytique des Alcools (cas de la spirale de platine). In: Bull. Soc. Chim. 3, 29, 1903, pp. 35ff. (Full text)
- ↑ P. Sabatier, J.-B. Senderens: Nouvelles méthodes générales d'hydrogénation. In: Ann. phys. chim. 8, 4, 1905, p. 398. (full text)
- ^ JF Counsel, DA Lee: Thermodynamic properties of organic oxygen compounds 30. Vapor heat capacity and enthalpy of vaporization of propanal. In: J. Chem. Thermodyn. 4, 1972, pp. 915-917, doi: 10.1016 / 0021-9614 (72) 90013-4 .
- ^ Carl L. Yaws: The Yaws Handbook of Vapor Pressure - Antoine Coefficients. 2nd Edition. Elsevier, 2015, ISBN 978-0-12-802999-2 , p. 13, doi: 10.1016 / B978-0-12-802999-2.00004-0 .
- ↑ a b K. B. Wiberg, LS Crocker, KM Morgan: Thermochemical studies of carbonyl compounds. 5. Enthalpies of reduction of carbonyl groups. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 1991, pp. 3447-3450.
- ↑ a b c A. D. Korkhov, IA Vasil'ev: Heat capacity and thermodynamic functions of propanal at low temperatures. In: Termodin. Org. Soedin. 6, 1977, pp. 34-37.
- ↑ JE Connett: Chemical equilibria. 5. Measurement of equilibrium constants for the dehydrogenation of propanol by a vapor flow technique. In: J. Chem. Thermodyn. 4, 1972, pp. 233-237.
- ↑ J. Tjebbes: Heats of combustion of propanal and 2-methyl propanal. In: Acta Chem. Scand. 16, 1962, pp. 953-957.
- ^ J. Chao: Thermodynamic properties of key organic oxygen compounds in the carbon range C1 to C4. Part 2. Ideal gas properties. In: J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data . 15, 1986, pp. 1369-1436.
- ↑ a b A. S. Teja, DJ Rosenthal: The Critical Pressures and Temperatures of Twelve Substances Using A Low Residence Time Flow Apparatus. In: AIChE Symp. Ser. 86, 279, 1990, pp. 133-137.
- ↑ MJ Anselme, AS Teja: The critical properties of rapidly reacting substances. In: AIChE Symp. Ser. 86, 279, 1990, pp. 128-132.
- ^ V. Majer, V. Svoboda: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1985, p. 300.








