Phosalone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
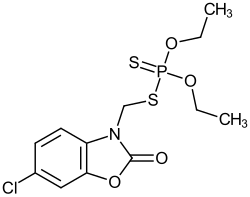
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phosalone | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 15 ClNO 4 PS 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid with a garlic-like odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 367.8 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.39 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
47.5-48 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Phosalone is an aromatic dithiophosphoric acid ester and a carbamate that has been widely used as an insecticide and acaricide . Phosalon was introduced in 1963 by Rhône-Poulenc (now Bayer CropScience ). A structurally very similar insecticide is the azamethiphos .
Extraction and presentation
Phosalone can be obtained from 2-aminophenol and urea . These condense to benzoxazolone , which is then chlorinated . With formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride , a chloromethyl group is added to the nitrogen atom. In the last step, the intermediate reacts with DEPA to form phosalone.
properties
Phosalone forms flammable, white crystals and has a characteristic, garlic-like odor. It is quickly absorbed in the body, where it is converted into a more potent oxo analog relatively quickly.
Admission
The compound was withdrawn from approval as a plant protection product in the EU in December 2006 due to the risks to humans . There are no longer any approvals for phosalone-containing pesticides in Switzerland, Germany and Austria.
safety instructions
Like most phosphoric acid esters, phosalone is a neurotoxin which, by blocking important enzymes such as cholinesterases , causes damage to the central nervous system as well as the lungs, liver and kidneys.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet: Phosalone .
- ↑ a b c d Entry on Phosalone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet Phosalone at Extoxnet.
- ↑ Entry on Phosalone in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ a b Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR), Monograph for Phosalone , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ^ Entry on Phosalone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 2, 2015.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 431 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ DECISION OF THE COMMISSION of December 22, 2006 on the non-inclusion of phosalone in Annex I of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and the revocation of the authorizations for plant protection products containing this active substance (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Phosalone in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 11, 2016.

