Rhenium (VII) oxide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
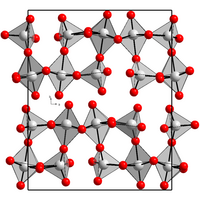
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Re 7+ __ O 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
orthorhombic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
P 2 1 2 1 2 1 (No. 19) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 1250 pm, b = 1520 pm and c = 540 pm |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Rhenium (VII) oxide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Rhenium heptoxide |
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | Re 2 O 7 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow, almost odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 484.40 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
6 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
220 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
363 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1128 kJ mol −1 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Rhenium (VII) oxide Re 2 O 7 is a chemical compound and is one of the oxides of rhenium . It is a yellow, hygroscopic solid. Compared to the unstable and explosive manganese (VII) oxide , rhenium (VII) oxide is significantly more stable.
Extraction and presentation
Rhenium (VII) oxide is formed when rhenium or rhenium compounds are heated in air.
properties
Physical Properties
Rhenium (VII) oxide crystallizes in an orthorhombic crystal structure with the space group P 2 1 2 1 2 1 (space group no. 19) . The lattice constants are a = 1250 pm, b = 1520 pm and c = 540 pm. In the crystal , rhenium (VII) oxide forms ReO 4 - tetrahedra and ReO 6 - octahedron , which alternate and are linked via the corners.
Chemical properties
Rhenium (VII) oxide is very hygroscopic and dissolves well in water. When dissolving, the strong acid perrhenic acid is formed . Rhenium (VII) oxide is carried hydrogen at 300 ° C to rhenium (IV) oxide reduced.
use
Rhenium (VII) oxide is an intermediate product in the extraction of elemental rhenium. It is created when roasting manganese ores containing rhenium. The rhenium (VII) oxide is dissolved in water after separation from the remaining fly ash . From the resulting perrhenic acid, the rhenium is precipitated as ammonium perrhenate and reduced to the element with hydrogen .
Rhenium (VII) oxide can be used as a catalyst in various reactions in organic chemistry . With the help of rhenium (VII) oxide, alkanes can be converted into carboxylic acids . Other reactions catalyzed by rhenium (VII) oxide are metathesis reactions of olefins . The catalyst methyltrioxorhenium (MTO) can be obtained from rhenium (VII) oxide .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b B. Krebs, A. Müller and H. Beyer: The Crystal Structure of Rhenium (VII) Oxide . In: Inorg. Chem. , 1969, 8, 3, pp. 436-443.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Data sheet rhenium (VII) oxide (PDF) from Merck , accessed on December 25, 2019.
- ↑ a b c Georg Brauer (Ed.) U. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume III, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1981, ISBN 3-432-87823-0 , p. 1616.
- ^ AF Holleman , N. Wiberg : Inorganische Chemie . 103rd edition. Volume 2: Subgroup elements, lanthanoids, actinides, transactinides. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin / Boston 2016, ISBN 978-3-11-049590-4 , p. 1921 (Reading sample: Part C - Subgroup elements. Google book search ).
- ↑ M. Kirillova et al .: Group 5-7 transition metal oxides as efficient catalysts for oxidative functionalization of alkanes under mild conditions . In: Journal of Catalysis , 2007, 248, pp. 130-136.
- ↑ M. Onaka, T. Oikawa: Olefin Metathesis over Mesoporous Alumina-supported Rhenium Oxide Catalyst. In: Chemistry Letters 2002 , 850-851.
- ↑ W. Herrmann et al .: Inexpensive, efficient and environmentally friendly synthesis of the versatile catalyst methyltrioxorhenium (MTO) . In: Angew. Chem. , 2007, 119, pp. 7440-7442.
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , pp. 1628-1629.


