Rorschach-Heiden mountain railway
| Rorschach – Heiden | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
BDeh 2/4 24 with bicycle and summer carriages
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
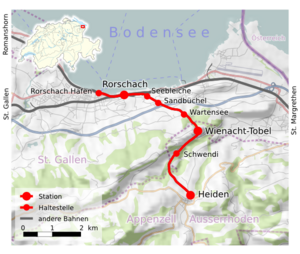
Course of the route traveled by the trains to Heiden
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timetable field : | 857 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route length: | 5.60 km | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gauge : | 1435 mm ( standard gauge ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Power system : | 15 kV 16.7 Hz ~ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum slope : | 93.6 ‰ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum radius : | 150 m | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rack system : | Riggenbach | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn is a railway line in northern Switzerland . The former operating company of the same name, abbreviated RHB , went into the Appenzeller Bahnen (AB) in 2006 . Built by the RHB route is 5.60 km long standard gauge - cog railway from Rorschach at Lake Constance in the nearly 400 meters higher elevation Gentiles .
Route
The property line begins a good half a kilometer east of the Rorschach train station, shortly after it branches off from the Rorschach – Chur line belonging to the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) . The property line is exactly at kilometer 64.41483. The entry signal from Heiden to the Rorschach train station is at kilometer 64.476. This position is often incorrectly stated as the property limit, but in fact it is the operational limit. The property line between SBB and AB and the zero point of the kilometers in the direction of Heiden are behind the SBB depot, directly in front of the two points in the Appenzeller Bahnen parking facility. The rack also begins immediately after the two switches. The gradient that begins afterwards is on average 91 ‰, the maximum value is 93.6 ‰. Above Wienacht-Tobel the route is a little flatter and only reaches 79.6 ‰.
The route continues via the stations Seebleiche , Sandbüchel , Wartensee , Wienacht-Tobel and Schwendi bei Heiden to Heiden. All intermediate stations are demand stops . The terminal station in Heiden is at an altitude of 794 meters. The trains to Heiden already start at Rorschach Hafen station, initially following a piece of the Romanshorn – Rorschach railway line operated by SBB to Rorschach station and from there the route towards St. Margrethen to the junction.
The route runs through the political communities of Rorschacherberg (Seebleiche, Sandbüchel), Thal (Wartensee), Lutzenberg (Wienacht-Tobel), Heiden (Schwendi) and Grub (without a station) and ends in the municipality of Heiden.
history
The first efforts to establish a rail connection for Heiden began in 1871. Early plans for an adhesive railway were soon discarded in favor of the rack-and- pinion line to Rorschach. After receiving the concession in January 1874, construction work began in the spring of the same year. After a year and a half of construction, the line was ready. It was built in such a way that an extension to Trogen was possible. That was specified by the Swiss Federal Assembly. The line was opened on September 6, 1875. The entire route was 7,163 m long when the company opened, of which 5,784 m were owned by the railway company. The construction costs of the line amounted to CHF 2,225,000, the costs for the rolling stock amounted to CHF 218,200. At the beginning, the railway company had three steam locomotives , nine passenger cars with a total capacity of 400 people and eight freight cars with a total capacity of 56 t.

In 1897 the company was issued a concession allowing the construction of a junction of its line of km. 2.666 to a quarry in the “Chrennen” (then “Krinnen”) near Wienacht. For this purpose, a new track with a length of around 250 m was laid, which became an integral part of the entire railway system.
Since 1930 it has been electrified with the same power system as the SBB network, with single-phase alternating current 15,000 volts and a frequency of 16.7 Hertz.
With retrospective effect on January 1, 2006, the 2006 General Assembly resolved to merge with Bergbahn Rheineck-Walzenhausen (RhW), Trogenerbahn (TB) and the former Appenzeller Bahnen (AB). The four railways now operate under the name Appenzeller Bahnen.
Due to declining frequencies and a cost recovery rate of less than 30 percent, the cantons of Appenzell Ausserrhoden and St. Gallen have an engineering office checked in 2019 whether for the three cogwheel railways of the Appenzeller Bahn from Rorschach Hafen to Heiden, from Altstätten Stadt to Gais , and from Rheineck to Walzenhausen "More customer-friendly and cheaper alternatives" would be feasible. A switch to bus operation or fully automatic operation is under discussion.
Train operation
history

For the first two years, the trains had to be transported from the end of the rack in Rorschach to the Rorschach station with a third-party steam locomotive, whereby the RHB steam locomotive, which was only driven by a gearwheel, was towed the 560 meters. Since it was dependent on the goodwill of the then VSB , it was decided to equip its own locomotives with an auxiliary adhesion drive. Thus, from 1877 onwards, it was possible to reach Rorschach train station on one's own. Soon the trains were extended to Rorschach Hafen in order to pick up passengers directly from the steamers. This type of operation has been retained to this day, although today the tourist-oriented connection between ship and rail is of secondary importance compared to the needs of local commuting.
Until the delivery of the BDeh 3/6 in 1998, the RHB offered two car classes . This was the second and third class until the class reform of 1956, and the first and second class until 1998.
For a long time, the rack railway had a brisk volume of goods, as there was a siding to the Starrag machine factory near today's Seebleiche station and a grain mill in Wolfhalden, about 200 m from Heiden train station. Normal freight wagons can be transported on the route, as it allows all wagons of the UIC / RIC design to be transported, but only as individual wagons for weight reasons. Until the mill was shut down, wagons weighing up to 90 tons were delivered. In the end, these had to be delivered between two BDeh 2/4 using the “sandwich process”, since after a change in the regulations only a front load of 73 tons was permitted.
present
Today there is an hourly train in each direction between Rorschach Hafen and Heiden. The clock times in the morning differ from those after 9:00 a.m.
In the summer, public steam rides are also offered, with the former Rosa plant locomotive coming onto the route. The historic summer wagons are used in regular operation, a bicycle wagon is used to transport bicycles.
Freight traffic no longer takes place, with the exception of our own construction trains, as the main customers Starrag and Grain Mill Wolfhalden have ceased to exist. During the reorganization of Swiss freight traffic, many service points with lower freight volumes, including all of the RHB, were discontinued.
The motor car BDeh 3/6 25 was from September 2009 to May 2010 for revision in the main workshop of the Rhaetian Railway in Landquart. As part of this revision, it was repainted in the current colors and given the AB logo.
The Rorschach-Heiden-Bergbahn is included in the Ostwind tariff association.
Incidents
On December 1, 2002, an extra train crashed into a buffer stop in Wienacht-Tobel because of an incorrectly set point. 38 passengers suffered injuries.
Rolling stock
| model series | Manufacturer | Construction year | origin | number of pieces | Discarded | Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| series | Numbers | total | today | ||||||
| Locomotives | |||||||||
|
H 1/2 HG 1/2 |
1 | Aarau | 1875 | 3 | 0 | 1949 | |||
| 2-3 | 1930 | ||||||||
| 4th | SLM | 1900 | 1 | 0 | 1949 | ||||
| H 2/2 | 3 II | SLM | 1951 | Rüti (1997) | (Ex) 1 | hist. 1 | "Pink"; ex MF Rüti H 2/2 3; Property EV | ||
| Railcar | |||||||||
| BCFZm 2/2 | 21st | SLM | 1910 | 1 | 0 | 1917 | at RVT sold | ||
|
FZeh 2/4 DZeh 2/4 |
21-22 | SLM / MFO | 1930 | 2 | 2 | ||||
|
BCFeh 2/4 ABDeh 2/4 |
23 | SLM / BBC | 1953 | 2 | 2 | remotely controllable with Bt 31 | |||
| 24 | 1967 | ||||||||
| BDeh 3/6 | 25th | STAG | 1998 | 1 | 1 | Radio remote control | |||
| Control car | |||||||||
| Bt | 31 | SLM / BBC | 1962 | BT (1985) | (Ex) 1 | 0 | 2017 | ex BT ABt 142; at EV sold | |
| Passenger coaches | |||||||||
| BC | 1-2 | 1875 | 2 | 0 | 1930 | open summer carriages | |||
| B 2 | 3-7 | 1875 | 6th | 5 | open summer carriages | ||||
| 8th | 1970 | ||||||||
| C 2 | 9 | 1875 | 1 | 0 | 1994 | Conversion to D 2 9 | |||
| D 2 | 9 | 1875/1994 | (At) 1 | 0 | 2017 | ex C 2 9; Velotransportwagen; at EV sold | |||
| B 4 | 10 II -11 II | 1962 | SBB (1971) | (Ex) 2 | 2 | ex SBB B 8202-8203 (aluminum box EW I ) | |||
| FROM 2 | 12-13 | SIG | 1930 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| B 4 | 14 II | SIG | 1948 | World Cup (1974) | (Ex) 1 | 1 | ex WM B 25 | ||
| tractor | |||||||||
| Tmh 2/2 | 20th | SLM / BBC | 1962 | KUMA (2006) | (Ex) 1 | 1 | ex MF Rüti 4, KUMA Thm 237 916 | ||
| Ub = takeover from outside stock (used vehicle); Um = conversion from our own stock | |||||||||
Company car
- X 152 (1859/1935) SCB / RHB, snow plow
- X 257, 262, 264 (1898) flat wagons (from the M4 SP 252–264 series)
- X 602, 603, 631, 641 formerly MThB
- X 633
- X 9054 formerly BT
gallery
literature
- Eisenbahn-Kurier Special number 64: The railway on Lake Constance . Freiburg 2002, pages 50-53.
Web links
- Hans Waldburger 125 years of Rorschach - Heiden-Bergbahn (RHB) in the Swiss Amateur Railway Club Zurich (SEAK) , 2000:
- (Part 1) ( Memento from February 4, 2005 in the Internet Archive ),
- (Part 2) ( Memento from February 17, 2005 in the Internet Archive ),
- (Part 3) ( Memento from February 17, 2005 in the Internet Archive ),
- (Part 4) ( Memento from February 17, 2005 in the Internet Archive ),
- (Part 5) ( Memento from February 17, 2005 in the Internet Archive ),
- (Part 6) ( Memento from February 18, 2005 in the Internet Archive )
Individual evidence
- ↑ SBB track plan of Rorschach station, edition of November 3, 2011
- ^ EA 9/2009 page 452
- ^ Concession for a Rorschach – Heiden railway (approved draft). Federal Archives, accessed on December 10, 2013 .
- ^ ViaStoria. Center for Traffic History, accessed December 10, 2013 .
- ↑ Approved draft . Federal Archives, accessed on December 10, 2013 .
- ↑ Tobias Gafafer: Eastern Switzerland cog railways are on the red list In: Neue Zürcher Zeitung from February 28, 2019
- ^ Peter Eggenberger: Pioneering work 110 years ago . In the Appenzeller Zeitung (online edition). 5th January 2018
- ^ The worst rail accidents in Switzerland. In: Tages-Anzeiger . January 10, 2013, accessed January 14, 2013
- ↑ EUROVAPOR, Sulgen section: Pink cogwheel steam locomotive on the Rorschach-Heiden mountain railway ( Memento from August 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
Coordinates: 47 ° 27 '54 " N , 9 ° 32' 24" E ; CH1903: 758416 / 259257