SMS Wolf (1878)
|
The sister ship Hyena
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
The gunboat SMS Wolf (not to be confused with the auxiliary cruiser SMS Wolf in World War I ) was the first German warship to be stationed in East Asia . It was launched on March 21, 1878 at the Imperial Shipyard in Wilhelmshaven and commissioned on October 1, 1878.
The wolf , which is intended for deployment abroad , already left Wilhelmshaven on October 26 with the destination China. The first commander of the gunboat was Korvettenkapitän (Korvettenkapitän) Paschen. Despite a machine failure, Singapore reached Singapore as planned on February 2, 1879 . From 18th August 1880 to 10. August 1882 was Lieutenant / Captain Franz Strauch commander.
The Wolf , equipped with auxiliary sails to save coal, looked more like a sailor than a steamboat . It was built as a barquentine with a sail area of 541 m². The sails were later reduced to 290 m².
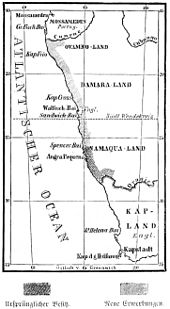
The ship did five years of station service and began its journey home on May 30, 1884. Since this passed on the west coast of Africa, it took part in the occupation of German South West Africa . The Wolf marked the stretch of coast between the Lüderitzland and Portuguese West Africa as a German colony. Thereafter, the voyage home continued, and the ship was taken out of service for overhaul on October 30, 1884.
After the repairs were finished, it was put into service again on April 8, 1886. The technically unchanged Wolf was to replace its sister ship SMS Iltis at the East Asian station. The Wolf left Wilhelmshaven on April 18. In 1890 she was involved in the rescue operation of the Ottoman frigate Ertuğrul , which ran aground in front of Ōshima . Until 1895, the boat was serving its station in East Asia, before it was taken out of service again for overhaul in Gdansk on September 27th .
The next commissioning, on October 1, 1897, was followed by an assignment abroad in Africa until 1905. On July 18 of the same year it was finally decommissioned in Danzig. On February 3, 1906, the Wolf was removed from the list of warships. Until 1919 the boat served the Imperial Shipyard as a repair ship; then it was scrapped.
Footnotes
- ↑ Willi A. Boelcke: This is how the sea came to us - The Prussian-German Navy in Übersee 1822 to 1914. Ullstein, Frankfurt / Main, Berlin, Vienna 1981, ISBN 3-550-07951-6 , p. 143.
- ^ History of the Turkish frigate Ertuğrul . 1965, p. 16 , urn : nbn: de: gbv: 3: 5-2259 (English, 28 pages).