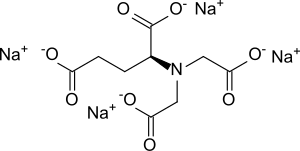
Tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 9 NO 8 Na 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White dust |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 351.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.466 g cm −3 (20 ° C ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
280 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate (GLDA-Na 4 ) is the tetrasodium salt of L -glutamic acid N , N -diacetic acid (GLDA-H 4 ), which is derived from the amino acid glutamic acid and is known as Complexing agents of the aminopolycarboxylate type are characterized by particularly high biodegradability and solubility.
GLDA-Na 4 is being discussed as a “green” alternative to the most common chelators ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA).
Extraction and presentation
The starting material for GLDA-Na 4 is L- glutamic acid and especially the much more water-soluble monosodium glutamate (MSG), which is produced as a flavor enhancer in quantities of over 3 million tons per year . To achieve acceptable yields, MSG is converted to sodium glutamate diacetonitrile, a substituted iminodiacetonitrile , in a cyanomethylation at pH <7 with aqueous formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide .
The diacetonitrile is hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide solution with elimination of ammonia in a yield of over 90% to give the tetrasodium salt of L -glutamic acid- N , N- diacetic acid.
The use of sodium cyanide instead of hydrogen cyanide represents a simplification of the process. The yields obtained are 90% with contents of the by-product nitrilotriacetic acid of well below 0.1% by weight. The reaction can be carried out discontinuously as a batch process or as a continuous process .
properties
Tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate is a white, very water-soluble, hygroscopic solid that forms alkaline (typically pH 11.5) and pale yellow aqueous solutions. In contrast to EDTA and NTA, GLDA-Na 4 dissolves very well in aqueous media over a wide pH range from 1 to 12. The thermal stability (decomposition> 280 ° C) is well above that of EDTA and NTA (> 150 ° C).
use
Because of the (currently) accepted but ultimately unsatisfactory ecological and toxicological profiles of the most common complexing agents EDTA and NTA based on petrochemical raw materials, more environmentally friendly alternatives are being sought. In addition to β-alanine diacetic acid (β-ADA), methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA), tetrasodium iminodisuccinate (IDHA) as well as citrates and gluconates , tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate was produced as a biodegradable and largely from renewable raw materials - here L -glutamic acid - developed complexing agent. GLDA-Na 4 is classified as easily biodegradable according to the OECD method OECD 301 D (> 60% after 28 days).
The following table shows the complex formation constants log K of GLDA compared to the standards EDTA and NTA, as well as to the biodegradable complexing agents methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA) and tetrasodium iminodisuccinate (IDS) compared to polyvalent metal ions:
| Metal ions | GLDA | EDTA | NTA | MGDA | IDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 3+ | 12.2 | 16.4 | 11.4 | - | 14.1 |
| Ba 2+ | 3.5 | 7.9 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 3.4 |
| Ca 2+ | 5.9 | 10.7 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 5.2 |
| Cd 2+ | 9.1 | 16.5 | 9.8 | 10.6 | 8.4 |
| Co 2+ | 10.0 | 16.5 | 10.4 | 11.1 | 10.5 |
| Cu 2+ | 13.1 | 18.8 | 13.0 | 13.9 | 13.1 |
| Fe 2+ | 8.7 | 14.3 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 8.2 |
| Fe 3+ | 11.7 | 25.1 | 15.9 | 16.5 | 15.2 |
| Hg 2+ | 14.3 | 21.5 | 14.3 | - | 14.9 |
| Mg 2+ | 5.2 | 8.8 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.1 |
| Mn 2+ | 7.6 | 13.9 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 7.7 |
| Ni 2+ | 10.9 | 18.4 | 11.5 | 12.0 | 12.2 |
| Pb 2+ | 10.5 | 18.0 | 11.5 | 12.1 | 11.0 |
| Sr 2+ | 4.1 | 8.7 | 5.0 | 5.2 | 4.1 |
| Zn 2+ | 10.0 | 16.5 | 10.7 | 10.9 | 10.8 |
Compared to other chelators, EDTA has significantly higher complex formation constants than all cations and therefore also forms more stable complexes than GLDA, which usually has slightly lower log K values with metal ions than NTA.
The most important property of chelators is that they form complexes with calcium and magnesium ions, which are the main causes of water hardness . Chelating the hardness-forming Ca 2+ ions with GLDA-Na 4 can prevent the precipitation of calcium carbonate , even at high temperatures, and promote the dissolution of calcium deposits. Thereby acting tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate a so-called builder in washing and cleaning agents by the emulsifying effect of surfactants improved.
Due to its very good solubility in water and stability even at high pH values, GLDA-Na 4 is suitable for replacing sodium tripolyphosphate ( STPP ) in automatic dishwashing detergents or phosphate-free detergents.
GLDA-Na 4 increases the effectiveness of biocides by complexing Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ ions, which leads to the destabilization of the membranes of microorganisms and thus increases their sensitivity to preservatives and biocides.
The complex-forming properties of GLDA-Na 4 are used in oil and gas production to dissolve deposits of strontium sulfate , barium sulfate and calcium sulfate and to prevent the precipitation of poorly soluble iron salts.
Complexes of trace elements with tetrasodium N , N -bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate (Find engl. Micronutrients as micronutrients ) in fertilizers and as food and feed additives ( Supplement ) use.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on TETRASODIUM GLUTAMATE DIACETATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on December 29, 2019.
- ↑ a b c d e entry for tetrasodium N, N-bis (carboxylatomethyl) - L -glutamate in the GESTIS database of IFA , retrieved on April 23, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Green chelating agent. In: Chemical Engineering. February 1, 2007, accessed April 28, 2016 .
- ↑ a b c Dissolvine® GL technical brochure. (PDF; 5.8 MB) (No longer available online.) In: akzonobel.com. Akzo Nobel Functional Chemicals, archived from the original on April 26, 2016 ; accessed on April 28, 2016 .
- ↑ a b Patent US5948748 : Detergent composition. Applied October 2, 1997 , published September 7, 1999 , Applicant: Kao Corp., Inventor: G. Hagino, S. Tagata, S. Kamioka.
- ↑ Glutamic Acid and Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) Market Size, Potential, Industry Outlook, Regional Analysis, Application Development, Competitive Landscape & Forecast, 2016-2023. In: Global Market Insights. Retrieved April 28, 2016 .
- ↑ Patent WO2009109544A1 : Process for the production of aminodicarboxylic acid-N, N-diacetic acids. Registered on March 2, 2009 , published on September 11, 2009 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: A. Oftring, A. Stamm, F. Wirsing, G. Braun.
- ↑ Patent US8399705 : Alkali metal salt of glutamic acid N, N-diacetic acid, a process to prepare such salt, and the use thereof. Registered on August 14, 2008 , published on March 19, 2013 , applicant: Akzo Nobel NV, inventor: TO Boonstra, M. Heus.
- ↑ Patent WO2010139755A1 : Process to prepare a chelating agent or precursor thereof using a cyanide salt. Registered on June 3, 2010 , published on December 9, 2010 , applicant: Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV, inventors: H. Lammers, M. Heus, TO Boonstra, AM Reichwein.
- ^ A b J. Seetz, GP Stafford: Bound by biodegradability . In: Soap, Perfumery & Cosmetics . 2007, p. 75-76 ( PDF; 1.6 MB ).
- ↑ a b Chelates Product Guide. (PDF; 4.9 MB) (No longer available online.) In: akzonobel.com. Akzo Nobel Functional Chemicals, archived from the original on April 26, 2016 ; accessed on April 28, 2016 .
- ^ BASF SE, Technical Information, Trilon® M types : Trilon M types
- ^ Lanxess AG, General Product Information : Baypure
- ↑ Patent US20160097020A1 : Aqueous solutions containing a complexing agent in high concentration. Registered on May 13, 2014 , published on April 7, 2016 , applicant: BASF SE, inventor: MC Biel, T. Greindl, M. Hartmann, W. Staffel, M. Reinoso Garcia.
- ↑ Patent WO2012146895A1 : Treatment fluids Containing biodegradable chelating agents and methods for use thereof. Filed April 26, 2012 , published November 1, 2012 , applicant: Halliburton Energy Services, Inc., inventor: EA Reyes, TD Welton.
- ↑ Patent WO2015036374A2 : Acidic fertilizer compositions containing a metal complex of glutamic acid N, N'-diacetic acid or iminosuccinic acid. Registered on September 9, 2014 , published on March 19, 2015 , applicant: Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV, inventor: AM Reichwein, MHJ Bugter.
- ↑ Patent WO2011051295A1 : Use of a metal supplement in animal feed. Registered on October 26, 2010 , published on May 5, 2011 , applicant: Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV, inventors: CTJ Wreesmann, AM Reichwein, MA van Doorn, J. Martintereso López.
