Tetscha
|
Techa Теча |
||
|
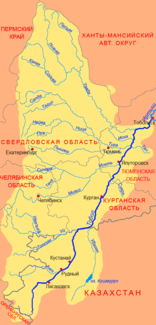
Course of the Tetscha (Теча) in the western catchment area of the Tobol |
||
| Data | ||
| Water code | RU : 14010500712111200003085 | |
| location | Chelyabinsk Oblast , Oblast Kurgan ( Russia ) | |
| River system | If | |
| Drain over | Isset → Tobol → Irtysh → Ob → Arctic Ocean | |
| origin | Outflow from Lake Irtyash 55 ° 46 ′ 7 ″ N , 60 ° 44 ′ 2 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 227 m | |
| muzzle | in Isset coordinates: 56 ° 14 ′ 13 " N , 62 ° 57 ′ 4" E 56 ° 14 ′ 13 " N , 62 ° 57 ′ 4" E |
|
| Mouth height | 79 m | |
| Height difference | 148 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.61 ‰ | |
| length | 243 km | |
| Catchment area | 7500 km² | |
| Discharge at the Muslumowo A Eo gauge : 3690 km² Location: 162 km above the mouth |
MQ 1963/1989 Mq 1963/1989 |
3 m³ / s 0.8 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Pererschinskoje A Eo gauge : 7120 km² Location: 27 km above the estuary |
MNQ 1941/1980 MQ 1941/1980 Mq 1941/1980 MHQ 1941/1980 |
1.8 m³ / s 6.7 m³ / s 0.9 l / (s km²) 28 m³ / s |
| Medium-sized cities | Osjorsk | |
| Small towns | Dalmatowo | |
| Navigable | not navigable | |
The Tetscha ( Russian Теча ) is a 243 km long right tributary of the Isset east of the Urals , in the southwest of the West Siberian lowlands in Russia.
The river became known in particular for its heavy radioactive contamination as a result of regular operations and accidents in the Mayak nuclear facility .
course
The Tetscha flows directly east of the city of Osjorsk from the 227 m high lake Irtjasch at the eastern foot of the Southern Urals , in the Chelyabinsk Oblast north of the Oblast capital.
The river initially flows in an easterly direction, then turns almost to the north, reaches the Kurgan Oblast and finally flows into the Isset near the town of Dalmatowo .
Apart from Osjorsk (the former secret city of Chelyabinsk-40 , later Chelyabinsk-65 ) and Dalmatowo (not located directly on the Tetscha, but not far from its mouth on the other bank of the Isset) there are no cities along the river.
Hydrography
The catchment area of the Tetscha covers around 7,500 km². The mean monthly water flow in the village of Perschinskoje, about 25 kilometers above the estuary, is 6.7 m³ / s (minimum in January 1.8 m³ / s, maximum during the snowmelt in April 28 m³ / s).
Near the mouth, the river is about 30 meters wide at normal water level, less than a meter deep and has a flow speed of 0.3 m / s.
The Tetscha has no major tributaries; therefore the width, depth and water flow are practically constant over their entire length.
Infrastructure
A good 40 kilometers downstream (east) of the source of the Tetscha, it is crossed by the motorway M36 , which has been developed like a motorway and connects the megacities of Yekaterinburg and Chelyabinsk . A little further to the east, the railway line (Ekaterinburg–) Kamensk-Uralsky –Chelyabinsk crosses the Tetscha. Further down the river, a local road runs for large sections through the villages along the river and crosses it several times.
ecology
From 1949 to 1951, the Mayak nuclear plant (“chemical plant”) located south of the Tetscha upper reaches near Osjorsk led to huge amounts of radioactive wastewater, the radioactivity of which was 12 petabecquerels (PBq) for 90 strontium , 13 PBq for 137 cesium and 106 PBq for short-lived radionuclides . In the years up to 1956 the discharge was greatly reduced, but continued. A total of 76 million m³ of radioactive waste water ended up in the river during this time.
On September 29, 1957, the so-called Kyshtym accident occurred in the facility , again causing large amounts of radioactive material to get into the river.
After the accident, between 1958 and 1964, some of the radioactive wastewater was created from natural lakes, including the largest of them the Kysyltash immediately near Osjorsk, on the upper reaches of the Tetscha, four collecting basins ( W-3 , W-4 , W-10 and W-11 ; combined the Tetscha cascade ), which were closed off from the Tetscha by earth and concrete dams. Since then, most of the water flowing from Lake Irtjasch has been channeled around the catchment basin. The basins have a total area of 67.4 km² and a total volume of 357.9 million m³. The heavily contaminated Karachay Lake , located south of the Tetscha in its catchment area, was sealed with concrete.
Direct access to the Tetscha is still not possible on large sections of the upper and middle reaches; several villages on the upper reaches were cleared after President Yeltsin was personally present in the area in 1993 and first informed the residents of the contamination. However, in the event of an exceptional water supply due to melting snow or precipitation, there is a risk of the catchment basins overflowing and seeping through leaks. For the latter reason, up to 60 million m³ of radioactive waste water should again have entered the river between 2001 and 2004. In this context, investigations were started against the Mayak general director Vitaly Sadownikov, but were discontinued in 2006.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Tetscha in the State Water Register of the Russian Federation (Russian)
- ↑ Tetscha at the Muslumowo gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Tetscha at the Pererschinskoje gauge - hydrographic data from R-ArcticNET
- ↑ Main principles of the distribution of radionuclides in the river system of the Tetscha according to the results of long-term observations on the website of the Chelyabinsk department of the Hydrometeorological Service of Russia (Russian)
- ↑ The Tetschakaskade in the election campaign ( Memento of the original of September 29, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. in Expert magazine , July 4, 2007 (Russian)
- ↑ Russia's toxic water: Techa river's history of contamination , Al-Jazeera, April 1, 2018
- ↑ The insidious glow of Mayak (pun: Mayak means lighthouse in Russian ) in the newspaper Trud , February 1, 2007 (Russian)