The Great Global Warming Swindle
| Movie | |
|---|---|
| German title | Global Warming - Truth or Fake? |
| Original title | The Great Global Warming Swindle |
| Country of production | United Kingdom |
| original language | English |
| Publishing year | 2007 |
| length | 75 minutes |
| Rod | |
| production | Martin Durkin |
Global Warming - Truth or Fake? (Original title: The Great Global Warming Swindle , translated: The great fraud with global warming ) is a climate-skeptical British documentary by Martin Durkin from 2007, which turns against the prevailing scientific view of global warming . The main message of the film is that man-made climate change is "a fraud that was invented by anti-industrial environmentalists , along with participating scientists , journalists and politicians , and is supported by unreliable scientific evidence". It first aired on Channel 4 on March 8, 2007 and is widely used on the Internet.
The film was widely criticized for serious errors in content. Among other things, the results of climate research were twisted or misrepresented in the film , the comments of interview partners were processed and data graphics were manipulated in such a way that the impression was given that humans are not responsible for global warming. Channel 4 describes the film as follows: "It is essentially a polemic and we expect it will cause a stir, but such is the controversial programming that Channel 4 is known for."
In the UK, the film was seen by around 2.5 million viewers. Six weeks after the film was first broadcast, around 250 complaints had been received by the UK's Office of Communications . Some time later, director Martin Durkin admitted many problems and inaccuracies in the film; By then, however, the film had already contributed significantly to public disinformation regarding man-made global warming.
The documentary ran in a revised German version under the title Der Klimaschwindel for the first time on June 11, 2007 in RTL's late evening program , n-tv repeated the broadcast on July 7, 2007.
content
The film claims that the increased amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is not the cause of global warming. The effects of cosmic rays and changes in solar activity could better explain the temperature changes. According to Durkin, a strengthening of the solar wind leads to less exposure to cosmic rays, which in turn leads to less cloud formation . The reduced cloud formation in turn leads to a lower albedo of the earth and thus to an increased absorption of solar radiation.
According to Durkin, it can be established that there is a correspondence between sunspot activity and the mean annual temperatures of the past four hundred years, far greater than with the mean CO 2 concentration in the earth's atmosphere over the same period. In particular, between the 1940s and 1980s, the mean temperature fell by around 0.2 degrees Celsius, while the CO 2 concentration increased significantly over the same period . This is reason enough to be skeptical about the causal relationship between CO 2 concentration and warming.
One of the criticisms of the computer model calculations , which had a decisive influence on the IPCC reports, is that they all made the assumption to be proven that carbon dioxide is the main cause of global warming a prerequisite. The largest factor of the greenhouse effect - water vapor - which causes two thirds of the greenhouse effect and whose concentration is naturally subject to strong fluctuations, is not taken into account. The climate models are not able to reproduce the climate development of the past 10,000 years, a well-researched period. It is not compatible with scientific criteria and soon borders on misleading to make the model calculations the basis of a statement that claims to be a scientifically sound prognosis.
Concentrating on measures to reduce CO 2 emissions has negative consequences for development in the Third World. The media and science would not publish this as it would be against their interests.
The film also deals with the question of why established science is almost unanimously based on the assumption that anthropogenic CO 2 production is the cause of warming. One explanatory approach highlights one aspect of the financial structure of research, namely the dependence of research on public funds. In the meantime, a state has been reached in which man-made climate change is a political and social, but above all an economic factor, which generates around four billion US dollars a year. This causes dependencies and interests that are not always conducive to objectivity.
Another aspect is the overall distortion of the presentation of the IPCC report; this in no way reflects the prevailing opinion of climatology , but rather a section. A number of participating scientists in no way support the statement of the IPCC report that still others have left the participation, but they are still referring to them.
The interaction of politics, UN bodies and publicly funded scientists shows a psychological dynamic: In the meantime, the conviction of man-made climate change has quasi-religious traits, which among other things means that one is no longer part of the scientific discourse as a representative of a different view but treated more like a heretic. With these statements, the film takes part in the political controversy surrounding global warming .
criticism
The film was sharply criticized. For example, he contains serious errors that reduce credibility, and uses graphics that are out of date, distorted, incorrectly labeled or simply wrong to support his theses. Conflicting facts would be completely withheld, such as the fact that developing countries are exempt from CO 2 reduction under the Kyoto Protocol . Meanwhile, an employee of Channel 4 described the documentation as "polemical".
The climate researcher Stefan Rahmstorf called the film a "bizarre brew with many [...] false claims, deceptive graphics and falsified data". Among other things, it was claimed in the film that volcanoes emit more carbon dioxide than humans. In fact, human carbon dioxide emissions are around 100 times greater than volcanic ones.
Meteorologist Alan Thorpe wrote in a comment in the New Scientist that the main message of the film was false and that there was no credible evidence that cosmic rays played a significant role.
Timothy Ball , who appeared in the film with many minutes of speaking time as an expert (belly band “Former Professor of Climatology”), admitted in court in the year of publication that he had been a professor for eight instead of the 28 years stated in the film. He also did a PhD in geography , not climatology. At the time of the film production, his professorship was more than 10 years ago. Ball last published in peer-reviewed journals in the 1980s on the subjects of “migration of geese as an indicator of climate change” and “relocation of the forest tundra in central Canada”.
The Danish scientist Eigil Friis-Christensen , who appears as an expert in the film , and whose hypothesis of a connection between the length of the sunspot cycle and the temperature development over the last 400 years is taken up in the film, criticized the film after its release. His data were falsified in the film and the film incorrectly rules out human greenhouse gas emissions as the cause of global warming. Knud Lassen, co-author of Christensen's work on this hypothesis, himself determined in 2000 that there was no longer any correlation for the period from 1990 onwards. Christensen also later rejected a connection for the period from 1986 onwards.
The British Royal Society accuses the film of playing a dangerous game by representing marginal opinions, disregarding evidence and thus distracting from necessary climate protection measures.
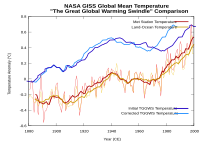
For example, the film presents data taken from the IPCC report on the development of solar activity and on the annual temperature change by means of two superimposed graphs in a time diagram. Using the synchronous course of the two graphs, it should be shown that the sun is responsible for the global temperature development. However, the curves ended in the Durkin presentation in 1980, although the IPCC report provided more up-to-date data, according to which solar activity lagged well behind the increasing temperature change.
George Monbiot accused Channel 4 of twisting the facts to create a sensation-seeking controversy. If, like this film, you use work that has already been refuted and select results one-sidedly, you can portray practically everything as true. Actually, the broadcaster already knew that the producer of the film, Martin Durkin, had already worked dubiously on an earlier documentary, and that the broadcaster had to broadcast a public apology at the time for having deceived interviewees and misrepresenting their statements. In connection with “The Great Global Warming Swindle”, Durkin is also accused of having put statements from interview partners in the wrong context. Carl Wunsch , an affected professor, speaks of a “twisting” of his statements and “pure propaganda like nothing since the Second World War”. Durkin was also often accused of spreading conspiracy theories with his film .
literature
- David Jones, Andrew Watkins, Karl Braganza, Michael Coughlan: “The Great Global Warming Swindle”: a critique . In: Bulletin of the Australian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society . tape 20 , no. 3 , 2007, p. 63-72 ( psu.edu [PDF; 613 kB ]).
Web links
- Official homepage for the film ( Memento from September 28, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) from WAG TV, with numerous links and documents (English)
- The Great Global Warming Swindle in the Internet Movie Database (English)
- Climate fraud at RTL , film criticism by S. Rahmstorf, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
- Bob Ward: Misrepresentations of scientific evidence, March 30, 2007
- “The Great Global Warming Swindle”: a critique (PDF) from the Australian Science Media Center (English; 551 kB)
- The geologist and journalist Peter Hadfield explained in the YouTube video, the misrepresentations in the film "The great Global Warming Swindle" "was year 800" with respect to the: The 800 year was unraveled (English)
swell
- ↑ Lorraine Whitmarsh: Skepticism and uncertainty about climate change: Dimensions, determinants and change over time . In: Global Environmental Change . tape 21 , 2011, p. 690–700 , doi : 10.1016 / j.gloenvcha.2011.01.016 .
- ↑ Maxwell T. Boykoff: Who Speaks for the Climate. Making Sense of Media Reporting on Climate Change . Cambridge 2011, p. 59.
- ↑ Life Style Extra: “Global Warming Is Lies” Claims Documentary ( Memento from August 18, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Quotation in the English original: “It is essentially a polemic and we are expecting it to cause trouble, but this is the controversial programming that Channel 4 is renowned for. "
- ↑ Maxwell T. Boykoff: The real swindle . In: Nature Reports Climate Change . tape 2 , 2008, p. 31 f ., doi : 10.1038 / climate.2008.14 .
- ↑ RTL: EXTRA Special: 'The climate swindle' .
- ↑ n-tv: Climate Change - Is it all a hoax? ( Memento from January 2, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) .
- ↑ Channel 4 : The Great Global Warming Swindle from Channel4.com (accessed April 1, 2007).
- ^ Steve Connor: The real global warming swindle ( Memento July 15, 2007 in the Internet Archive ). In: The Independent , March 14, 2007 (accessed April 1, 2007).
- ↑ Stefan Rahmstorf : Is journalism failing on climate? In: Environmental Research Letters . tape 7 , no. 041003 , 2012, doi : 10.1088 / 1748-9326 / 7/4/041003 .
- ^ Alan Thorpe: Fake fights are not helping climate science . In: New Scientist (Vol. 24), March 17, 2007.
- ↑ Petroleum and Propaganda: The Anatomy of the Global Warming Denial Industry [1]
- ↑ The migration of geese as an indicator of climate change in the southern Hudson Bay region between 1715 and 1851 doi : 10.1007 / BF02423429
- ↑ Historical evidence and climatic implications of a shift in the boreal forest tundra transition in central Canada doi : 10.1007 / BF00139750
- ^ Extracts from Ofcom Complaint, by Category: Misrepresentation of Eigil Friis-Christensen's Views. In: ofcomswindlecomplaint.net. Retrieved August 17, 2016 (complaint to the UK Office of Communications (Ofcom) regarding Channel 4's film The Great Global Warming Swindle , filed June 11, 2007).
- ↑ Peter Thejll and Knud Lassen: Solar forcing of the Northern hemisphere land air temperature: New data . In: Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics . September 2000, doi : 10.1016 / S1364-6826 (00) 00104-8 .
- ↑ Sun sets on skeptics' case against climate change. In: The Independent. September 14, 2009, accessed August 17, 2016 .
- ^ Royal Society : The Royal Society's response to the documentary “The Great Global Warming Swindle” ( Memento of March 22, 2007 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of July 4, 2007 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ George Monbiot : Don't let truth stand in the way of a red-hot debunking of climate change . In: The Guardian , March 13, 2007 (accessed April 1, 2007).
- ↑ George Monbiot : Don't be fooled by Bush's defection: his cures are another form of denial . In: The Guardian , January 30, 2007 (accessed April 1, 2007).
- ^ Office of Communications : Program Complaints & Interventions Report (accessed April 1, 2007).
- ↑ Ben Goldacre and David Adam: Climate scientist 'duped to deny global warming' . In: The Observer , March 11, 2007, quoted by The Guardian (accessed April 2, 2007).
- ↑ , so z. B. John Quiggin, Denial lobby strikes again , in: Australian Financial Review, March 29, 2007; Interview of ABC reporter Tony Jones with Durkin in July 2007 (PDF; 68 kB)