Triazamate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
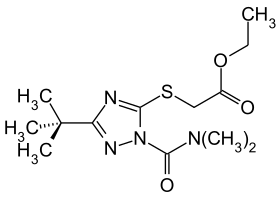
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Triazamate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 7 N 3 S | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to off-white, crystalline solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 189.24 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.22 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
52.7 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.13 mPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very sparingly soluble in water (0.433 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Triazamate is a chemical compound from the group of carbamates and triazoles . Triazamate is used as an insecticide (trade name Aztec ) and works by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase . It was introduced by Rohm and Haas (now Dow AgroSciences ) in the mid-1990s .
Extraction and presentation
Triazamate can be obtained through a multi-stage reaction. Trimethylacetyl chloride ( pivalic acid chloride ) and thiosemicarbazide react first .
The product continues to react with sodium hydroxide
and ethyl chloroacetate .
The intermediate product reacts with dimethylcarbamoyl chloride , according to
from phosgene and dimethylamine is accessible to the end product.
use
Triazamat was mainly used against aphids in pome fruit, ornamental plants and sugar beet growing.
Admission
The active ingredient triazamate is not approved for use in plant protection products in the European Union . In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry on triazamate in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB) of the University of Hertfordshire , accessed on December 3, 2013.
- ↑ a b Triazamate data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 21, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on triazamate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 17, 2019.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 725 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Instructions of the Canton of Aargau from 2008 ( Memento from May 2, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Decision of the Commission of July 4, 2005 (PDF) on the non-inclusion of triazamate in Annex I of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and the revocation of the authorizations for plant protection products containing this active substance, accessed on December 3, 2013.
- ^ Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on triazamates in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on February 18, 2016.






