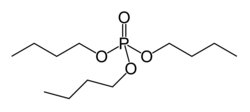
Tri- n -butyl-phosphate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tri- n -butyl-phosphate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 27 O 4 P | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, almost odorless liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 266.32 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
0.98 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−79 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
293 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
0.8 Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4224 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Tri- n -butyl-phosphate (usually called tributyl phosphate , TBP or TNBP for short ) is a phosphoric acid ester that is used, for example, as a defoamer in the textile and paper industry, as a defoamer for concrete liquefiers or as an extractant in the reprocessing of spent fuel elements .
Extraction and presentation
Tributyl phosphate can be prepared by reacting n-butanol with phosphorus oxytrichloride. Alternatively, it can also be produced from white phosphorus and butan-1-ol in the presence of oxidation catalysts or by oxidation of tributyl phosphite .
properties
Tributyl phosphate is a colorless and almost odorless liquid under normal conditions (1013 mbar and 20 ° C). Further properties are:
- very difficult to ignite ( flash point 146 ° C)
- very sparingly soluble in water
- little fleeting
- Vapors much heavier than air
The compound enters into exothermic reactions with strong oxidizing agents in the presence of acids, bases, dry hydrogen chloride , phosphoryl chloride and phenol . With water, hydrolysis occurs in the heat .
use
Tributyl phosphate is used as a defoamer in the textile and paper industry, a flame retardant in hydraulic fluids, as a defoamer for concrete liquefiers or as an extraction agent in the reprocessing of spent fuel elements , chromatography and the extraction of rare metals. It also serves as a plasticizer for celluloid, nitrocellulose lacquers and plastics. It is also used in the solvent-detergent process (S / D process) for virus inactivation of blood plasma preparations, where it works with a surfactant to dissolve the lipid envelope of enveloped viruses and thus inactivate them.
Risk assessment
Tri- n -butyl-phosphate was 2012 by the EU under Regulation (EC) no. 1907/2006 (REACH) under the substance evaluation in the ongoing Community Action Plan ( CoRAP added). The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reason for the inclusion of tri- n -butyl phosphate were the concern for the classification as CMR -substance, high (aggregated) tonnage, other risk-related concerns and widespread use. The re-evaluation took place from 2012 and was carried out by Hungary . A final report was then published.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on tributyl phosphate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 29, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on tributyl phosphate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-490.
- ↑ Entry on tributyl phosphate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 126-73-8 or tri-n-butyl phosphate ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Åke Bergman , Andreas Rydén, Robin J. Law, Jacob de Boer, Adrian Covaci, Mehran Alaee, Linda Birnbaum, Myrto Petreas, Martin Rose, Shinichi Sakai, Nele Van den Eede, Ike van der Veen: A novel abbreviation standard for organobromine , organochlorine and organophosphorus flame retardants and some characteristics of the chemicals . In: Environment International . tape 49 , 2012, p. 57–82 , doi : 10.1016 / j.envint.2012.08.003 , PMC 3483428 (free full text).
- ↑ a b Toxicological assessment of tributyl phosphate (PDF) at the professional association raw materials and chemical industry (BG RCI), accessed on October 19, 2019.
- ↑ A. Musil, W. Haas, G. Weidmann: The use of n-tributyl phosphate as an extractant and as a solvent in paper chromatography. In: Microchimica Acta. 50, 1962, p. 883, doi : 10.1007 / BF01219029 .
- ↑ SD-GFP: Production / Indication of Frozen Fresh Plasma (GFP)
- ^ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Report and Conclusion Document .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Tributyl phosphate , accessed on March 26, 2019.


