Vargem Grande do Sul
| Município de Vargem Grande do Sul "A Pérola da Mantiqueira" Vargem Grande do Sul |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| Coordinates | 21 ° 50 ′ S , 46 ° 54 ′ W | ||
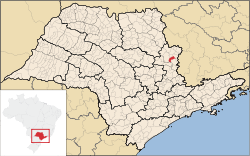 Location of Vargem Grande do Sul in the state of São Paulo Location of Vargem Grande do Sul in the state of São Paulo
|
|||
| Symbols | |||
|
|||
|
Motto "Ergo, possvm" |
|||
| founding | December 1921 | ||
| Basic data | |||
| Country | Brazil | ||
| State | São Paulo | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | BR-SP | ||
| Região intermediária | Campinas (since 2017) | ||
| Região imediata | São João da Boa Vista (since 2017) | ||
| Mesoregion | Campinas (until 2017) | ||
| Microregion | São João da Boa Vista (until 2017) | ||
| structure | 1 multiple district | ||
| height | 721 m | ||
| Waters | Rio Jaguari-Mirim, Rio Fartura, Rio Verde (São Paulo) | ||
| surface | 267.2 km² | ||
| Residents | 39,266 (2010) | ||
| density | 147 Ew. / km² | ||
| estimate | 42,845 Ew. (July 1, 2019) | ||
| Parish code | IBGE : 355640 | ||
| Time zone | UTC −3 | ||
| Website | www.vgsul.sp.gov.br (Brazilian Portuguese) | ||
| politics | |||
| City Prefect | Amarildo Duzi Moraes (2017-2020) | ||
| Political party | PSDB | ||
| economy | |||
| GDP | 891,383 thousand R $ 21,193 R $ per person (2016) |
||
| HDI | 0.737 (2010) | ||
Vargem Grande do Sul , officially Município de Vargem Grande do Sul , formerly Vargem Grande , is a medium- sized town in the Brazilian state of São Paulo . The municipal city is 235 km from the capital São Paulo .
According to the 2010 census, the municipality has 39,266 inhabitants, who are called Vargem-Grandenser. As of July 1, 2019, the IBGE estimated the population to be 42,845. The area is 267,178 km² (as of 2018); the population density in 2010 was around 147 people per km².
history
Since the 17th century, the territories north and west of São Paulo were dominated by Bandeirantes , the area was then divided into Sesmarias , including the Sesmaria Várzea Grande and the Fazenda Várzea Grande , which by 1874 already led to 60 hamlets. The city cited September 26, 1874 as the founding date when a Father José Valeriano de Souza, vicar from São João da Boa Vista , established a parish on the banks of the Rio Verde. In the province of São Paulo , Provincial Law No. 14 of February 18, 1888 established the Distrito de Vargem Grande and subordinated it to the city of São João da Boa Vista. The district received political independence by hiving off as Município de Vargem Grande by law on December 1, 1921, and independence came into force on February 24, 1922. On November 30, 1944, the place was renamed Vargem Grande do Sul , because there is still a place of the same name in Maranhão.
The municipality is strongly influenced by Italian immigrants, agriculture is the main industry. At harvest time, the population grows with migrant workers from the north and northeast.
geography
In the center, the city is at an altitude of 721 meters. The Rio Jaguari-Mirim , Rio Fartura and Rio Verde rivers belong to the catchment area of the Paraná Basin . The high altitude climate is specified as humid and tropical, class Cfa according to Köppen and Geiger .
language
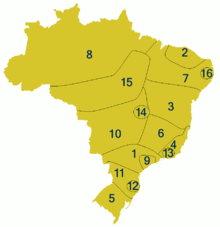
1 - Caipira
2 - Costa norte
3 - Baiano
4 - Fluminense
5 - Gaúcho
6 - Mineiro
7 - Nordestino
8 - Nortista
9 - Paulistano
10 - Sertanejo
11 - Sulista
12 - Florianopolitano
13 - Carioca
14 - Brasiliense
15 - Serra amazônica
16 - Recifense
The entire area is known for its own peasant language, the Caipira dialect ( Dialeto caipira ), which came into the interest of linguists in the early 1920s. The phonetics shows influences the Provencal, Andalusian, French, Spanish, Galego, Italian, Old Catalan and Aragonese.
City administration
City prefect (executive) is Amarildo Duzi Moraes of the Partido da Social Democracia Brasileira (PSDB) for the term 2017 to 2020 after the local elections in 2016 ; the legislature lies with the Câmara Municipal, German: Stadtverordnungenkammer or City Council, which consists of 13 members. The place is also the seat of the only and eponymous district.
Together with 13 other municipalities, it formed the São João da Boa Vista microregion until 2017 , which was one of five microregions of the Campinas mesoregion .
Population development

Infrastructure
Vargem Grande do Sul is connected to the state roads SP-344 and SP-215 .
Sons and daughters
- José Junqueira de Oliveira , Junqueira , (1910–19885), Brazilian football player
- Hélio Paschoal (1927–2005), Roman Catholic religious, Bishop of Livramento de Nossa Senhora
- Washington Novaes (* 1934), journalist and author
- Tião do Carro is João Benedito Urbano , (1946–2009), violinist, singer and composer
Web links
- City Prefecture Official Website (Brazilian Portuguese)
- Câmara Municipal de Vargem Grande do Sul (Brazilian Portuguese)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c IBGE : Cidades @: Vargem Grande do Sul - Panorama. Retrieved September 19, 2019 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ IBGE : São Paulo: Vargem Grande do Sul - produto interno bruto dos municípios - 2016. Retrieved on September 19, 2019 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ IBGE : Cidades @: Vargem Grande do Sul: Histórico. Retrieved November 18, 2016 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Vandersi Sant'Ana Castro: A resistencia de traços do dialeto caipira. Estudo com base em atlas linguisticos regionais brasileiros. Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Instituto de Estudos da Linguagem 2006 ( online ) (PDF; 4039 KB; Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Amadeu Amaral : O dialeto caipira. São Paulo 1920 ( online ) (PDF; 927 KB; Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Eleições 2016: Amarildo 45 on the website www.eleicoes2016.com.br . Retrieved March 14, 2018 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Câmara Municipal de Vargem Grande do Sul ( Memento of November 19, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) (Brazilian Portuguese).