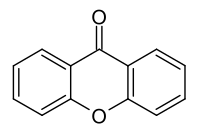
Xanthone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Xanthone | |||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 13 H 8 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless needles |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 196.19 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
174-176 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
351 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Xanthone (also xanthen-9-one or dibenzo-γ-pyrone ) is a heterocyclic chemical compound that belongs to the ethers and ketones and gives its name to the substance group of xanthones . The reduction product xanthene forms the basic body of the xanthene plant dyes . It is isomeric to fluorone ( xanthen-3-one ).
Occurrence and representation
Xanthone itself does not occur naturally, but about 200 of its derivatives such as euxanthone , corymbiferin and gentisin . Xanthone is produced by distillation of phenyl salicylate .
Properties and use
Xanthone forms colorless, easily sublimable needles that melt from 174 to 176 ° C and boil at around 351 ° C. It is slightly soluble in ethanol , ether , chloroform and benzene , but insoluble in water. In concentrated sulfuric acid , the compound with its yellow color dissolves to form a liquid with an intense light blue fluorescence. Under reductive conditions, xanthone can be converted into xanthene and xanthydrol ; the action of Grignard compounds produces xanthylium salts . The only known use of xanthone is as a specific insecticide , which acts primarily as a so-called larvicide on moth larvae .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on xanthone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 30, 2014.
- ↑ a b Data sheet Xanthone at AlfaAesar, accessed on January 22, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Xanthones data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 3, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ US Army Armament Research & Development Command. Chemical Systems Laboratory, NIOSH Exchange Chemicals. Vol. NX # 01611.
- ↑ a b Entry on xanthone in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ^ National Academy of Sciences. National Research Council, Chemical-Biological Coordination Center, Review. Vol. 5, p. 25, 1953.
- ↑ Steiner, LF and SA Summerland. 1943. Xanthones as an ovicide and larvicide for the codling moth. Journal of economic entomology 36, 435-439.