Time zones in Brazil
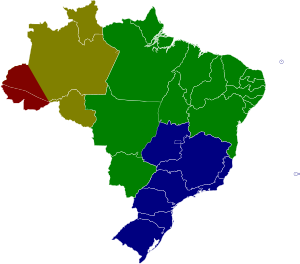
Valid in the summer months from November 4, 2018 to February 28, 2019.
Brazil has four time zones . Officially, there is talk of a Brasília time and a zone Brasília + 1, a Brasília-1 and a zone Brasília-2. In some southern states, summer time was also observed until 2019 , which was abolished by a decree of President Jair Bolsonaro .
Time zones
Brasília time (UTC − 3)
The time zone of Brasilia is UTC − 3 ; during summer time it becomes UTC − 2 , which is not understood by all states in this zone. The states (only the continental part) of the southeast region ( Espírito Santo , Minas Gerais , Rio de Janeiro , São Paulo ), the southern region ( Paraná , Rio Grande do Sul , Santa Catarina ), the northeast region ( Alagoas , Bahia , Ceará , Maranhão , Paraíba , Pernambuco , Piauí , Rio Grande do Norte , Sergipe ), the states of Goiás , Tocantins , Pará and Amapá , as well as the federal district . The vast majority of the Brazilian population lives in this time zone.
Brasília time + 1 (UTC − 2)
This time zone corresponds to UTC − 2 . It applies to some Brazilian Atlantic islands ( Fernando de Noronha , Trindade , Martim Vaz , Atol das Rocas , Saint-Peter-and-Saint-Pauls-Felsen ). There is no summer time in it.
Brasília Time-1 (UTC − 4)
This time zone corresponds to UTC − 4 ; during the summer time it becomes UTC − 3 , which is not understood by all states. It is used by Amazonas , Mato Grosso , Mato Grosso do Sul , Rondônia , and Roraima and, since 2008, also in Acre . Until 2008 the western part of Pará was also in this time zone.
Brasília time-2 (UTC − 5)
The fourth time zone in Brazil corresponds to UTC − 5 and covers the state of Acre and the western part of the Amazon. On June 23, 2008, these areas put the clock forward one hour and became part of UTC − 4. However, after five years it was switched back again in 2013.
Summertime
Summer time was observed by the following states until 2019: Espírito Santo (excluding the Atlantic islands in the year-round zone UTC − 2), Goiás , Mato Grosso , Mato Grosso do Sul , Minas Gerais , Paraná , Rio de Janeiro , Rio Grande do Sul , Santa Catarina , São Paulo and the capital district . With the exception of Bahia , these are the states that are wholly or partially south of the capital Brasilia . Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul changed in October from UTC − 4 to UTC − 3, the other states from UTC − 3 to UTC − 2.
Daylight saving time was introduced in Brazil in 1931. Originally it was valid for the whole country, only in 1988 the equatorial states were excluded again. Fixed start and end times of daylight saving time and the affected states were only set in 2008, before they were decided every year by decree.
Daylight saving time began on the first Sunday in November and ended on the third Sunday in February. If the carnival falls on this February weekend, the changeover has been postponed by a week. By 2017, the clock was changed to daylight saving time on the third Sunday in October in the southern states. The time change thus regularly occurred between the first and second round of the elections . From the point of view of the President of the Supreme Electoral Court, this caused confusion. The former President Temer therefore shortened the summer time by three weeks by decree and moved the beginning to November. The new rule first came into force on November 4, 2018. The normal / winter time has been in effect again since February 18, 2019.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Brazil Scraps DST in 2019. Accessed December 26, 2019 .
- ↑ Bolsonaro decreta fim do horário de verão; Senado tinha projetos sobre o tema. Retrieved December 26, 2019 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Brazil Abolishes Its Fourth Time Zone in 2008 . Retrieved June 25, 2008.
- ↑ IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics): Estimativas da População Residente nos Municípios Brasileiros com Data de Referência em 1º de Julho de 2013 ( Portuguese , PDF) July 1, 2013. Accessed October 20, 2013.
- ↑ HISTÓRICO DO HORÁRIO DE VERÃO . Retrieved January 23, 2007. (Portuguese)
- ↑ a b Decretos sobre o Horário de Verão no Brasil . Retrieved January 23, 2007. (Portuguese)
- ↑ Shortening of summer time from November 2018 (Portuguese)
- ↑ Decreto 6.558 de 2008, sobre o Horário de Verão no Brasil . Retrieved November 8, 2008. (Portuguese)


