Goiás
| Goiás | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Symbols | |||
|
|||
| Basic data | |||
| Country | Brazil | ||
| Capital | Goiânia | ||
| surface | 340,086.7 km² | ||
| Residents | 6,004,045 (2010) | ||
| density | 18 inhabitants per km² | ||
| ISO 3166-2 | BR-GO | ||
| Website | www.goias.gov.br (Brazilian Portuguese) | ||
| politics | |||
| governor | Ronaldo Caiado (since 2019) | ||
| Political party | DEM | ||
| economy | |||
| GDP | 65.210 million R $ 11,548 R $ per capita (2007) |
||
| The capital Goiânia | |||
Coordinates: 16 ° S , 49 ° W
Goiás [ ɡoˈjas ] ( abbreviation : GO ) is a federal state in the " Midwest " ( Portuguese : Região Centro-Oeste ) of Brazil .
Its capital and the most populous city with a little over 1.5 million inhabitants (2019) is Goiânia . It was planned to replace the old capital Goiás Velho , previously known as Goiás , from 1933 onwards. Goiás is located in the center of Brazil and is divided into 246 municipalities ( Portuguese : municípios ) with a total of almost six million inhabitants as of the last census in 2010. As of July 1, 2019, the population was estimated at 7,018,354.
Goiás borders (starting clockwise from the north) on the Brazilian states of Tocantins , Bahia , Minas Gerais , Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso . The Federal District with the Brazilian capital Brasília is almost completely enclosed by the Goiás area.
flag
Like the national flag, the green horizontal stripes symbolize the mighty Brazilian forests and the yellow ones stand for the color of gold that was found in Goiás in the 17th century. The blue rectangle at the top left symbolizes the sky with five white stars, which represent the Southern Cross . The flag was introduced on July 30, 1919.
- See also the coat of arms of Goiás
geography
With an area of 340,087 km², Goiás is the smallest of the three states in the Midwest (apart from the Distrito Federal do Brasil ) and is almost as large as Germany (357,112 km²). In a size comparison with all 26 federal states, Goiás is in seventh place with an area share of 3.99%, but only in twelfth place in terms of population. The population density is only 17.7 inhabitants per km².
| The geography of Goiás is largely shaped by the central Brazilian plateau (port .: planalto central ) with its low mountain ranges . It connects to the west of the mountains running along the Atlantic coast (port. Mata Atlântico ). This landscape, heavily weathered by erosion , is relatively low in height compared to the peaks of the low mountain ranges.
Some well-known plateaus are:
|
|
|
The plateau, which extends to the southwest of Goiás in the west adjoining state of Mato Grosso, forms by several low mountain range, the watershed between the Amazon basin in the north and the southern river system Paraná , which via the Río de la Plata between Argentina and Uruguay in the Atlantic flows out. In the east Goiás borders on the third river system, the northeast flowing Rio São Francisco .
In the northwest of Goiás is located Araguaia - lowland with a height of only 300 meters. |
Hydrography
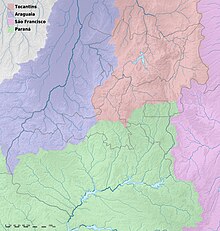
Of the total of twelve hydrographic basins in Brazil, three touch Goiás:
- To the west and north the Tocantins / Araguaia basin
- To the south the Río Paraná basin
- In the east, the Serra Geral de Goiás mountain range, which runs along the border, forms the watershed to the Rio-São Francisco basin. Only the municipality of Cabeceiras drains completely and the southern part of Formosa and the northern part of Cristalina partially drain into the basin of the Rio São Francisco.
| Hydrographic basins | Catchment area (km 2 ) | proportion of |
|---|---|---|
| Tocantins / Araguaia | 196,500.04 | 57.63% |
| Paraná | 141,350.03 | 41.46% |
| Sao Francisco | 3,117.29 | 0.91% |
| Total: | 340,967.36 | 100% |
Flowing waters

The most important rivers and their tributaries within Goiás are:
- Rio Tocantins
-
Rio Paranaíba which, after association with the Rio Grande in Minas Gerais to Parana is
- Rio Meia Ponte
- other right tributaries are: Rio Aporé , Rio dos Bois, Rio São Marcos, Rio Corumbá , Rio Claro, Rio Maranhão.
The southwest border between Mato Grosso do Sul and Goiás is formed by the Rio Aporé (also called Rio do Peixe), which flows south into the Rio Paranaíba. The western border from Goiás to Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso is marked by the northward flowing Rio Araguaia , a left tributary into the Rio Tocantins. The latter flows into the South Atlantic south of the Amazon delta .
Standing waters

Goiás has relatively few and only very small natural lakes for its size. This "shortcoming" was eliminated in the 20th century by building several reservoirs . Some of them are among the largest in the world, depending on their characteristics such as area, storage volume, etc.
| Reservoir |
Length in m |
Height in m |
Area (max.) In km² |
Storage volume (max.) In million m³ |
Depth Ø in m |
Power plant output in MW |
Flowing waters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serra da Mesa reservoir | 1544 | 154 | 1,784 | 54,400 | 30.5 | 1275 | Rio Tocantins |
| Emborcação reservoir | 1611 (1507?) | 158 | 446 | 23.644 | 1192 | Rio Paranaíba | |
| Itumbiara reservoir | 6780 | 106 | 778 | 17,000 | 21.9 | 2082 | Rio Paranaíba |
| Cachoeira Dourada Reservoir | Rio Paranaíba | ||||||
| São Simão Reservoir | 3,600 | 127 | 722 (674?) | 12,700 | 1,710 | Rio Paranaíba | |
| Represa Corumbá I | 90 | 65 | 1.5 | 375 | Rio Corumbá | ||
| Represa Corumbá II | Rio Corumbá | ||||||
| Represa Corumbá III | Rio Corumbá | ||||||
| Represa Corumbá IV | 76 | 173 | 1,242.29 | 127 | Rio Corumbá | ||
| Represa do Halley, in Catalão | |||||||
| Represa do Rochedo | Rio Meia Ponte |
climate
In Goiás, despite its geographical location in the intertropical climate zone, different climatic regions can be identified depending on the altitude and the duration of the dry period in winter.
climate zone
The northernmost point of Goiás is at 12 ° 23 ′ 45 ″ South in the municipality of São Miguel de Araguaia . The southernmost point at 19 ° 29 ′ 55 ″ South is in the municipality of Itajá on the Rio Paranaíba. Goiás is completely north of the Tropic of Capricorn and is therefore within the tropics . The climatic zone in which Goiás is located is called Tropical Brasil Central ("Central Brazilian Tropics") and has two clear seasons: a dry period of several months in winter (May – September) and a humid, rainy summer. Since the dry period is shorter than six months, this climate is commonly referred to as semihumid (semi-humid).
Climate values
| Annual climate values | Area: | |
|---|---|---|
| West and South Goiás | Central and Northeast Goiás | |
| Average min. Temp. | 15-18 ° C | |
| Average max. Temp. | 31-34 ° C | 28-31 ° C |
| avg. Temp. | 24-26 ° C | 22-24 ° C |
| Humidity: | 70-75% | 60-70% |
| Annual sunshine duration : | 2200-2500 hours | 2500–2800 hours |
| Rainfall: | 1500-1800 mm | |
At higher altitudes and / or during the colder months of the year in winter, the temperatures at night can sometimes fall into the single-digit range.
Climate regions in Goiás
The dry season lasts four to five months in Goiás (semi-humid region), with the exception of the area in the southwestern part of Goiás (southwest of Rio Verde), where the dry season only lasts three months (humid region).
| Areas | height | temperature | Duration of the dry season | Annual rainfall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowlands: Most of Northwest Goiás , North Goiás and next to them river valleys such as Meia Ponte , Rio Paranã |
less than 500 m | above 18 ° C (hot port . quente ) |
4–5 months semi-moist |
1500-1800 mm |
|
| Plateau and low mountain range : Anápolis , Federal District and the surrounding area |
500–1700 m | 15-18 ° C ( subquente ) |
|||
| Exception: | |||||
| Southwest of Rio Verde | In the extreme southwest of Goiás ( Caçu , Gouvelândia , Itajá , Itarumã , Lagoa Santa , Paranaiguara , Quirinópolis , São Simão ) and along the river plain of the Rio dos Bois ( Castelândia , Gouvelândia , Inaciolândia , Turvelândia ): | less than 500 m | above 18 ° C ( quente ) |
3 months wet |
|
| ditto, but at an altitude: | over 500 m | 15-18 ° C ( subquente ) |
|||
Flora and fauna


Due to the periodically dry climate, Goiás has a typical savannah vegetation , which in Brazil is called Cerrado and thus forms the Cerrado ecoregion with a very species-rich fauna. New species are still being discovered in Goiás today.
Attempts have recently been made to protect this unique, diverse ecosystem by creating parks and using it by promoting nature-based tourism ( ecotourism ).
National parks
- Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park
- This national park is famous for the diversity of its landscape and the richness of its flora and fauna. In existence since November 1st, 1961, 600 km², near Alto Paraíso de Goiás
- This national park in the mountains of central Brazil was established in 1961 and, together with the Chapada dos Veadeiros, declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2001 . Emas are flightless ratites , similar to the African ostrich (cf. rheas ). In existence since November 1, 1974, 1,318.68 km², near Mineiros .
State protected areas
- since July 3, 1992, 41.23 km², near Goiânia
- Since 1970, 123 km², at Caldas Novas
- 32.5 km²
- 9.01 km², near Pirenópolis
- In São Domingos , since July 7, 1989, 5,000 km². Protected area in the Serra Geral de Goiás , which separates Goiás from Bahia. Waterfalls and caves worth seeing.
Nature reserves ( Portuguese : APA: Área de proteção ambiental ):
- Bacia do Rio Descoberto in DF and GO (1983)
- In Águas Lindas de Goiás and Brazlândia (Distrito Federal) Brazlândia with the reservoir Rio Descoberto DF
- Meandros do Rio Araguaia in Nova Crixás (1998)
- Nature reserve on the Rio Araguaia with some endangered or disappeared animal species. You can see animal species such as: arraus tortoise, sotalia (dolphin) , swamp deer , pampas deer , brown howler monkey , neotropical otter , ocelot , jaguar and even black caiman
- Headwaters of the Rio Vermelho around Goiás Velho (2001)
- Known for rock climbing, mountaineering and caving in the Serra Dourada
structure
Mesoregions
From 1989 to 2017, Goiás was divided into five mesoregions and 18 microregions by the Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics (IBGE) for geostatistical purposes . The mesoregions were:
The 18 geostatistical microregions were formed from the 246 political communities, the municípios , which each have common economic and social conditions.
See also: Mesoregions and Microregions in Goiás
Cities
The twenty largest cities, out of a total of 246 municipalities, with more than 50,000 inhabitants according to the 2010 Census in Goiás in economic comparison:
| city |
Residents |
Area (km²) |
Inhabitant / km² |
GDP 2007 (1,000 R $ ) |
GDP 2007 ranked in GO |
GDP per capita (R $) |
GDP per capita rank in GO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goiânia | 1,301,982 | 739 | 1,761.8 | 17,867,338 | 1 | 14,355 | 33 |
| Aparecida de Goiânia | 455.735 | 288 | 1,582.4 | 3,082,081 | 4th | 6,484 | 171 |
| Anápolis | 335.032 | 918 | 364.9 | 4,681,250 | 2 | 14,380 | 32 |
| Luziânia | 174,546 | 3,962 | 44.1 | 1,628,876 | 7th | 8,309 | 111 |
| Rio Verde | 176.502 | 8,388 | 21.2 | 3,083,919 | 3 | 20,645 | 16 |
| Águas Lindas de Goiás | 159.505 | 191 | 835.1 | 399.113 | 23 | 3,026 | 246 |
| Valparaíso de Goiás | 132,947 | 60 | 2,215.8 | 492,308 | 20th | 4,302 | 233 |
| Trindade | 104.506 | 713 | 146.6 | 580.929 | 17th | 5,959 | 195 |
| Formosa | 100.084 | 5,807 | 17.2 | 561,334 | 19th | 6.222 | 181 |
| Itumbiara | 92,942 | 2,461 | 37.8 | 1,537,323 | 8th | 17,448 | 21st |
| Novo Gama | 95.013 | 192 | 494.9 | 277,530 | 37 | 3,321 | 243 |
| Jataí | 88,048 | 7.174 | 12.3 | 1,329,999 | 9 | 16,225 | 26th |
| Catalão | 86,597 | 3,778 | 22.9 | 2,909,021 | 5 | 38,467 | 6th |
| Planaltina | 81,612 | 2,539 | 32.1 | 293.226 | 33 | 3,839 | 240 |
| Senador Canedo | 84,399 | 245 | 344.5 | 2,036,085 | 6th | 28,856 | 9 |
| Caldas Novas | 70,463 | 159 | 443.2 | 640.609 | 13 | 10,299 | 73 |
| Santo Antonio do Descoberto | 63.166 | 938 | 67.3 | 182,400 | 53 | 3,279 | 245 |
| Goianésia | 59,545 | 1,548 | 38.5 | 578.375 | 18th | 10,749 | 62 |
| Cidade Ocidental | 55,883 | 388 | 144.0 | 175,461 | 57 | 3,611 | 242 |
| Mineiros | 52,964 | 8,896 | 6.0 | 622.824 | 14th | 13,783 | 35 |
| Table total / average: | 3,718,507 | 40,488 | 91.8 | 42,336,551 | n / A | 11,407 | n / A |
| Comparative values from Goiás: | 6.004.045 | 340.087 | 17.6 | 65.210.147 | n / A | 11,548 | n / A |
| Share (deviation): | 61.9% | 11.9% | (+520.2%) | 64.9% | n / A | (−1.2%) | n / A |
What is striking is:
- That in almost half of the largest cities the GDP per capita is among the below average in Goiás. The vast majority of them belong to the worst communities (five communities in the last six places!).
- Five of the ten weakest municipalities are among the largest, which is probably also due to the increasing rural exodus that has been observed in recent years.
- Only two municipalities are in the top ten in terms of GDP per capita
See also:
politics
Ronaldo Caiado of the Democratas (DEM) has been acting governor since the 2018 elections in Brazil . The official seat of the executive branch has been the Palácio das Esmeraldas in Goiânia since 1937 . The legislature rests with 41 elected representatives of the Legislative Assembly of Goiás .
The state is represented by 17 federal representatives in the Chamber of Deputies of the National Congress and sends three senators to the Federal Senate .
economy
In terms of gross domestic product (GDP) , Goiás ranks ninth with a Brazilian share of 2.45%. The GDP per capita is R $ 11,548.
Agriculture
Goiás is an important producer of grain , pulses and oilseeds and is fourth in Brazil after Paraná , Mato Grosso and Rio Grande do Sul . Goiás takes the top spot for tomatoes and sorghum , with garlic it is only behind Minas Gerais , third place goes to cotton and sunflowers , although the cultivation area for the latter was reduced to a third of the previous year. Other important products are sugar cane , soy and corn .
The yield comparison between Goiás and Brazil in the table below shows that the yield in kg / ha in Goiás is predominantly higher than the average yield in Brazil (comparison of the columns yield (kg / ha) with BRA yield (kg / ha) ).
Agricultural production 2009 in Goiás
| Cultivation product |
Harvested area (ha) |
Harvest volume (t) |
Yield (kg / ha) |
BRA share area (%) |
BRA share harvest (%) |
BRA yield (kg / ha) |
Yield comparison (%) |
Rank in BRA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pineapple (in 1,000 pieces) |
2,060 | 49,304 | 23,934 | 3.6 | 3.4 | 25,751 | −7.1 | 8th |
| Bananas | 13,290 | 171,695 | 12,919 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 13,924 | −7.2 | 9 |
| cotton | 54,870 | 227,307 | 4.143 | 6.8 | 7.7 | 3,623 | +14.4 | 3 |
| Beans | 113.930 | 261,929 | 2,299 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 842 | +173.0 | 6th |
| coffee | 8,770 | 18,502 | 2.110 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1,139 | +85.3 | 7th |
| Potatoes | 5,570 | 232.250 | 41,697 | 4.0 | 6.7 | 24,654 | +69.1 | 6th |
| garlic | 1,650 | 21,260 | 12885 | 17.1 | 24.1 | 9,464 | +36.1 | 2 |
| Corn | 898.015 | 4,937,847 | 5,477 | 6.5 | 9.7 | 3,704 | +47.9 | 4th |
| manioc | 21,090 | 331,786 | 15,732 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 14,077 | +11.8 | 20th |
| Oranges | 6,725 | 122,288 | 18,184 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 22.008 | −17.4 | 7th |
| rice | 102,945 | 252,582 | 2,454 | 3.6 | 2.0 | 4,366 | −44.2 | 7th |
| soy | 2,315,890 | 6,808,587 | 2,940 | 10.7 | 11.9 | 2,624 | +12.0 | 4th |
| sunflowers | 4,940 | 6,718 | 1,360 | 6.7 | 7.0 | 1,945 | −30.1 | 3 |
| Sorghum | 302.715 | 758,667 | 2,506 | 38.5 | 41.2 | 2,338 | +7.2 | 1 |
| tomatoes | 18,110 | 1,405,996 | 77,636 | 27.6 | 33.6 | 63,739 | +21.8 | 1 |
| wheat | 22,440 | 84,472 | 3,764 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 2,040 | +84.5 | 6th |
| Sugar cane | 522.985 | 44.064.470 | 84,256 | 6.1 | 6.4 | 79,691 | +5.7 | 4th |
| TOTAL: | 4,411,055 | 8.1 | 9.9 |
Industry
In Goiás u. a. Coal , gravel , phosphate ore, nickel and gold mined.
Important industries are the agrochemicals , food industry , metal processing , furniture and wood processing industry, as well as clothing industry.
Service sector
tourism
Well-known tourist destinations are:
- Until 1937 the former capital of Goiás. In 2001, the historic center with many was baroque buildings from the 18th century in the UNESCO - World Heritage List was added.
- Pirenópolis is a picturesque town in the interior of the Goiás state, famous for its many natural beauties, well-preserved colonial mansions and its steep cobbled streets.
- A nationally popular seaside resort with natural thermal springs .
Popular bathing spots during the dry season (June, July) are:
History and culture
The name of the state of Goiás is derived from the indigenous Goyaz people who originally lived in the area of the Rio Vermelho .
Gold was discovered in the area of Goiás Velho as early as 1592 , but it was not until the second half of the 18th century that the search for the precious metal gained momentum through the discovery of more abundant deposits. In 1748 the Capitania de Goiás was founded and thus separated from São Paulo. In 1824 it was converted into a province. In 1988 the northern part was separated from the national territory and today forms the state of Tocantins .
See also
Web links
- Meyers Konversations-Lexikon, 1888: Volume 7, Page 7.580, Goyaz
- Pierer's Universal Lexicon, Volume 7. Altenburg 1859, p. 518 Goyaz
- Governo do Estado de Goiás website , government website (Brazilian Portuguese)
- ftp://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/mapas_tematicos/fisico/unidades_federacao/go_fisico.pdf IBGE : Map of Goiás, (5 MB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Goiás - Panorama. In: cidades.ibge.gov.br. IBGE , accessed September 3, 2019 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ brasilrepublica.com: Goiás flag , (Portuguese)
- ↑ Superintendência de Geologia e Mineração / Secretaria de Indústria e Comércio Elaboração: SEPLAN-GO / SEPIN / Gerência de Estatística Socioeconômica - 2009 ( Memento of the original of April 17, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked . Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Sociedade Brasileira de Ictiologia: A new species of Hemiancistrus from the rio Araguaia basin , (PDF; 452 kB; English)