Camelopardalis: Difference between revisions
NGC 1501 as an individual object. |
rm categories added by a sockpuppet (hocimi/zingvin/various ip addresses) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 36 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2019}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2019}} |
||
{{Infobox constellation |
{{Infobox constellation |
||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
| genitive = Camelopardalis{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
| genitive = Camelopardalis{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
| pronounce = {{IPAc-en|k|ə|ˌ|m|ɛ|l|ə|ˈ|p|ɑːr|d|əl|ᵻ|s}}, genitive the same |
| pronounce = {{IPAc-en|k|ə|ˌ|m|ɛ|l|ə|ˈ|p|ɑːr|d|əl|ᵻ|s}}, genitive the same |
||
| symbolism = Giraffe{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
| symbolism = [[Giraffe]]{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
| RA = {{RA|03|15|36.2232}}–{{RA|14|27|07.8855}}<ref name=boundary>{{Cite journal | title=Camelopardalis, constellation boundary | |
| RA = {{RA|03|15|36.2232}}–{{RA|14|27|07.8855}}<ref name=boundary>{{Cite journal | title=Camelopardalis, constellation boundary | journal=The Constellations | publisher=[[International Astronomical Union]] | url=https://www.iau.org/public/themes/constellations/#cam | access-date=14 February 2014 | archive-date=4 June 2013 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130604014156/http://www.iau.org/public/constellations/#cam | url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
| dec= {{dec|86.0975418}}–{{dec|52.6655540}}<ref name=boundary/> |
| dec= {{dec|86.0975418}}–{{dec|52.6655540}}<ref name=boundary/> |
||
| family = [[Ursa Major Family|Ursa Major]] |
| family = [[Ursa Major Family|Ursa Major]] |
||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
| month = February |
| month = February |
||
| notes=}} |
| notes=}} |
||
'''Camelopardalis''' {{IPAc-en|k|ə|ˌ|m|ɛ|l|ə|ˈ|p|ɑːr|d|əl|ᵻ|s}} is a large but faint [[constellation]] of the [[celestial sphere|northern sky]] representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by [[Petrus Plancius]].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google. |
'''Camelopardalis''' {{IPAc-en|k|ə|ˌ|m|ɛ|l|ə|ˈ|p|ɑːr|d|əl|ᵻ|s}} is a large but faint [[constellation]] of the [[celestial sphere|northern sky]] representing a [[giraffe]]. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by [[Petrus Plancius]].<ref>{{cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-EJOCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA164 |page=164 |title=Knowledge Encyclopedia Space! |publisher=Dorling Kindersley Ltd |year=2015 |isbn=9780241245347 |access-date=14 September 2020 |archive-date=10 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231110011256/https://books.google.com/books?id=-EJOCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA164 |url-status=live }}</ref>{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} Some older astronomy books give '''Camelopardalus''' or '''Camelopardus''' as alternative forms of the name, but the version recognized by the [[International Astronomical Union]] matches the genitive form, seen suffixed to most of its key stars.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
First attested in English in 1785, the word ''camelopardalis'' comes from [[Latin]],<ref>{{cite web |url |
First attested in English in 1785, the word ''camelopardalis'' comes from [[Latin]],<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0059%3Aentry%3Dcamelopardalis |title=camelopardalis |last1=Lewis |first1=Charlton T. |last2=Short |first2=Charles |work=A Latin Dictionary |publisher=[[Perseus Digital Library]] |access-date=8 June 2012 |archive-date=3 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121003055440/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0059:entry=camelopardalis |url-status=live }}</ref> and it is the [[romanization]] of the [[Greek language|Greek]] "καμηλοπάρδαλις" meaning "giraffe",<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dkamhlopa%2Frdalis |title=καμηλοπάρδαλις |first1=Henry George |last1=Liddell |first2=Robert |last2=Scott |work=A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher=Perseus Digital Library |access-date=8 June 2012 |archive-date=3 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121003055500/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057:entry=kamhlopa%2Frdalis |url-status=live }}</ref> from "κάμηλος" (''kamēlos''), "[[camel]]"<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dka%2Fmhlos |title=κάμηλος |first1=Henry George |last1=Liddell |first2=Robert |last2=Scott |work=A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher=Perseus Digital Library |access-date=8 June 2012 |archive-date=3 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121003055529/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057:entry=ka%2Fmhlos |url-status=live }}</ref> + "πάρδαλις" (''pardalis''), "[[spotted]]",<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dpa%2Frdalis |title=πάρδαλις |first1=Henry George |last1=Liddell |first2=Robert |last2=Scott |work=A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher=Perseus Digital Library |access-date=8 June 2012 |archive-date=3 October 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121003055540/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0057:entry=pa%2Frdalis |url-status=live }}</ref> because it has a long neck like a camel and spots like a leopard. |
||
|first1 = Henry George |last1 = Liddell |first2 = Robert |last2 = Scott |work = A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher = Perseus Digital Library |accessdate =8 June 2012}}</ref> from "κάμηλος" (''kamēlos''), "[[camel]]"<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dka%2Fmhlos |title = κάμηλος |first1 = Henry George |last1 = Liddell |first2 = Robert |last2 = Scott |work = A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher = Perseus Digital Library |accessdate =8 June 2012}}</ref> + "πάρδαλις" (''pardalis''), "[[leopard]]",<ref>{{cite web |url = http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Dpa%2Frdalis |title = πάρδαλις |first1 = Henry George |last1 = Liddell |first2 = Robert |last2 = Scott |work = A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher = Perseus Digital Library |accessdate =8 June 2012}}</ref> because it has a long neck like a camel and spots like a leopard. |
|||
==Features== |
==Features== |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
{{See also|List of stars in Camelopardalis}} |
{{See also|List of stars in Camelopardalis}} |
||
Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. In fact, it only contains four stars |
Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. In fact, it only contains four stars brighter than magnitude 5.0.{{sfn|Staal|1988|p=241}} |
||
*[[Alpha Camelopardalis|α Cam]] is a blue-hued supergiant star of magnitude 4.3, |
*[[Alpha Camelopardalis|α Cam]] is a blue-hued supergiant star of magnitude 4.3, over 6,000 light-years from Earth. It is one of the most distant stars easily visible with the naked eye.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
*[[Beta Camelopardalis|β Cam]] is the brightest star in Camelopardalis with an [[apparent magnitude]] of 4.03. This star is a [[double star]], with components of magnitudes 4.0{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} and 8.6. The primary is a yellow-hued supergiant 1000 light-years from Earth.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
*[[Beta Camelopardalis|β Cam]] is the brightest star in Camelopardalis with an [[apparent magnitude]] of 4.03. This star is a [[double star]], with components of magnitudes 4.0{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} and 8.6. The primary is a yellow-hued supergiant 1000 light-years from Earth.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
*[[11 Camelopardalis|11 Cam]] is a star of magnitude 5.2, 650 light-years from Earth. It |
*[[11 Camelopardalis|11 Cam]] is a star of magnitude 5.2, 650 light-years from Earth. It appears without intense magnification very close to magnitude 6.1 [[12 Camelopardalis|12 Cam]], at about the same distance from us, but the two are not a true double star; they have considerable separation.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
*[[Struve 1694|Σ 1694]] (Struve 1694, 32 Cam) is a [[binary star]] 300 light-years from Earth. Both components have a blue-white hue; the primary is of magnitude 5.4 and the secondary is of magnitude 5.9.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
*[[Struve 1694|Σ 1694]] (Struve 1694, 32 Cam) is a [[binary star]] 300 light-years from Earth. Both components have a blue-white hue; the primary is of magnitude 5.4 and the secondary is of magnitude 5.9.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
*[[CS Camelopardalis|CS Cam]] is the second brightest star, though it has neither a [[Bayer designation|Bayer]] nor a [[Flamsteed designation]]. It is of magnitude 4.21 and is slightly [[variable star|variable]].{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} |
*[[CS Camelopardalis|CS Cam]] is the second brightest star, though it has neither a [[Bayer designation|Bayer]] nor a [[Flamsteed designation]]. It is of magnitude 4.21 and is slightly [[variable star|variable]].{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} |
||
*[[Z Camelopardalis|Z Cam]] is frequently observed as part of a program of [[AAVSO]].<ref> |
*[[Z Camelopardalis|Z Cam]] (varying from amateur telescope visibility to extremely faint) is frequently observed as part of a program of [[AAVSO]].<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.aavso.org/vsots_zcam| title=American Association of Variable Star Observers| access-date=28 January 2015| archive-date=10 September 2012| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120910113103/http://www.aavso.org/vsots_zcam| url-status=live}}</ref> It is the prototype of [[Z Camelopardalis variable stars]]. |
||
Other variable stars are [[U Camelopardalis]], [[VZ Camelopardalis]], and [[Mira variable]]s [[T Camelopardalis]], [[X Camelopardalis]], and [[R Camelopardalis]].{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} [[RU Camelopardalis]] is one of the brighter [[Type II Cepheid]]s visible in the night sky. |
Other variable stars are [[U Camelopardalis]], [[VZ Camelopardalis]], and [[Mira variable]]s [[T Camelopardalis]], [[X Camelopardalis]], and [[R Camelopardalis]].{{sfn|Norton|1973|pp=118–119}} [[RU Camelopardalis]] is one of the brighter [[Type II Cepheid]]s visible in the night sky. |
||
In 2011 a supernova was discovered in the constellation.<ref>{{cite journal |url |
In 2011 a supernova was discovered in the constellation.<ref>{{cite journal |url=http://www.popsci.com/science/article/2011-01/10-year-old-canadian-girl-youngest-discover-supernova |title=10-Year-Old Canadian Girl Is The Youngest Person Ever to Discover a Supernova |last=Boyle |first=Rebecca |access-date=8 June 2012 |journal=Popular Science |date=3 January 2011 |archive-date=18 March 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200318051635/https://www.popsci.com/science/article/2011-01/10-year-old-canadian-girl-youngest-discover-supernova/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
===Deep-sky objects=== |
===Deep-sky objects=== |
||
Camelopardalis is in the part of the celestial sphere facing away from the [[galactic plane]]. Accordingly, many distant galaxies are visible within its borders. |
Camelopardalis is in the part of the celestial sphere facing away from the [[galactic plane]]. Accordingly, many distant galaxies are visible within its borders. |
||
* [[NGC 2403]] is a galaxy in the [[M81 group]] of galaxies, located approximately 12 million light-years from Earth{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}}{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} with a redshift of 0.00043. It is classified as being between an [[elliptical galaxy|elliptical]] and a [[spiral galaxy]] because it has faint arms and a large central bulge. NGC 2403 was first discovered by the 18th century astronomer [[William Herschel]], who was working in England at the time.{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}} It has an [[integrated magnitude]] of 8.0 and is approximately 0.25° long.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
* [[NGC 2403]] is a galaxy in the [[M81 group]] of galaxies, located approximately 12 million light-years from Earth{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}}{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} with a redshift of 0.00043. It is classified as being between an [[elliptical galaxy|elliptical]] and a [[spiral galaxy]] because it has faint arms and a large central bulge. NGC 2403 was first discovered by the 18th century astronomer [[William Herschel]], who was working in England at the time.{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}} It has an [[integrated magnitude]] of 8.0 and is approximately 0.25° long.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} |
||
* [[NGC 1502]] is a magnitude 6.9 [[open cluster]] about 3,000 [[light year]]s from Earth. It has about 45 bright members, and features a double star of magnitude 7.0 at its center.<ref>Revised NGC/IC Data 2013. Dr. Wolfgang Steinicke.</ref> NGC 1502 is also associated with [[Kemble's Cascade]], a simple but beautiful asterism appearing in the sky as a chain of stars 2.5° long that is parallel to the Milky Way and is pointed towards [[Cassiopeia (constellation)|Cassiopeia]].{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} * [[NGC 1501]] is a planetary nebula located roughly 1.4° south of NGC 1502. |
* [[NGC 1502]] is a magnitude 6.9 [[open cluster]] about 3,000 [[light year]]s from Earth. It has about 45 bright members, and features also a double star of magnitude 7.0 at its center.<ref>Revised NGC/IC Data 2013. Dr. Wolfgang Steinicke.</ref> NGC 1502 is also associated with [[Kemble's Cascade]], a simple but beautiful asterism appearing in the sky as a chain of stars 2.5° long that is parallel to the Milky Way and is pointed towards [[Cassiopeia (constellation)|Cassiopeia]].{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} * [[NGC 1501]] is a planetary nebula located roughly 1.4° south of NGC 1502. |
||
* Stock 23 is an open star cluster at the southern part of the border between Camelopardalis and Cassiopeia. It is also known as ''Pazmino's Cluster''. It could be categorized as an ''asterism'' because of the small number of stars in it (a small telescopic ''constellation''). |
* Stock 23 is an open star cluster at the southern part of the border between Camelopardalis and Cassiopeia. It is also known as ''Pazmino's Cluster''. It could be categorized as an ''asterism'' because of the small number of stars in it (a small telescopic ''constellation''). |
||
* [[IC 342]] is one of the brightest two galaxies in the [[IC 342/Maffei Group]] of galaxies. |
* [[IC 342]] is one of the brightest two galaxies in the [[IC 342/Maffei Group]] of galaxies. |
||
* The dwarf irregular galaxy [[NGC 1569]] is a magnitude 11.9 [[starburst galaxy]], about 11 million light years away. |
* The dwarf irregular galaxy [[NGC 1569]] is a magnitude 11.9 [[starburst galaxy]], about 11 million light years away. |
||
* [[NGC 2655]] is a large [[lenticular galaxy]] with visual magnitude 10.1. |
* [[NGC 2655]] is a large [[lenticular galaxy]] with visual magnitude 10.1. |
||
* UGC 3697 is known as the ''Integral Sign Galaxy'' (its location is 7:11:4 / +71°50'). |
|||
* [[MS0735.6+7421]] is a galaxy cluster with a [[redshift]] of 0.216, located 2.6 billion light-years from Earth. It is unique for its [[intracluster medium]], which emits [[X-ray]]s at a very high rate. This galaxy cluster features two cavities 600,000 light-years in diameter, caused by its central [[supermassive black hole]], which emits jets of matter. MS0735.6+7421 is one of the largest and most distant examples of this phenomenon.{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}} |
* [[MS0735.6+7421]] is a galaxy cluster with a [[redshift]] of 0.216, located 2.6 billion light-years from Earth. It is unique for its [[intracluster medium]], which emits [[X-ray]]s at a very high rate. This galaxy cluster features two cavities 600,000 light-years in diameter, caused by its central [[supermassive black hole]], which emits jets of matter. MS0735.6+7421 is one of the largest and most distant examples of this phenomenon.{{sfn|Wilkins|Dunn|2006}} |
||
* Tombaugh 5 is a fairly dim open cluster in Camelopardalis. It has an overall magnitude of 8.4 and is located 5,800 light-years from Earth. It is a Shapley class c and Trumpler class III 1 r cluster, meaning that it is irregularly shaped and appears loose. Though it is detached from the star field, it is not concentrated at its center at all. It has more than 100 stars which do not vary widely in brightness,{{sfn|Levy|2005|p=89}} mostly being of the 15th and 16th magnitude.{{sfn|Levy|2005|p=91}} |
* Tombaugh 5 is a fairly dim open cluster in Camelopardalis. It has an overall magnitude of 8.4 and is located 5,800 light-years from Earth. It is a Shapley class c and Trumpler class III 1 r cluster, meaning that it is irregularly shaped and appears loose. Though it is detached from the star field, it is not concentrated at its center at all. It has more than 100 stars which do not vary widely in brightness,{{sfn|Levy|2005|p=89}} mostly being of the 15th and 16th magnitude.{{sfn|Levy|2005|p=91}} |
||
| Line 69: | Line 70: | ||
<!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before you save your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. It is always best to anchor an old section header that has been changed so that links to it won't be broken. See [[Template:Anchor]] for details. (This text: [[Template:Anchor comment]]) --> |
<!-- This Anchor tag serves to provide a permanent target for incoming section links. Please do not move it out of the section heading, even though it disrupts edit summary generation (you can manually fix the edit summary before you save your changes). Please do not modify it, even if you modify the section title. It is always best to anchor an old section header that has been changed so that links to it won't be broken. See [[Template:Anchor]] for details. (This text: [[Template:Anchor comment]]) --> |
||
The annual May meteor shower Camelopardalids from comet [[209P/LINEAR]] have a [[Radiant (meteor shower)|radiant]] in Camelopardalis. |
The annual May meteor shower Camelopardalids from comet [[209P/LINEAR]] have a [[Radiant (meteor shower)|radiant]] in Camelopardalis. |
||
=== Space exploration === |
|||
The [[space probe]] ''[[Voyager 1]]'' is moving in the direction of this constellation, though it will not be nearing any of the stars in this constellation for many thousands of years, by which time its power source will be long dead. |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
[[Image:Sidney Hall - Urania's Mirror - Camelopardalis, Tarandus and Custos Messium.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Camelopardalis as depicted in ''[[Urania's Mirror]]'', a set of constellation cards published in London c.1823. Above it are shown the now-abandoned constellations of [[Tarandus (constellation)|Tarandus]] and [[Custos Messium]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nms.ac.uk/explore-our-collections/collection-search-results/?item_id=218603 |title=The constellations Camelopardalis, Tarandus and Custos Messium | |
[[Image:Sidney Hall - Urania's Mirror - Camelopardalis, Tarandus and Custos Messium.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Camelopardalis as depicted in ''[[Urania's Mirror]]'', a set of constellation cards published in London c.1823. Above it are shown the now-abandoned constellations of [[Tarandus (constellation)|Tarandus]] and [[Custos Messium]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nms.ac.uk/explore-our-collections/collection-search-results/?item_id=218603 |title=The constellations Camelopardalis, Tarandus and Custos Messium |publisher=National Museums Scotland |access-date=25 November 2018 |archive-date=25 November 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181125204423/https://www.nms.ac.uk/explore-our-collections/collection-search-results/?item_id=218603 |url-status=live }}</ref>]] |
||
Camelopardalis is not one of [[Ptolemy]]'s 48 constellations in the ''[[Almagest]]''.<ref name="ley196312">{{Cite magazine |
Camelopardalis is not one of [[Ptolemy]]'s 48 constellations in the ''[[Almagest]]''.<ref name="ley196312">{{Cite magazine |
||
| Line 87: | Line 86: | ||
}}</ref> It was created by Petrus Plancius in 1613.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} It first appeared in a globe designed by him and produced by [[Pieter van den Keere]]. One year later, [[Jakob Bartsch]] featured it in his atlas. [[Johannes Hevelius]] depicted this constellation in his works which were so influential that it was referred to as Camelopardali Hevelii or abbreviated as Camelopard. Hevel. |
}}</ref> It was created by Petrus Plancius in 1613.{{sfn|Ridpath|2001|pp=92–93}} It first appeared in a globe designed by him and produced by [[Pieter van den Keere]]. One year later, [[Jakob Bartsch]] featured it in his atlas. [[Johannes Hevelius]] depicted this constellation in his works which were so influential that it was referred to as Camelopardali Hevelii or abbreviated as Camelopard. Hevel. |
||
Part of the constellation was hived off to form the constellation Sciurus Volans, the Flying Squirrel, by William Croswell in 1810. However this was not taken up by later cartographers.<ref>{{cite book | first=Nick | last=Kanas | date=2007 | title=Star maps: history, artistry, and cartography | page=131 |url=https://books.google.com |
Part of the constellation was hived off to form the constellation Sciurus Volans, the Flying Squirrel, by William Croswell in 1810. However this was not taken up by later cartographers.<ref>{{cite book | first=Nick | last=Kanas | date=2007 | title=Star maps: history, artistry, and cartography | page=131 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bae3LP4tfP4C&pg=PA131 | publisher=Springer | location=New York City | isbn=978-0-387-71668-8 | access-date=14 September 2020 | archive-date=10 November 2023 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231110011257/https://books.google.com/books?id=bae3LP4tfP4C&pg=PA131#v=onepage&q&f=false | url-status=live }}</ref> |
||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
| Line 101: | Line 100: | ||
;References |
;References |
||
{{ |
{{Refbegin}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |title=Deep Sky Objects |last=Levy |first=David H. |publisher=Prometheus Books |year=2005 |isbn=1-59102-361-0 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/deepskyobjects00davi }} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |last=Norton |first=Arthur P. |title=Norton's Star Atlas |year=1973 |pages=[https://archive.org/details/nortonsstaratlas0000nort/page/118 118–119] |isbn=0-85248-900-5 |url=https://archive.org/details/nortonsstaratlas0000nort/page/118 }} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |first=H. A. |last=Rey |title=The Stars—A New Way To See Them |publisher=Houghton Mifflin |year=1997 |isbn=0-395-24830-2 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/stars00hare }} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |first=Ian |last=Ridpath |year=2001 |title=Stars and Planets Guide |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=0-691-08913-2}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |first=Ian |last=Ridpath |others=Wil Tirion |year=2007 |title=Stars and Planets Guide |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-13556-4 |edition=4th}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |first=Julius D.W. |last=Staal |title=The New Patterns in the Sky |year=1988 |publisher=McDonald and Woodward Publishing Company |isbn=0-939923-04-1}} |
||
* {{ |
* {{cite book |title=300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe |last1=Wilkins |first1=Jamie |last2=Dunn |first2=Robert |publisher=Firefly Books |year=2006 |edition=1st |isbn=978-1-55407-175-3}} |
||
{{ |
{{Refend}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{Wiktionary}} |
||
{{Commons |
{{Commons and category|Camelopardalis|Camelopardalis}} |
||
* [http://www.allthesky.com/constellations/camelopardalis/ The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Camelopardalis] |
* [http://www.allthesky.com/constellations/camelopardalis/ The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Camelopardalis] |
||
* [http://www.ianridpath.com/startales/camelopardalis. |
* [http://www.ianridpath.com/startales/camelopardalis.html Star Tales – Camelopardalis] |
||
* [ |
* [https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/interstellar-mission/ NASA – Voyager Interstellar Mission Characteristics] |
||
{{Stars of Camelopardalis}} |
{{Stars of Camelopardalis}} |
||
{{ |
{{Constellations}} |
||
{{Portal bar|Astronomy|Stars|Spaceflight|Outer space|Solar System}} |
|||
{{Dutch constellations}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{Sky|06|00|00|+|70|00|00|10}} |
{{Sky|06|00|00|+|70|00|00|10}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Camelopardalis, Constellation}} |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Camelopardalis| ]] |
||
[[Category:Northern constellations]] |
[[Category:Northern constellations]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Constellations listed by Petrus Plancius]] |
||
Latest revision as of 21:05, 30 April 2024
| Constellation | |
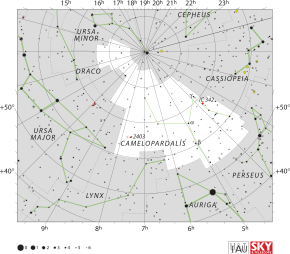 | |
| Abbreviation | Cam[1] |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Camelopardalis[1] |
| Pronunciation | /kəˌmɛləˈpɑːrdəlɪs/, genitive the same |
| Symbolism | Giraffe[1] |
| Right ascension | 03h 15m 36.2232s–14h 27m 07.8855s[2] |
| Declination | 86.0975418°–52.6655540°[2] |
| Area | 757 sq. deg. (18th) |
| Main stars | 2, 8 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 36 |
| Stars with planets | 4 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 0 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 3 |
| Brightest star | β Cam (4.03m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | October Camelopardalids |
| Bordering constellations | Draco Ursa Minor Cepheus Cassiopeia Perseus Auriga Lynx Ursa Major |
| Visible at latitudes between +90° and −10°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of February. | |
Camelopardalis /kəˌmɛləˈpɑːrdəlɪs/ is a large but faint constellation of the northern sky representing a giraffe. The constellation was introduced in 1612 or 1613 by Petrus Plancius.[3][1] Some older astronomy books give Camelopardalus or Camelopardus as alternative forms of the name, but the version recognized by the International Astronomical Union matches the genitive form, seen suffixed to most of its key stars.[1]
Etymology[edit]
First attested in English in 1785, the word camelopardalis comes from Latin,[4] and it is the romanization of the Greek "καμηλοπάρδαλις" meaning "giraffe",[5] from "κάμηλος" (kamēlos), "camel"[6] + "πάρδαλις" (pardalis), "spotted",[7] because it has a long neck like a camel and spots like a leopard.
Features[edit]

Stars[edit]
Although Camelopardalis is the 18th largest constellation, it is not a particularly bright constellation, as the brightest stars are only of fourth magnitude. In fact, it only contains four stars brighter than magnitude 5.0.[8]
- α Cam is a blue-hued supergiant star of magnitude 4.3, over 6,000 light-years from Earth. It is one of the most distant stars easily visible with the naked eye.[1]
- β Cam is the brightest star in Camelopardalis with an apparent magnitude of 4.03. This star is a double star, with components of magnitudes 4.0[9] and 8.6. The primary is a yellow-hued supergiant 1000 light-years from Earth.[1]
- 11 Cam is a star of magnitude 5.2, 650 light-years from Earth. It appears without intense magnification very close to magnitude 6.1 12 Cam, at about the same distance from us, but the two are not a true double star; they have considerable separation.[1]
- Σ 1694 (Struve 1694, 32 Cam) is a binary star 300 light-years from Earth. Both components have a blue-white hue; the primary is of magnitude 5.4 and the secondary is of magnitude 5.9.[1]
- CS Cam is the second brightest star, though it has neither a Bayer nor a Flamsteed designation. It is of magnitude 4.21 and is slightly variable.[9]
- Z Cam (varying from amateur telescope visibility to extremely faint) is frequently observed as part of a program of AAVSO.[10] It is the prototype of Z Camelopardalis variable stars.
Other variable stars are U Camelopardalis, VZ Camelopardalis, and Mira variables T Camelopardalis, X Camelopardalis, and R Camelopardalis.[9] RU Camelopardalis is one of the brighter Type II Cepheids visible in the night sky.
In 2011 a supernova was discovered in the constellation.[11]
Deep-sky objects[edit]
Camelopardalis is in the part of the celestial sphere facing away from the galactic plane. Accordingly, many distant galaxies are visible within its borders.
- NGC 2403 is a galaxy in the M81 group of galaxies, located approximately 12 million light-years from Earth[12][1] with a redshift of 0.00043. It is classified as being between an elliptical and a spiral galaxy because it has faint arms and a large central bulge. NGC 2403 was first discovered by the 18th century astronomer William Herschel, who was working in England at the time.[12] It has an integrated magnitude of 8.0 and is approximately 0.25° long.[1]
- NGC 1502 is a magnitude 6.9 open cluster about 3,000 light years from Earth. It has about 45 bright members, and features also a double star of magnitude 7.0 at its center.[13] NGC 1502 is also associated with Kemble's Cascade, a simple but beautiful asterism appearing in the sky as a chain of stars 2.5° long that is parallel to the Milky Way and is pointed towards Cassiopeia.[1] * NGC 1501 is a planetary nebula located roughly 1.4° south of NGC 1502.
- Stock 23 is an open star cluster at the southern part of the border between Camelopardalis and Cassiopeia. It is also known as Pazmino's Cluster. It could be categorized as an asterism because of the small number of stars in it (a small telescopic constellation).
- IC 342 is one of the brightest two galaxies in the IC 342/Maffei Group of galaxies.
- The dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 1569 is a magnitude 11.9 starburst galaxy, about 11 million light years away.
- NGC 2655 is a large lenticular galaxy with visual magnitude 10.1.
- UGC 3697 is known as the Integral Sign Galaxy (its location is 7:11:4 / +71°50').
- MS0735.6+7421 is a galaxy cluster with a redshift of 0.216, located 2.6 billion light-years from Earth. It is unique for its intracluster medium, which emits X-rays at a very high rate. This galaxy cluster features two cavities 600,000 light-years in diameter, caused by its central supermassive black hole, which emits jets of matter. MS0735.6+7421 is one of the largest and most distant examples of this phenomenon.[12]
- Tombaugh 5 is a fairly dim open cluster in Camelopardalis. It has an overall magnitude of 8.4 and is located 5,800 light-years from Earth. It is a Shapley class c and Trumpler class III 1 r cluster, meaning that it is irregularly shaped and appears loose. Though it is detached from the star field, it is not concentrated at its center at all. It has more than 100 stars which do not vary widely in brightness,[14] mostly being of the 15th and 16th magnitude.[15]
- NGC 2146 is an 11th magnitude barred spiral starburst galaxy conspicuously warped by interaction with a neighbour.
- MACS0647-JD, one of the possible candidates for the farthest known galaxies in the universe (z= 10.7), is also in Camelopardalis.
Meteor showers[edit]
The annual May meteor shower Camelopardalids from comet 209P/LINEAR have a radiant in Camelopardalis.
History[edit]

Camelopardalis is not one of Ptolemy's 48 constellations in the Almagest.[17] It was created by Petrus Plancius in 1613.[1] It first appeared in a globe designed by him and produced by Pieter van den Keere. One year later, Jakob Bartsch featured it in his atlas. Johannes Hevelius depicted this constellation in his works which were so influential that it was referred to as Camelopardali Hevelii or abbreviated as Camelopard. Hevel.
Part of the constellation was hived off to form the constellation Sciurus Volans, the Flying Squirrel, by William Croswell in 1810. However this was not taken up by later cartographers.[18]
Equivalents[edit]
In Chinese astronomy, the stars of Camelopardalis are located within a group of circumpolar stars called the Purple Forbidden Enclosure (紫微垣 Zǐ Wēi Yuán).
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- Citations
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Ridpath 2001, pp. 92–93.
- ^ a b "Camelopardalis, constellation boundary". The Constellations. International Astronomical Union. Archived from the original on 4 June 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Knowledge Encyclopedia Space!. Dorling Kindersley Ltd. 2015. p. 164. ISBN 9780241245347. Archived from the original on 10 November 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- ^ Lewis, Charlton T.; Short, Charles. "camelopardalis". A Latin Dictionary. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert. "καμηλοπάρδαλις". A Greek-English Lexicon. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert. "κάμηλος". A Greek-English Lexicon. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert. "πάρδαλις". A Greek-English Lexicon. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on 3 October 2012. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Staal 1988, p. 241.
- ^ a b c Norton 1973, pp. 118–119.
- ^ "American Association of Variable Star Observers". Archived from the original on 10 September 2012. Retrieved 28 January 2015.
- ^ Boyle, Rebecca (3 January 2011). "10-Year-Old Canadian Girl Is The Youngest Person Ever to Discover a Supernova". Popular Science. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ a b c Wilkins & Dunn 2006.
- ^ Revised NGC/IC Data 2013. Dr. Wolfgang Steinicke.
- ^ Levy 2005, p. 89.
- ^ Levy 2005, p. 91.
- ^ "The constellations Camelopardalis, Tarandus and Custos Messium". National Museums Scotland. Archived from the original on 25 November 2018. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
- ^ Ley, Willy (December 1963). "The Names of the Constellations". For Your Information. Galaxy Science Fiction. pp. 90–99.
- ^ Kanas, Nick (2007). Star maps: history, artistry, and cartography. New York City: Springer. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-387-71668-8. Archived from the original on 10 November 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- References
- Levy, David H. (2005). Deep Sky Objects. Prometheus Books. ISBN 1-59102-361-0.
- Norton, Arthur P. (1973). Norton's Star Atlas. pp. 118–119. ISBN 0-85248-900-5.
- Rey, H. A. (1997). The Stars—A New Way To See Them. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0-395-24830-2.
- Ridpath, Ian (2001). Stars and Planets Guide. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-08913-2.
- Ridpath, Ian (2007). Stars and Planets Guide. Wil Tirion (4th ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13556-4.
- Staal, Julius D.W. (1988). The New Patterns in the Sky. McDonald and Woodward Publishing Company. ISBN 0-939923-04-1.
- Wilkins, Jamie; Dunn, Robert (2006). 300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe (1st ed.). Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1-55407-175-3.
