1,3-diamino-2-propanol
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,3-diamino-2-propanol | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 10 N 2 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to pale yellow solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 90.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | |||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point | |||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
1,3-Diamino-2-propanol is the simplest amino alcohol with two primary amino groups and one secondary alcohol group . Aqueous solutions of diamine have an alkaline reaction and absorb similarly to solutions of e.g. B. Diethanolamine in amine scrubbers very efficiently acidic gases such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from industrial exhaust gases.
Extraction and presentation
Already in 1873 A. Claus received indications of the formation of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol (in addition to higher condensation products) from the reaction of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol with ammonia .
An early standard specification describes the conversion of 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol (from glycerol and hydrogen chloride ) with excess ammonia at 30 ° C. in the presence of sodium hydroxide as an acid scavenger to give 1,3-diamino-2-propanol
The yields in this synthesis route are below 40%.
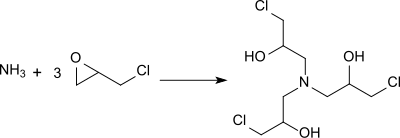
The reaction of epichlorohydrin, which is much cheaper than 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol, with ammonia in a large excess (> 20-fold) at 30 ° C and subsequent heating mainly leads to the formation of more highly condensed amines and provides only approx. 15% 1,3-diamino-2-propanol.
In a two-stage process, epichlorohydrin reacts with a 30-50-fold excess of ammonia at 10 ° C, initially opening the oxirane ring . Then an amount of sodium hydroxide solution equimolar to the epichlorohydrin is added at 10-20 ° C. After removing the excess ammonia and filtering off the precipitated NaCl, the crude diamine is obtained in about 80% yield, which still contains 15-20% higher amines. After vacuum distillation, 64% pure 1,3-diamino-2-propanol are obtained.
A more recent process variant uses a strongly alkaline anion exchanger to bind the hydrogen chloride formed and avoid the separation of sodium chloride as in the Enders variant, with reproducible yields of 52-55% being achieved.
The isomeric 2,3-diamino-1-propanol is not formed. The attempt to convert 2,3-dibromo-1-propanol with phthalimide potassium in a Gabriel synthesis to diphthalimide and its subsequent cleavage with 48% hydrobromic acid also provides indications of the comparatively higher stability of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol to 2,3-diamino-1-propanol, in which, however, 1,3-diamino-2-propanol is formed - probably via an epoxide formed as an intermediate.
The preparation of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol requires the addition of epichlorohydrin and a very high excess of ammonia at temperatures below 30 ° C. in order to suppress the formation of by-products, mostly oligomeric condensation products. With a 1: 3 ratio of ammonia to epichlorohydrin in methanol, N , N , N -Tris (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) amine is formed
or in the reaction of equimolar amounts at 70-75 ° C highly branched polymers, which can be used in papermaking.
properties
1,3-Diamino-2-propanol is a white solid with an amine-like odor that is very soluble in water and readily soluble in alcohols.
use
In a Strecker synthesis with hydrocyanic acid and formaldehyde and subsequent hydrolysis of the resulting tetranitrile, the complexing agent 1,3-diamino-2-propanol-N, N, N ', N'-tetraacetic acid can be obtained, the chelate complexes of which with divalent cations have significantly lower stabilities than those with the EDTA standard
The reaction of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol with paraformaldehyde produces the six-membered saturated heterocycle 5-hydroxy-1,3-diazacyclohexane, a water-soluble hygroscopic solid, in 88% yield .
which reacts with 100% nitric acid and phosphorus pentoxide in 80% yield to form 1,3-dinitro-5-nitrato-1,3-diazacyclohexane, a potential explosive .
The reaction of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol with long-chain carboxylic acid chlorides gives N, N'-diacyl-1,3-diamino-2-propanols. These represent amide isosteres of 1,3-diacylglycerol, the synthesis precursor for membrane lipids .
The poor solubility of diacylamido-2-propanols in practically all solvents and the not very reactive secondary alcohol group force alternative routes for conversion into the reactive phosphorus dichloridate, the intermediate stage for 1,3-diamidophospholipids as analogues to natural membrane lipids such as e.g. B. Lecithins .
The artificial 1,3-diamidophospholipids obtained in this way form liposomes which - in contrast to liposomes from natural and other artificial phospholipids - do not activate the complement system and could therefore be used as drug carriers .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1,3-diamino-2-propanol from AlfaAesar, accessed on March 24, 2016 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c data sheet 1,3-diamino-2-propanol from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 24, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Entry on 1,3-diamino-2-propanol at TCI Europe, accessed on March 24, 2016.
- ↑ a b Patent EP0359956A2 : Process and device for the production of 1,3-diaminopropanol-2. Registered on August 3, 1989 , published on March 28, 1990 , applicant: Deutsche Solvay-Werke GmbH, inventor: G. Jakobson, M. Klumpe.
- ↑ a b c d Patent US1985885 : Preparation of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol. Applied on November 23, 1931 , published January 1, 1935 , Applicant: The Girdler Corp., Inventor: RR Bottoms.
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition . CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA 2015, ISBN 978-1-4822-6097-7 , pp. 3-146 .
- ↑ A. Claus: III. Effect of ammonia on dichlorohydrin . In: Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. Band 168 , no. 1 , 1873, p. 29-41 , doi : 10.1002 / jlac.18731680104 .
- ↑ JB Conant, OR Quayle: Glycerol, α, γ-dichlorohydrin In: Organic Syntheses . 2, 1922, p. 29, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.002.0029 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 292 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Patent US3432553 : Process for manufacturing 1,3-diaminopropanol- (2). Registered on September 28, 1966 , published on March 11, 1969 , applicant: Chemische Fabrik Pfersee GmbH, inventor: H. Enders, G. Pusch.
- ↑ Patent US2864775 : Process for curing polyepoxides by amine adducts and resulting products. Applied on September 20, 1955 , published December 16, 1958 , applicant: Shell Development Co., inventor: HA Newey.
- ↑ MS Okamoto, EK Barefield: Synthesis and stereochemistry of cobalt (III) complexes of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol and related ligands . In: Inorg. Chem. Band 13 , no. 11 , 1974, p. 2611-2617 , doi : 10.1021 / ic50141a016 .
- ↑ JB McKelvey, BG Webre, RR Benerito: Reaction of epichlorohydrin with ammonia, aniline, and diethanolamine . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 25 , no. 8 , 1960, pp. 1424-142 , doi : 10.1021 / jo01078a035 .
- ↑ Patent US7431799B2 : Epichlorohydrin-based polymers containing primary amino groups used as additives in papermaking. Applied on February 23, 2005 , published on October 7, 2008 , Applicant: FPInnovations, Inventor: M. Antal, II Pikulik, X. Hua.
- ↑ V. Jokl, J. Majer: Investigation of complex compounds in solution using paper electrophoresis. IV. Complexes of 1,3-diamino-2-propanol-N, N, N ', N'-tetraacetic acid . In: Chem. Pap. Volume 19 , no. 4 , 1965, pp. 249-258 ( chempap.org ).
- ↑ T. Axenrod, J. Sun, KK Das, PR Dave, F. Forohar, M. Kaselj, NJ Trivedi, RD Gilardi, JL Flippen-Anderson: Synthesis and Characterization of 5-substituted-1,3-diazacyclohexane derivatives . In: J. Org. Chem. Band 65 , no. 4 , 2000, pp. 1200-1206 , doi : 10.1021 / jo991524o .
- ↑ F. Mergen, DM Lambert, JH Poupaert, A. Bidaine, P. Dumont: Synthesis of 1,3-diacylaminopropan-2-ols and corresponding 2-acyl derivatives as amide isosteres of natural lipids . In: Chem. Phys. Lipids . tape 59 , no. 3 , 1991, pp. 267-272 , doi : 10.1016 / 0009-3084 (91) 90027-9 .
- ↑ P.-L. Zaffalon, V. D'Anna, H. Hagemann, A. Zumbuehl: Study of surfactants alcohols with various chemical moieties at the hydrophilic-hydrophobic interface . In: RSC Advances . tape 3 , 2013, p. 7237-7244 , doi : 10.1039 / c3ra40704g .
- ↑ IA Fedotenko, P.-L. Zaffalon, F. Favarger, A. Zumbuehl: The synthesis of 1,3-diamidophospholipids . In: Tetrahedron Lett. tape 51 , 2010, p. 5382-5384 , doi : 10.1016 / j.tetlet.2010.07.140 .
- ↑ S. Bugna et al .: Surprising lack of liposome-induced complement acivation by artificial 1,3-diamidophospholipids in vitro . In: Nanomedicine . tape 12 , no. 3 , 2016, p. 845-849 , doi : 10.1016 / j.nano.2015.12.364 .