2-fluoroethanol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
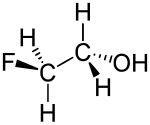
|
||||||||||||||||
| Wedges to clarify the spatial structure | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 2-fluoroethanol | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Ethylene fluorohydrin |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 5 FO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
volatile, colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 64.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.1040 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−26.3 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
103.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
28.3 mbar (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
14.42 |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3647 (18 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
1 (based on 100 years) |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
2-Fluoroethanol is a chemical compound from the group of substituted alcohols and organic fluorine compounds.
history
In search of new pesticides, the systematic research into fluorocarbon compounds began in Germany in 1934 by Gerhard Schrader ( IG-Farben ), which revealed a high level of toxicity on humans and livestock. The reason for terminating the research may include a. in the discovery of organophosphorus compounds, which can be used as even more toxic chemical warfare agents due to minor modifications in the molecule, but are also better suited for pest control (faster degradation and other more suitable properties). The fluorocarbon compounds remain stable for a very long time due to their firm F – C bond, so that the soil is poisoned for far too long.
Extraction and presentation
2-Fluoroethanol can be produced by reacting ethylene oxide with hydrogen fluoride under pressure. Furthermore, the representation succeeds through the reaction of ethylene carbonate with potassium fluoride or diethyl carbonate with potassium hydrogen fluoride . The compound can also be obtained by nucleophilic substitution reactions on ethylene glycol , 2-chloroethanol or 2-bromoethanol using potassium fluoride.
properties
2-Fluoroethanol is a colorless liquid with an odor similar to ethanol . The boiling point at normal pressure is 103 ° C. The vapor pressure function results according to August according to log 10 (P) = −A / T + B (P in mmHg, T in K) with A = 2306 and B = 9.060. The compound melts at −26 ° C. It can be mixed with water and ethanol in any ratio. Due to the fluorine substitution is the acid strength with a pK s value of 14:42 somewhat higher than with pure ethanol having a pK s value of the 16th
Toxic properties
Fluoroethanol is easily oxidized in the body to fluoroacetic acid, which causes the toxic phenomena. Fluoroethanol can develop its toxic effect after oral ingestion, after inhalation and to a lesser extent after percutaneous absorption.
The latency period is 0.5 to 6 hours. The symptoms of intoxication are muscle twitching, tremor, breathing disorders, clonic spasms of the muscles of the face and neck, backward flexion of the trunk, dilation of the pupils, vomiting, tingling, numbness of the skin, states of excitement and anxiety, epilepsy-like spasms that recur irregularly. Death can result from cardiac arrest, lack of oxygen during convulsions, or from stopping breathing. Since there is no special antidote, poisoning with fluoroethanol and similar fluorocarbon compounds in large amounts of poison is always fatal. Treatment can only relieve symptoms. The main focus is on the hypocalcemia triggered by fluorine , the cholinesterase inhibition and the interventions in the intermediate metabolism (citric acid cycle). Cramps can be fought with hexobarbital or diazepam . After the acute phase, side effects and sequelae can occur: drop in blood pressure, arrhythmia, ventricular fibrillation and myocardial damage.
use
2-Fluoroethanol is used in the manufacture of pesticides.
safety instructions
The vapors of 2-fluoroethanol can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 34 ° C).
literature
- G. Ahrens: Poison Law and Poison Traffic, A Compendium for Managers, Agents and Examiners, 5th Edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig, 1987.
- M. Bäsig, H. Gorges, H. Kießlich-Köcher, B. Martin, R. Stohr: Chemical warfare agents and protection against chemical warfare agents , Military Publishing House of the GDR, Berlin 1977.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Entry on 2-fluoroethanol. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 19, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on 2-fluoroethanol in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on 2-fluoroethanol in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-260.
- ↑ a b c data sheet 2-fluoroethanol from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 18, 2010 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ IL Knunjanz: Akademii Nauk SSSR 55 (1947) p. 223.
- ^ I. Shahak, ED Bergmann: Chemical Communications (London) 1965; P. 122.
- ↑ N. Tsukimori, N. Nanbu, T. Noritoshi, M. Takehara, M. Ue, Y. Sasaki: Electrolytic Properties of Ethyl Fluoroethyl Carbonate and Its Application to Lithium Battery . In: Chemistry Letters 37 (2008) pp. 368-369. doi : 10.1246 / cl.2008.368
- ^ FW Hoffmann: Preparation of Aliphatic Fluorides In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70 (1948) 2596-2597. doi : 10.1021 / ja01187a506
- ↑ PS Bhadury, SK Raza, DK Jaiswal: A semi-molten mixture of hexadecyltributylphosphonium bromide and potassium fluoride in the synthesis of organofluorine compounds In: J Fluor Chem . 99 (1999) 115-118. doi : 10.1016 / S0022-1139 (99) 00121-9
- ↑ H. McCombie; BC Saunders: Fluoroacetates and Allied Compounds In: Nature 158 (1946) 382-385. doi : 10.1038 / 158382a0 .
- Jump up ↑ CE Redemann, SW Chaikin, RB Fearing, GJ Rotariu, J. Savit, D. van Hoesen: The Vapor Pressures of Forty-one Fluorine-containing Organic Compounds in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70 (1948) 3604-3606. doi : 10.1021 / ja01191a017
- ↑ Ahrens, Poison Law and Poison Traffic, 5th Edition.

