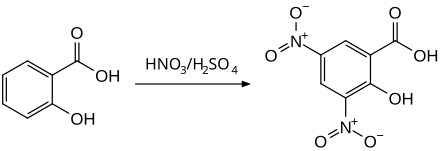
3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 4 N 2 O 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow crystals with a faint odor |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 228.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.70–1.72 g cm −3 (monohydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
170-174 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) is a phenolic acid , which gives a typical color reaction with reducing sugars or other reducing molecules .
Presentation and extraction
3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid, by the nitration of salicylic acid by means of nitrating acid are prepared. An alternative method uses the combination of nitric acid and acetic acid as a nitrating reagent, with acetyl nitrate reacting as an intermediate .
properties
3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid is a carboxylic acid having a pK s value of 2.96 for the carboxy group and 7.61 for the phenolic OH group. The octanol-water partition coefficient (log K OW ) is 1.71. It was possible to isolate two different crystal forms from the monohydrate , whose densities also differ with 1.702 g / cm 3 (crystallized from ethanol ) and 1.719 g / cm 3 (crystallized from water).
use
With reducing sugars , 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid is reduced to 3-amino-5-nitrosalicylic acid, which strongly absorbs light at 540 nm . During this reaction, the color of the solution changes from orange-yellow to red.
The colorimetric reaction was first introduced to determine reducing substances in urine and has been widely used since then, e.g. B. to quantify carbohydrates in blood . Mainly using the detection reaction when α- amylase - assay . The method combines the oxidation of a carbonyl compound with the reduction of a nitro group in 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid under alkaline conditions. An alkaline reaction solution with 2% DNS and 2% Na 2 CO 3 is used . Other urine components do not have a disruptive effect.
Today, however, enzymatic methods are usually preferred to determination with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid because they are more specific.
Web links
- Entry for 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM) .
- Laboratory use of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (in English) Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Maryland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (PDF) from Merck , accessed on October 17, 2017.
- ↑ a b V. S. Senthil Kumar; Srinivasan S. Kuduva; Gautam R. Desiraju: Pseudopolymorphs of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid , in: J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 , 1999 , pp. 1069-1073; doi : 10.1039 / a902134e ; PDF .
- ↑ a b S. S. Dube; SS Dhindsa: Dissociation constants of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid , Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Section A, 642, 1968.
- ↑ Alexander Apelbalt; Emanuel Manzurola: Solubilities of o-acetylsalicylic, 4-aminosalicylic, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic, and p-toluic acid, and magnesium-DL-aspartate in water from T = (278 to 348) K , in: J. Chem. Thermodyn . , 1999 , 31 (1) , pp. 85-91; doi : 10.1006 / jcht.1998.0424 .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-290.
- ↑ a b Entry on 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 20, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Thiel, W .; Mayer, R .; Jauer, E.-A .; Modrow, H .; Dost, H .: Synthesis and Spectral Characterization of Blue Dyes of the Benzene Series ; in: J. Prakt. Chem. (Leipzig) 328 (1986), pp. 497-514, doi : 10.1002 / prac.19863280406 .
- ↑ Andreozzi, R .; Caprio, V .; Di Somma, I .; Sanchirico, R .: Kinetic and safety assessment for salicylic acid nitration by nitric acid / acetic acid system in J. Hazard. Mat. A134 (2006), pp. 1-7, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2005.10.037 .
- ↑ JB Sumner: Dinitrosalicylic acid: a reagent for the estimation of sugar in normal and diabetic urine. In: Journal of Biological Chemistry (1921), Volume 47, p. 5.
- ↑ United States Patent 3869348 Determination of amylase , Pierce Chemical Company (Rockford, IL) 1975.
- ↑ James B. Sumner, Charles V. Noback: The estimation of sugar in diabetic urine, using dinitrosalicylic acid , in: J. Biol. Chem. , 1924 , 62 , pp. 287-290; PDF .
- ↑ James B. Sumner: Dinitrosalicylic Acid: A Reagent for the Estimation of Sugar in Normal and Diabetic Urine , in: J. Biol. Chem. , 1921 , 47 , pp. 5-9; PDF .
- ↑ Gail Lorenz Miller: Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar , in: Anal. Chem. , 1959 , 31 (3) , pp. 426-428; doi : 10.1021 / ac60147a030 .