Azərbaycan Dəmir Yolları
| Azerbaijan Demir Yollan | |
|---|---|
| legal form | Closed joint stock company |
| founding | July 20, 2009 |
| Seat | Baku , Azerbaijan |
| management | Javid Gurbanov |
| Number of employees | 7,490 |
| Branch | Transport and logistics |
| Website | ady.az |
| Status: 2017 | |
Azerbaijan Demir Yollari ( Azerbaijani "Azərbaycan Dəmir Yolları" QSC (ADY) , Russian ЗАО "Азербайджанские железные дороги" , English Azerbaijan Railways CJSC , German Azerbaijan Railways CJSC) is the national railway company of Azerbaijan , based in Baku .
Key figures
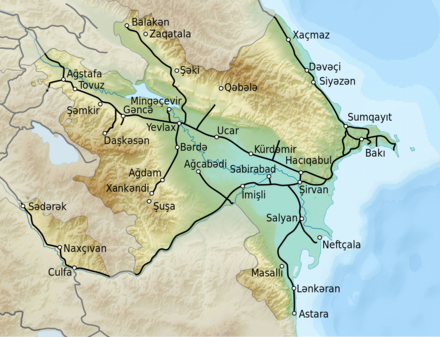
The ADY route network covers about 2,910 km and is built in Russian broad gauge . 802 km are double-track , 1,241 km are electrified . A total of 1528 km are equipped with train protection. In 2017, the company transported almost 2.5 million passengers and 14.6 million t of goods. The importance of rail traffic in Azerbaijan is minor: only 0.1% of passenger and 7% of freight traffic is carried out by rail. In 2017 ADY employed around 7500 people.
In freight transport, import traffic is 30% and transit traffic is 25%. The main border station is Bejuk-Kjasik with Georgia , where 80% of the cross-border freight traffic is handled. Traffic with Russia is handled through the Jalama border station. Both of the aforementioned border crossings are also open to passenger traffic. The ADY is also connected to Tajikistan and Kazakhstan via rail ferry connections. Iran can be reached via the Astara border station . This border station is of little importance, and international traffic is hindered by the different gauges , because the railway lines in Iran are laid out in standard gauge .
In 2016, Azerbaijan Railways owned 153 diesel locomotives , 94 electric locomotives and 27 electric multiple units , as well as 214 passenger cars and 13,649 freight cars .
history
The foundation stone for the Azerbaijani Railway was laid in 1878, when the Committee of Ministers, in the presence of Tsar Alexander II , decided to build the first railway in Baku from the surrounding area to the city center. The 27 km long route, built by the British railway company Poti – Tiflis and opened in 1880, served to transport crude oil from the oil fields of Sabunçu, Suraxanı and Balaxanı to the oil refineries . It was much more efficient than the previously used caravans , which transported the oil in wooden barrels and boxes.
The first long-distance route was the connection to the Black Sea port of Poti in Georgia, opened in 1883 , which was used to export products from the petroleum processing industry. In the same year, the Poti – Tiflis railway company was part of the Transcaucasian Railway , which was established in 1889 by Tsar Alexander III. was nationalized for military strategic reasons. From then on, the railways in Armenia were part of the Russian Railways, which became the Soviet Railways (SŽD) in 1922 , with the Armenian Railways either being its own regional railway company or part of the regional railway company Transcaucasian Railway . The organizational form changed several times between these two states until it remained its own regional railway company from 1967.
The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 resulted in the regional railway company becoming Azərbaycan Dövlət Dəmir Yolu (ADDY) , Azerbaijan State Railway . On July 20, 2009, İlham Əliyev , the President of Azerbaijan, transformed the state railway into the current organizational form of a closed joint-stock company called "Azərbaycan Dəmir Yolları" QSC .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) of ADY CJSC. (PDF) ADY, 2017 (English).
- ↑ a b c OSJD (Ed.): Bulletin of the statistical data of OSJD on rail transport for 2016 . 2016 ( osjd.org ).
- ↑ a b c d e Our story. ADY, 2016, accessed November 16, 2018 (Azerbaijani).
- ^ ESCAP (Ed.): Monograph Series on Transport Facilitation of International Railway Transport in Asia and the Pacific . 2013, 2. Current operational status of international railway transport in the region ( unescap.org ).
- ↑ According to our story , the route was 25.2 werst long, which corresponds to 26.9 km.
- ↑ Russian Railways . In: Victor von Röll (Ed.): Encyclopedia of the Railway System . tape 8 , 1917 ( zeno.org ).