Bismuth (III) nitrate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
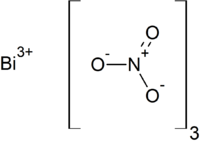
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Bismuth (III) nitrate | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | Bi (NO 3 ) 3 | |||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | ||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||
| density |
2.83 g cm −3 |
|||||||||
| Melting point |
30 ° C |
|||||||||
| boiling point |
75-80 ° C |
|||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Bismuth (III) nitrate is an inorganic chemical compound of bismuth from the group of nitrates .
Extraction and presentation
Bismuth (III) nitrate can be obtained by dissolving bismuth or bismuth (III) oxide in nitric acid. This creates the pentahydrate.
properties
Bismuth (III) nitrate pentahydrate is a colorless solid in the form of rod-shaped, triclinic crystals. When heated from around 60 ° C, it transforms into various basic bismuth (III) nitrates and at higher temperatures into bismuth (III) oxide. It is soluble in strong inorganic acids as well as in glycerine and glacial acetic acid . In water, hydrolysis takes place to form basic salts such as bismuth (III) subnitrate . It forms double salts with metal nitrates .
use
Bismuth (III) nitrate is an excellent oxidizing agent for a large number of 4-substituted Hantzsch- 1,4-dihydropyridines . It is a convenient reagent for the selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides . It is also used as a catalyst for a high-yield Michael addition of various substrates, including amines, imidazoles, and indoles to form enones .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet Bismuth (III) nitrate pentahydrate, 99.999% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 2, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Bismuth (III) nitrate pentahydrate, ACS, 98% from AlfaAesar, accessed on January 2, 2014 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on bismuth trinitrate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 602.
- ^ G. Gattow, G. Kiel: About bismuth nitrates. IV. Representation and properties of Bi (NO3) 3 * 5 H2O. In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 335, 1965, pp. 61-73, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19653350106 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 826.



